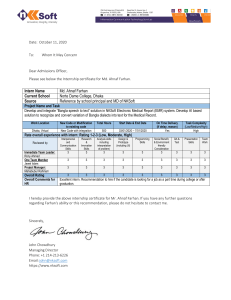
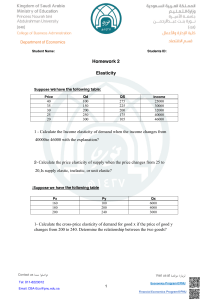
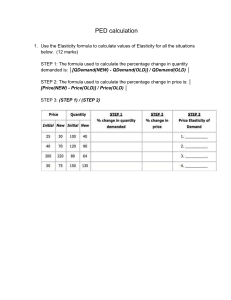
Golden Generation Group BUSINESS CHAPTR ONE: PUBLIC FINANCE Public Finance: is the study how the governments collect revenues through taxation and how spend that revenue on public services. The Components of public finance are: Public revenue, debt, and Expenditure A government: is an organization that has authority over society and provides public services. Elements Of public finance 1. Resource allocation 2. Income distribution 3. Economic stabilization Public goods: are the products and services that we all consume in which no one can exclude anyone else from the advantages that come with their use. Fiscal policy: is a decision made by a government regarding spending or taxation. Government Budget A government Budget : is a quantified plan showing expected revenue and expenditure. Government budgets can be classified into two main elements: a) Revenue budget and b) Capital budget. Capital budget: is a budget for acquiring or up keeping fixes assets. Prepared by Farhan Mohamoud Shire [ Farhan Yare ] A budgeting Model: is a tool to align current economic performance with financial goals. Importance Of Government Budgeting 1. Budgets are vita policy tools to prevent government deficits. 2. Budget facilitates accountability and control of spending of government resources. Budgeting Models 1. Incremental Budgeting. 2. Zero-based budgeting. 3. Activity-based budgeting. 4. Rolling budgets. The puntland government uses incremental method. The advantages of incremental budgeting is a) It’s easy to calculate b) Quick to implement c) Easy to explain. Project budgets: are the financial resources allocated to the achievement of the project. Other important classification of budgets are master budgets, Functional budgets, and Cash budgets. Master budget: is a budget that recaps and integrates all the individual budgets of an organization. Functional budget: is a budget for a particular process or department within an organization. Cash budgets: is estimation of cash inflows and outflows of the government. Government Revenue Sources of public revenue are Tax and Non-tax. Government revenue is the income collected by the government from tax and non-tax source. Tax sources include: taxes on income, wealth, production and imports. Prepared by Farhan Mohamoud Shire [ Farhan Yare ] Non-tax source include: profit from government enterprises, property income and charges. Government Expenditure: is spending of government to provide essential goods and services to satisfy the needs of society. Main areas of government Expenditure 1. Recurrent expenditure. 2. Development expenditure. 3. Transfer payments. Recurrent expenditure: is the spending on consumer goods and services for the day-to-day activities. Development expenditure: is the spending on the acquisition, maintenance, and development of capital goods. Transfer payment: is sharing funds to individuals by the government without receiving anything in return. Public debt: is the total amount of debt owing to lenders by a government. Sources of public debt are Internal and External. TAXTION Purposes of taxation ● To raise revenue for the government ●To control of harmful products ● To influence the price system and protect domestic industries. Principals if taxation Fairness Efficiency Convenience Certainty Impact of taxation on the economy Prepared by Farhan Mohamoud Shire [ Farhan Yare ] ●Discourage work ●Reduce saving ●Lower investment ● Lower innovation and entrepreneurship. Classification of taxes Taxes can be classify in two main Direct taxes and Indirect taxes. In puntland there are two main categories of taxes levied by the state. Inland revenue tax and Custom duty. We can classify customs duty into Import duty and Export duty Import duty: is the tax levied on the goods imported. Export tax: is the one which the government levy on the goods exported by businesses and citizens. Direct tax: are the taxes that individuals directly pay to the government. Direct tax include income tax, property tax, and capital gains tax. Income tax: is a tax levied on the income earned by individuals and corporations. Personal income tax: is the tax that the government levies on the income earned by individuals A corporate tax is a tax that the government levies on the profit of limited liability companies and other incorporated businesses. Property tax: is the tax levied on the value of a property. Capital gains tax: tax that the government levies on the value gained from sales of an asset. Indirect taxes: are the taxes which the taxpayer shifts the tax burden to another person. Indirect tax can be classify according to how the government levies the tax in this way, taxes can be ad valorem tax and Specific tax. Ad valorem tax: is a tax based on the value of tax the base where specific tax: is tax government bases on the units sold. Prepared by Farhan Mohamoud Shire [ Farhan Yare ] Indirect tax also can be selective and general tax. The following are the most famous indirect tax levied: Sales tax Value-added tax Customs duty Excises duty Lump-sum tax: is a fixed sum that a person pays per period. Tax rate structure Tax rate structure describes the relationship