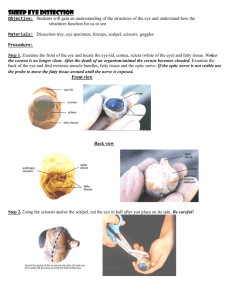
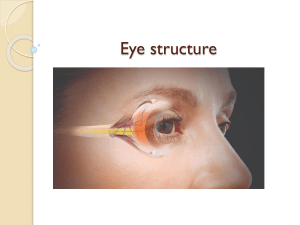
UNIT 14: COORDINATION AND RESPONSE 14.4 Sense Organs 14.5 More about the eye 14.2.1 Define sense organs as groups of receptor cells responding to specific stimuli: light, sound, touch, temperature and chemicals 14.2.1 Define sense organs as groups of receptor cells responding to specific stimuli: light, sound, touch, temperature and chemicals Receptor Type Responds to Stimulus Photoreceptor Rod cells in retina Chemicals Thermoreceptor Example in Humans Taste buds In Skin Mechanical changes such Hair cells in ear (hearing as changes in lenght and balance) 14.2.2 Identify the structures of the eye, limited to cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, optic nerve and blind spot THE EYE (PHOTORECEPTOR) Sight is the dominant sense in humans. 14.2.2 Identify the structures of the eye, limited to cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, optic nerve and blind spot 1. 2. 3. 10. 4. 11. 6. 7. 9. 8. 12. 5. 14.2.3 Identify the position of the fovea 14.2.2 Identify the structures of the eye, limited to cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, optic nerve and blind spot 14. 13. 14.2.4 Describe the function of each part of the eye, limited to: – cornea – refracts light, – iris – controls how much light enters pupil, – lens – focuses light onto retina, – retina – contains light receptors, some sensitive to light of different colours, – optic nerve – carries impulses to the brain 1. Sclera The tough outer coat which protects eye against damage. 2. Choroid A darky coloured layer which reduced reflections inside the eye and contains blood vessels which help to nourish the cells of the retina. 3. Retina Contains the light sensitive cells, called .............. & .......... 14.2.4 Describe the function of each part of the eye, limited to: – cornea – refracts light, – iris – controls how much light enters pupil, – lens – focuses light onto retina, – retina – contains light receptors, some sensitive to light of different colours, – optic nerve – carries impulses to the brain 1. ............ A transparent layer responsible for the most of refraction (bending) of light rays that enter the eye. 2. Aquous humour Watery fluid which supports the cornea and the front chamber of the eye. 3. Vitrous humour A Jelly like substance which helps to keep shape of the eyeball, supports the lens and keeps the retina in place at the back of the eye. 14.2.3 Describe the function of each part of the eye, limited to: – cornea – refracts light, – iris – controls how much light enters pupil, – lens – focuses light onto retina, – retina – contains light receptors, some sensitive to light of different colours, – optic nerve – carries impulses to the brain Together control light intensity on the retina 1. Pupil 2. Iris The circular opening which lets light into the eye. It appears balck because choroid is visible through it. ..................................................... ..................................................... ..................................................... ..................................................... ........ 14.2.4 Describe the function of each part of the eye, limited to: – cornea – refracts light, – iris – controls how much light enters pupil, – lens – focuses light onto retina, – retina – contains light receptors, some sensitive to light of different colours, – optic nerve – carries impulses to the brain Together control light focusing on the retina 1. Ciliary muscles Arranged around the pupil,changes thickness of the lens when focusing 2. Suspensory Hold the lens in place ligament 3. Lens ..................................................... ..................................................... ............................. 14.2.4 Describe the function of each part of the eye, limited to: – cornea – refracts light, – iris – controls how much light enters pupil, – lens – focuses light onto retina, – retina – contains light receptors, some sensitive to light of different colours, – optic nerve – carries impulses to the brain 1. Yellow spot (Fovea) This area has the highest density of cones, thus offers maximum sharpness but only works at full efficient in bright light. 2. .................... Composed of sensory neurones which carry nerve impulse to the visual centre at the rear of the brain. 3. Blind spot At the exit point of optic nerve. There are no light-sensive cells here so light falling on this region cannot be detected. VISUAL FIELD Stereoscopic vision is an adaptation for tree dwelling animals, such as monkey. 14.2.8 Explain the pupil reflex in terms of light intensity and pupil diameter only 14.2.9 Explain the pupil reflex in terms of light intensity and antagonistic action of circular and radial muscles in the iris Antagonistic Muscles occurs in pairs. The one muscle contracts, another relaxes simultaneously. