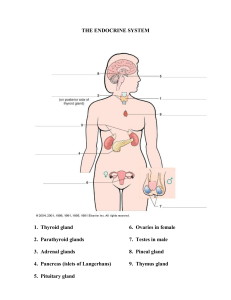
HORMONES Definitions Hormones: A chemical substance produced by a gland, carried by the blood, which alters the activity of one or more specific target organs and is then destroyed by the liver Endocrine gland or ductless gland: The gland, which has no duct for secretion and they secreted their chemical substances directly into the bloodstream is called endocrine or ductless gland. E.g. Thyroid gland, adrenal gland, pituitary gland etc. Exocrine gland or duct gland: The gland which secret its chemical substances through a duct is called exocrine or duct gland. E.g. Salivary gland, lacrimal gland, mammary gland etc. Mixed or heterocrine gland: This gland consists both exocrine and endocrine glands. E.g. Pancreas, testes and ovaries. 1|Page Pituitary gland: It is the master gland which is attached to the base of the brain. It produces many hormones like Growth Hormones, Luteinizing Hormone (LH), Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), Follicle stimulating Hormone (FSH), Oxytocin, Anti Diuretic Hormone (LTH) etc. Write the differences between endocrine and exocrine gland. Endocrine glands: • • • • • • A type of ductless glands Secrete into the blood Contain blood vessels Secrete hormones Target of the gland is located away from the gland Mainly control long term activities of the target organs. Exocrine gland: • • • • May or may not have duct Pour their secretions directly at the site of action Do not contain blood vessels Secrete enzymes 2|Page Write the properties of hormones. • Hormones are secreted from the cluster of living cells. • It travels through the blood to reach target organs. • Hormones serve as chemical messengers and bring about chemical coordination of varies parts in the body. • They do not catalyze any reactions, they function by stimulating or inhibiting the target organs. • Do not remain permanently in blood, soon after their function is over, they become destroyed, inactivated or excreted. • Like vitamins they act in very low concentration and amount. Write the differences between nervous system and hormonal system. Name different glands, hormones and their functions. Gland Hormones Functions Pituitary Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Stimulates egg development and estrogen secretion in female and sperm production. Luteinizing Hormone (LH) Stimulates egg release (Ovulation) in female and testosterone production in males. 3|Page Gland Hormone Functions Pituitary Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) Controls the water content of the blood. Thyroid Stimulating hormone (TSH) Stimulates the secretion of thyroxine from the thyroid glands. Control intake of iodine by the thyroid tissue. Human Growth Hormone Controls the growth of tissue, bone, muscle and internal organs. Also influences metabolic processes. Pancreas Testes Ovaries Insulin Lowers blood glucose Glucagon Raises blood glucose Testosterone Controls development of female secondary sexual characteristics. Estrogen Progesterone Adrenals Adrenaline Controls development of female secondary sexual characteristics. Regulates menstrual cycle Prepares body for physical activity. 4|Page Describe the effect of adrenaline. There is a pair of adrenal glands located on just above each kidney. It produces adrenaline hormones. It above each kidney. It produces adrenaline hormone. It is known as flight fright and fight hormones. 5|Page 6|Page