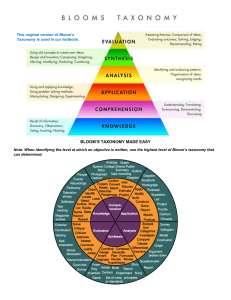
Let’s unpack few things about hierarchical ways in teaching and learning BLOOM’S VS SOLO We will have a look at what we already know………. Write a reflection on what is bloom's taxonomy and its use… 1. The reflection can be in the form of pictorial, definition for each level, paragraph writing or any other way of your preference 2. You can use internet for research What is the meaning of the word taxonomy? Think and give me the meaning and tell me how it relates to learning? Give me how is the word is useful when it comes to learning? Classification of learning in a classroom scenario Vertical- Horizontal- Bloom’s taxonomy Let’s think about the use of the bloom’s taxonomy…. Mainly to design the learning objectives. Second to design the questions in our assessments papers. Task: Quickly give me one question using one verb in one of the stages of bloom’s taxonomy related to the subject you deal with. Intro to solo taxonomy This helps teachers to build the thinking and knowledge from where they are. Which allows differentiation and student choice Difference between the two in simple language Bloom’s taxonomy: Student should cross each level to bloom in his thinking SOLO taxonomy: Each level of the taxonomy stands individually (SOLO)which allows any level student to kick start their thinking from the level where they are Key differences between the two ……. 1. SOLO allows task and outcome to be at different levels while Bloom’s not designed/cannot be used to level outcomes against each task. 2. SOLO enables us to distinguish between the cognitive complexity of a task and the difficulty of a task. 3. SOLO has clarity of verb use for each level. Clarity of verb level is a powerful advantage when educators are planning and writing learning intentions whereas Bloom’s has confused verb use across levels. 4. SOLO can be used to look at levels of declarative knowledge and functioning knowledge including metacognitive reflection. 5. SOLO is brutally and blissfully simple and can be used by students as young as five to look at their own learning outcome and the learning outcomes of their peers 6. SOLO is a model that shows students that learning is the result of effort and strategies NOT fixed ability or being liked. It shows learning progress and a plus 1 next step for every learner SOLO Taxonomy Examples Written below are some of the verbs associated with each stage of SOLO taxonomy, along with a series of respective examples. 1. Prestructural Level Failed, successful, flunked, learner missed the point, failed to comprehend. The students fail to execute the task due to a lack of understanding. 2. Unistructural Level Name, list, memorise, define, identify. Example- What is the weather today? 3. Multistructural Level Define, describe, classify, combine, do algorithms. Example- List some of the clothes that we might need to wear today? 4. Relational Explain, analyse, integrate, sequence, relate, apply, compare, contrast. Example- Which type of weather do you prefer? Explain your reasons. How does today’s weather compare with the weather at other times of the year? 5. Extended Abstract Evaluate, reflect, theorise, hypothesise, generalise, create and imagine. Example - what happens to the weather Let’s now learn how it works ● Make a copy of your recent question papers and try revamping the questions implementing SOLO taxonomy. ● Share when you are done. ● Lets peer assess using 2 stars and 1 wish strategy.