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Yj5-cJgVX3c 14.2.5 Outline the function of rods and cones, limited to greater sensitivity of rods for night vision and three different kinds of cones absorbing light of different colours for colour vision RETINA: is the innermost layer of the eye. • Contains light receptors. • Made up of rods and cones. • RODS: are responsible for vision in dim light, black and white vision. CONES: Function in bright light and responsible for colored vision. • At the rear of the eye, the retina is attached to optic nerve, which carries impulses to the brain. • YELLOW SPOT (FOVEA): The area of sharpest vision. Made entirely of ______________ Looking at a DISTANT OBJECT -the ciliary muscles relax -suspensory ligaments become tight -Lens is pulled into an elliptical shape -Light rays are refracted as they pass through the lens Looking at a NEAR OBJECT -the ciliary muscles contract -suspensory ligaments become slack -Lens becomes more spherical -Light rays are refracted MORE as they pass through the lens Mnemonic: CCC – Ciliary muscles Contracts for Close Objects - Accomodation is the term used to describe the changes that occur in the eye when focusing on far and near objects. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1yIpyitm6eE&t=5s 14.2.8 Explain the pupil reflex in terms of light intensity and pupil diameter only 14.2.9 Explain the pupil reflex in terms of light intensity and antagonistic action of circular and radial muscles in the iris Stimulus – light falls on retina Impulse in sensonry neurones of optive nerve Integration in the visual centre of the brain Impulses in motor neurones Low light intensity: Radial muscles of iris ...................., circular muscles of iris ............. and the pupil is opened wider, so more liht can eneter and reach retina. High light intensity: circular muscles of iris ................, radial muscles of iris ...................... And the pupil is reduced in siz, so ......... Light can enter, retina is protected from bleaching. DO NOT CONFUSE CIRCULAR AND CILIARY MUSCLES! Circular muscles affect the size of the iris!! Ciliary muscles affect the shape of the lens!! Describe the pupil reflex and explain its advantages. [5marks]. ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................... Distinguish between rods and cones in terms of function and distribution. [4marks] ............................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................. ............................................................................ If you look straight at an object when it is nearly dark, you may find it difficult to see it. It is easier to see if you look just to side of it. Explain why this is. [4 marks] ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ......................................................................................................................... ....................................... ....................................... ......... a. What is the choroid and what is its function? [2 marks] ........................................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................ b. Define accommodation. ........................................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................................ .......................................................................................................... 14.2.1 Define sense organs as groups of receptor cells responding to specific stimuli: light, sound, touch, temperature and chemicals 14.2.2 Identify the structures of the eye, limited to cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, optic nerve and blind spot 14.2.3 Identify the position of the fovea 14.2 Sense Organs Learning Obj.s 14.2.4 Describe the function of each part of the eye, limited to: – cornea – refracts light – iris – controls how much light enters pupil – lens – focuses light onto retina – retina – contains light receptors, some sensitive to light of different colours – optic nerve – carries impulses to the brain 14.2.5 Outline the function of rods and cones, limited to greater sensitivity of rods for night vision and three different kinds of cones absorbing light of different colours for colour vision 14.2.6 State the distribution of rods and cones in the retina of a human 14.2.7 Explain accommodation to view near and distant objects in terms of the contraction and relaxation of the ciliary muscles, tension in the suspensory ligaments, shape of the lens and refraction of light 14.2.8 Explain the pupil reflex in terms of light intensity and pupil diameter only 14.2.9 Explain the pupil reflex in terms of light intensity and antagonistic action of circular and radial muscles in the iris