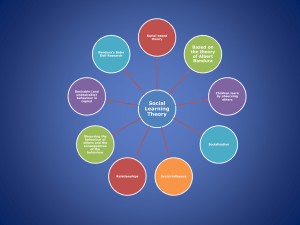
GOOD MORNING TO EACH AND EVERYONE, I ________ AND _______, WOULD LIKE TO PRESENT OUR PRESENTATION OF WHAT AND HOW SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY, BASED AND STUDIED ON ONE OF THE KNOWN PSYCHOLOGIST, ALBERT BANDURA. THE TITLE OF THIS REPORT IS GROUP NINE TITLE: ALBERT BANDURA ( 1977 SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY) INTRODUCTION: Albert Bandura, a prominent psychologist, is widely recognized for his groundbreaking work on social learning theory. His research revolutionized our understanding of how individuals acquire new behaviors, attitudes, and skills through observation and imitation. This report provides an overview of bandura’s social learning theory, it’s key concepts, and it’s significance in field of psychology.. SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY: Bandura’s social learning theory propose that people learn not only through direct experience but also by observing and imitating others. It emphasizes the role of the social interaction and cognitive processes in learning. According to bandura, individuals acquire new behaviors, attitude, and beliefs by observing the actions and consequences experienced by others. There are four key concepts one is (KEY CONCEPT AND EXPLANATION) 1.OBSERVATIONAL LEARNING: also known as social learning or modeling, is a type of learning and plays a significant role in how we acquire new skill, knowledge, and attitude. The process of observational learning was extensively studied by psychologist Albert Bandura, who developed the social learning theory. According to bandura, observational learning involves four key components Attention Retention Reproduction Motivation Observational learning can occur in various contexts, including formal educational setting, social interactions, and media exposure. 2.IMITATION: Refers to act of copying or replicating the behavior, actions, or characteristics of others. It is a fundamental aspect of human learning and social interaction and plays a crucial role in the development of skills, language, and cultural transmission. Imitation can be classified into two main types: Motor imitation: this involves copying the physical actions or movements of others. Observational imitation: this type of imitation goes beyond pure motor actions and involves replicating behaviors, attitude, and even emotional expression observed in others. Imitation serves several important functions: Learning Social bonding Identification and role modeling Communication and language It’s important to note that imitation is not a passive process but rather an active one. 3.VICARIOUS REINFORCEMENT AND PUNISHMENT: are concepts derived from social learning theory, particularly the work of psychologist Albert Bandura. They refer to the process of learning by observing the consequences that others experience for their behaviors, rather than directly experiencing those consequences oneself. 4.SELF-EFFICACY: Bandura introduced the concept of selfefficacy, which refers to an individual’s belief in their ability to successfully perform a specific task or achieve desired outcomes. Self-efficacy plays a crucial role in motivation, effort, and persistence in learning and behavior change. According to bandura, self-efficacy is not a measure of actual skills or abilities but rather a person’s perception of their own capabilities. It is influenced by four main sources: Mastery experiences Vicarious learning Verbal persuasion Emotional and physiological states Self-efficacy beliefs influence motivation, effort, persistence, and resilience. SIGNIFICANCE Bandura’s social learning theory has had a profound impact on various fields, including education, psychology, and social sciences. It challenged the traditional behaviorist perspective that focused solely on determinants of behavior. Bandura’s theory highlighted the importance of cognitive processes, observational learning, and the social environment in shaping human behavior. This theory has practical implications in areas such as education, parenting, and therapy. It underscores the significance of positive role models, providing appropriate models for learning, and creating supportive environments that foster observational learning…