between the tax collected during a given period and the tax base. Tax rates can be average tax rate (AMT) or Marginal tax rate( MTR). An ATR i the rate of total taxes divided by the value of taxable base. An MTR is the tax collected on the additional money value of the tax base as the tax base increases. We can classify taxes into proportional, progressive, and regressive. Proportional tax rate: is a tax that the rate is constant, regardless of the increase of the tax base. It’s also called a flat tax rate. Advantages 1. Easy to calculate and understand 2. It reduces tax evasion Disadvantages 1. Violation of the equity principle 2. Creates income in equity Progressive tax rate: is a tax that rate increases as income increases. Advantages 1. Equitable income distribution 2. It allows government collect more revenue. Disadvantage Prepared by Farhan Mohamoud Shire [ Farhan Yare ] 1. Discouraging high-income earners. Regressive tax rate: is a tax that rate increases as income decreases. Advantages 1. It rewards high-income earners and discourages tax evasion 2. It increases saving and investment. Disadvantage 1. Increased income inequality and oppression of the lower section of society. CHAPTER TWO: DEMAND AND SUPPLY Equilibrium: is a situation in which the forces of supply and demand are balanced. Equilibrium price: is the price at which the quantity demanded and supplied are equal. Equilibrium quantity: is the quantity demanded and supplied at the equilibrium price. Excess supply: it occurs when the product price is greater than the equilibrium price. Surplus = quantity supplied – quantity demanded Quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded Surplus Price decrease. Excess Demand: when the price of a good is lower than the equilibrium price. Shortage = quantity demanded – quantity supplied Quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied Shortage Price increase Market Structure ● Perfect competition Market ●Monopolistic competition market Prepared by Farhan Mohamoud Shire [ Farhan Yare ] ●Oligopoly market ●Duopoly market ●Monopoly market There are two extreme market structures: Perfectly competitive markets and Monopolies. Characteristics Of Market Structures a) Number of enterprises b) Similarity of the products they sell c) Ease of entering and exiting the market. Perfect Competition Market Price taking: Means accepting the price that market sets Characteristics of perfect competition market a) A large number of sellers b) Homogeneous products c) Easy entry and exit Monopolistic Competition Market: is a market in which many firms produce similar goods or services. Characteristics of Monopolistic Competition Market a) Many small sellers b) Heterogonous Products c) Easy entry and exit. Oligopoly Market AN oligopoly: is a market structure where few firms dominate the market supply of a particular good or services. A pure oligopoly exists when their products are un differentiable. Characteristics of oligopoly market a) Few sellers b) Homogeneous or heterogeneous products Prepared by Farhan Mohamoud Shire [ Farhan Yare ] c) Difficult Market entry. Duopoly Market Duopoly Market: is a market that has only two firms dominating the market. Characteristics of duopoly market a) Two sellers b) Homogeneous or heterogeneous products c) Difficult to entry Monopoly Market: Is where a single firm operates the entire market supply and has significant market power. A pure monopoly exists where there is one supplier in the entire market. Characteristics of monopoly market a) Single seller b) Unique product c) Difficult entry Price Elasticity of demand: is the responsiveness of the quantity demanded to a change in price. Price elasticity of demand = Ed = %∆𝑸𝒅 %∆𝒑 %∆𝑸 = Q = Quantity 𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐜𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐚𝐠𝐞 𝐜𝐡𝐚𝐧𝐠𝐞 𝐢𝐧 𝐪𝐮𝐚𝐧𝐭𝐢𝐭𝐲 𝐝𝐞𝐦𝐚𝐧𝐝𝐞 𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐜𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐚𝐠𝐞 𝐜𝐡𝐚𝐧𝐠𝐞 𝐢𝐧 𝐩𝐫𝐢𝐜𝐞 𝑸 𝟐−𝑸𝟏 𝑸𝟏 %∆𝒑 = 𝑷𝟐−𝒑𝟏 𝒑𝟏 p = Price The demand is: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Elastic, if price elasticity is greater than 1. In elastic, if price elasticity is less than 1. Perfectly in in elastic, if price elasticity is zero Perfectly elastic , if price elasticity is infinite Unitary elastic, if price elasticity is 1. Prepared by Farhan Mohamoud Shire [ Farhan Yare ] Price Elasticity of Supply: is the responsiveness of the quantity supplied to a change in price. Price elasticity of supplied = Es = %∆𝑸𝒔 %∆𝒑 %∆𝑸 = Q = Quantity 𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐜𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐚𝐠𝐞 𝐜𝐡𝐚𝐧𝐠𝐞 𝐢𝐧 𝐪𝐮𝐚𝐧𝐭𝐢𝐭𝐲 𝐬𝐮𝐩𝐥𝐢𝐞𝐝 𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐜𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐚𝐠𝐞 𝐜𝐡𝐚𝐧𝐠𝐞 𝐢𝐧 𝐩𝐫𝐢𝐜𝐞 𝑸 𝟐−𝑸𝟏 𝑸𝟏 %∆𝒑 = 𝑷𝟐−𝒑𝟏 𝒑𝟏 p = Price The supply is: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Elastic, if price elasticity is greater than 1. In elastic, if price elasticity is less than 1. Perfectly in in elastic, if price elasticity is zero Perfectly elastic , if price elasticity is infinite Unitary elastic, if price elasticity is 1. Prepared by Farhan Mohamoud Shire [ Farhan Yare ] Prepared by Farhan Mohamoud Shire [ Farhan Yare ]