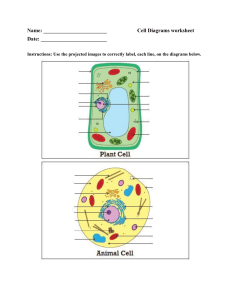
Project Cash Flows Introduction • Organization involved in implementation of project, receives and spends different amounts of money at different points of time • A cash flow diagram is a visual representation of the inflow and outflow of funds • This inflow and outflow does not follow a particular pattern • It is however, assumed that all transactions take place either at the beginning or end of a particular period (week, month, quarter, year etc.) • eg., if it is decided that all transactions in a month will be recorded as having occurred on the last day of that month, or first day of that month, either approach can be followed provided the system is consistently followed. Cash Flow Diagram • In a cash flow diagram, time is drawn on X axis in an appropriate scale in terms of weeks, months, year etc. ; Y axis represents the amount involved in the transaction. • Receipts and payments are drawn on positive and negative sides respectively on the Y axis. Representation on Y axis may not be to the scale but should be proportional. • Amount of transaction is written on the side of arrow. • • Time 0 1 2 3 n-1 n +ve incoming - ve outgoing Example • The details of transactions during the months of April, may and June for Alpha Industries are given below. Draw a cash flow diagram for the transactions using month as a single unit showing all transactions during a month at the end of that month. Example Date Description Amount (Rs.) April 05 Receipt of running account bill #9 150,000 April 10 Salary disbursement 80,000 April 16 Payment for supply of aggregates 20,000 April 21 Payment for supply of stationery 5,000 May 07 Receipt for RA bill # 10 May 10 Salary disbursement 80,000 May 28 Payment for supply of cement 50,000 June 06 Receipt for running account bill #11 June 10 Salary disbursement June 16 Payment for supply of structural steel 100,000 June 28 Payment of rent of premises for July and August 100,000 180,000 250,000 80,000 Compound Interest • Given transactions are summarised as given below : Month Receipts (Rs.) Expenditure (Rs.) April 150,000 105,000 May 180,000 130,000 June 250,000 280,000 Total 580,000 515,000 Cost & Revenue Cash Flow Diagrams • In construction economics, we come across two main types of problems : • (i) income expansion and (ii) Cost reduction • Correspondingly, the cash flow diagrams can also be distinguished as revenue dominated and cost dominated cash flow diagrams • In revenue dominated cash flow diagrams, incomes or savings are emphasized while the latter diagrams largely concentrate on periodic costs or expenditures. • Cash flow diagrams are frequently used to find the equivalence of money received paid or received at different times and many other objectives. Cost & Revenue Cash Flow Diagrams • Cost Dominated Cash Flow : • Revenue Dominated Cash Flow : Project Cash Flow Diagram • In the earlier problem, the information on the cash transactions and period of their occurrence was available. • In practice, we have to derive this information from some conditions. • Based on the concepts of cash flow diagram discussed earlier, we can draw cash flow diagram for a project as also for a company. • The former is known as project cash flow diagram while the latter is known as company cash flow diagram. • Project cash flow diagram is a graphical representation of receipts and disbursements versus time. Time is generally represented in months. Project Cash Flow Diagram : Information Required • Gross bill value and its time of submission • Measurement period – Contractors are generally paid once in a month. These conditions are found in ‘terms of payment’ of the contract. • Certification time taken by the Owner. • Retention money deducted by the owner and the time to release the retention money. • Mobilization advance and other advances and their terms of recovery • Details of costs incurred by the contractor for raising a particular bill value. • Credit period Factors Affecting Project Cash Flow • Profit Margin – Profit margin is the excess over costs. Thus higher the margin in a project, the better it is for Contractor’s cash flow. • Retention – Retention tends to reduce the margin obtained from a project. In case of very low margins, actual margin after retention can reduce to zero also. Retention affects contractor’s cash flow in a negative manner. Higher the retention bigger is the cash flow problem. These days, contractors request for retention in form of a Bank Guarantee. • Extra Claims – extra claims in a contract mainly result from extra work, changes in quantities, changes in specifications etc. These claim take long time to settle as they are not part of original contract. Sometimes they are settled even after completion of project. Thus in practice extra claims tend to worsen the cash flow position. Factors Affecting Project Cash Flow • Distribution of margin – Keeping the overall margin amount same, the margin can be distributed across different items of project either in a uniform manner, or it can be front and back loaded. • Front loading means the items that are executed early, carry higher margin than the item executed later which improves contractor’s cash flow although overall margin derived from the project remains same. Back loading is reverse of front loading. • Delay in receiving payment from Client – Any delay in receiving payment from the client, results in capital lock up. • Delay in paying labour, plant hires, material suppliers and sub contractors – The time interval between receiving goods or services and paying for these is the credit the contractor receives from his suppliers. Using cash Flow Diagrams • Determining Capital Lock Up – • While estimating the effect of margin and retention money on cash flows, one can see that a contracting company faces negative cash flows in the early stages of the project. • This negative cash flow is the locked up capital that is supplied either from internal reserves of the company or borrowed money. • A company borrowing money has to pay interest • A company utilising own funds has to forego interest on this money. • The negative cash flow indicates the requirement of funds to execute the project at a given instant. Using cash Flow Diagrams • Plot the month-wise cumulative cash out flows and cumulative cash inflows with time on X axis. • Plot the month wise net cash flow on Y axis with time on X axis.