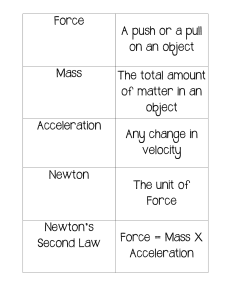
First Law: Newton's first law of motion is the law of inertia. It states that an object at rest tends to stay at rest, and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an external force. Basically, it means that objects will not change their state of motion unless a force is applied to them. Second Law: Newton's second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force applied to it and inversely proportional to its mass. This law is written as F = ma, where F represents the force applied to an object, m is the mass, and a is the resulting acceleration. Third Law: Newton's third law of motion states that for every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. When one object exerts a force on another object, the second object also exerts a force of equal magnitude but in the opposite direction on the first object. This is also the reason why your hand hurts when you punch a wall; the wall is also “punching” at you.