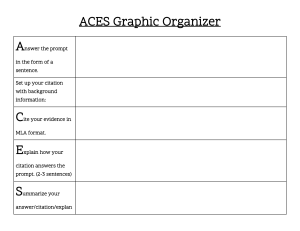
Lesson 2 Objectives 1. Outline the research process stages. 2. Explain the importance of a research question. 1. Identify the Research Problem or Topic Choose a specific research question or topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. 2. Review Existing Literature Conduct a thorough literature review to understand what is already known about your research topic. Identify gaps, controversies, or areas where further research is needed. 3. Formulate Research Questions or Hypotheses Based on your review, develop clear research questions or hypotheses that you aim to answer through your research. 4. Design the Research Methodology Determine the research methodology and data collection methods (e.g., surveys, experiments, interviews) that best suit your research objectives. Plan the sampling strategy if applicable. 5. Collect Data Implement your chosen data collection methods to gather relevant information. Ensure data accuracy and consistency. 6. Data Analysis Analyze the collected data using appropriate statistical or qualitative techniques. Interpret the results to draw meaningful conclusions. 7. Draw Conclusions Based on your analysis, draw conclusions that address your research questions or hypotheses. Discuss the implications of your findings. 8. Communicate Results Write a research paper or report following the appropriate format and structure. Clearly present your methodology, results, and conclusions. Use charts, graphs, and visuals to enhance understanding. 9. Cite Sources Properly cite all sources and references using a recognized citation style (e.g., APA, MLA) to give credit to previous research. 10. Peer Review and Feedback Share your research paper with colleagues or mentors for peer review. Incorporate feedback and make necessary revisions. 11. Publish or Present Consider publishing your research in a peer-reviewed journal or presenting it at conferences to contribute to your field. 12. Reflect and Revise Reflect on the research process and outcomes. If necessary, revise your research and methodology for future studies. 13. Ethical Considerations Ensure that your research follows ethical guidelines, especially when dealing with human subjects or sensitive data. 14. Funding and Resources Steps in the Writing Process: Step 1: Pre-writing Define your purpose and audience. Brainstorm ideas and gather relevant research material. Create an outline or structure for your document. Step 2: Drafting Write a rough draft following your outline. Don't worry about perfection at this stage; focus on getting your ideas down. Step 3: Revising Review your draft for clarity, organization, and coherence. Check for logical flow between paragraphs and sections. Remove redundant or irrelevant information. Clarify vague or confusing points. Step 4: Editing Proofread for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors. Ensure consistent formatting and citation style. Verify accuracy of data, facts, and references. Consider seeking feedback from peers or mentors. Step 5: Proofreading Carefully proofread the document one last time for any remaining errors. Pay attention to details like typos, formatting, and citation accuracy. Step 6: Finalizing Make any final adjustments based on proofreading feedback. Prepare a well-formatted, polished final document for submission or publication. Tips for Effective Technical Writing Here are some steps and tips to enhance the effectiveness of your technical writing and produce clear, impactful documents. Know Your Audience Understand the background and knowledge level of your readers and tailor your writing to meet their needs and expectations. Clarity and Simplicity Use clear and concise language and avoid jargon or overly technical terms unless necessary. Be sure to define acronyms and specialized terms. Structure and Organization Follow a logical and well-organized structure; use headings, subheadings, and lists to break up content. This will ensure a smooth flow from one section to the next. Visual Aids Include figures, charts, and tables to illustrate complex concepts, and don’t forget to label and explain visual aids clearly. Citation and References Properly cite all sources using the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA). Create a bibliography or reference list at the end of your document. Revision and Proofreading Revise and proofread your work thoroughly to eliminate errors. It is important to take breaks between writing and proofreading to maintain objectivity. Conciseness Avoid unnecessary repetition, and eliminate filler words or phrases. Be concise while conveying all essential information. Consistency Maintain consistency in formatting, style, and terminology throughout the document. Feedback Seek feedback from peers or mentors to improve the quality of your writing. Practice Writing is a skill that improves with practice. For this reason, you must keep writing and refining your technical writing skills over time.