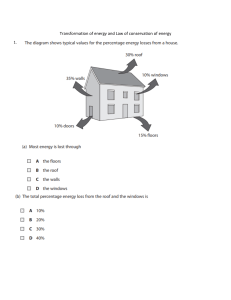
1/5 Lesson Plan Title KINETIC ENERGY Lesson Plan Lesson Plan: Differentiating Potential and Kinetic Energy Grade Level: 8th Grade Subject: Science Learning Objectives: 1. Define and differentiate potential and kinetic energy. 2. Identify examples of potential and kinetic energy in everyday life. 3. Understand the concept of energy conservation. 4. Apply knowledge of potential and kinetic energy to solve real-life problems. Standards in the Philippines: Grade 8 Physical Science Standard 1: Understand the nature and properties of matter and energy and the interactions between them. Grade 8 Physical Science Standard 2: Understand the structure and properties of matter. Grade 8 Physical Science Standard 3: Understand the interactions of matter and energy. Materials: Whiteboard or chalkboard Generate another lesson plan! 10/01/2023 Markers or chalk Poster paper Sticky notes Various objects representing potential and kinetic energy (e.g., roller coaster model, ramp and ball, wind-up toy, stretched rubber band, etc.) Stopwatch or timer Laptops or tablets (optional) Procedure: Introduction (10 minutes) 1. Begin by asking students if they have ever ridden a roller coaster or played with a toy car. Discuss the excitement and thrill they experienced during these activities. 2. Write the learning objectives on the board, ensuring students have a clear understanding of what they will learn. 3. Explain that today they will explore the concepts of potential and kinetic energy, which are fundamental to understanding the physical world around us. Engage: Potential vs. Kinetic Energy Sort (15 minutes) 1. Divide the class into small groups of 3-4 students and provide each group with a set of sticky notes. 2. On the board, create two columns labeled "Potential Energy" and "Kinetic Energy." 3. Instruct the groups to brainstorm and write down examples of potential and kinetic energy on the sticky notes, one example per note. 4. Have the groups take turns placing their sticky notes in the appropriate column on the board. 5. Discuss and clarify any misconceptions or uncertainties raised during Generate another lesson plan! 10/01/2023 the activity. 6. Summarize the definitions of potential and kinetic energy based on the examples provided. Explore: Energy Conversion Station (20 minutes) 1. Set up different stations in the classroom, each representing a specific example of potential and kinetic energy. For example: a) Roller coaster model: Demonstrate how the potential energy of the coaster at the top of the track is converted into kinetic energy as it descends. b) Ramp and ball: Show how potential energy is converted into kinetic energy as the ball rolls down the ramp. c) Wind-up toy: Explain how the potential energy stored in the toy's wound-up spring is converted into kinetic energy as it unwinds. d) Stretched rubber band: Demonstrate how potential energy is converted into kinetic energy when the rubber band is released to propel an object. 2. Allow students to rotate through each station in small groups, observing and discussing the conversion of energy at each station. 3. Provide opportunities for students to ask questions and make connections between the different examples. 4. Encourage students to take notes or draw diagrams to record their observations and understandings. Explain: Conservation of Energy Demonstration (15 minutes) 1. Gather the students back together and ask if they noticed any patterns or similarities in the energy conversions they observed. 2. Introduce the concept of energy conservation, explaining that energy cannot be created or destroyed but can only change forms. 3. Perform a simple demonstration, such as using a pendulum or a swinging pendulum toy, to show how potential energy is converted into kinetic energy and vice versa, without any energy being lost. Generate another lesson plan! 10/01/2023 4. Discuss the conservation of energy and its implications in various reallife situations. 5. Connect the concept of energy conservation to the examples previously explored, highlighting how potential and kinetic energy are interconnected and constantly changing. Elaborate: Energy Problem-Solving Activity (20 minutes) 1. Distribute a worksheet or digital copy of energy problem-solving activities to each student. 2. Instruct students to work individually or in pairs to solve the given problems, which involve calculating potential and kinetic energy or determining the energy conversions in a given scenario. 3. Encourage students to use the knowledge and examples discussed earlier to guide their problem-solving process. 4. Circulate around the classroom, providing guidance and support as needed. 5. After completion, review the answers as a class, discussing the methods used and reinforcing the correct understanding of potential and kinetic energy. Conclusion (5 minutes) 1. Summarize the key points discussed throughout the lesson, emphasizing the definitions and examples of potential and kinetic energy. 2. Review the concept of energy conservation and its significance. 3. Allow students to ask any final questions or provide feedback on the lesson. 4. Provide a brief preview of the next lesson or related topics to be covered. Assessment: Generate another lesson plan! 10/01/2023 Observation during the Engage, Explore, and Elaborate activities to assess students' active participation, understanding, and ability to differentiate potential and kinetic energy. Review of students' worksheets or problem-solving activities to evaluate their problem-solving skills and understanding of potential and kinetic energy concepts. Note: This lesson plan aligns with the Philippines K-12 Curriculum Standards for Grade 8 Physical Science. Generate another lesson plan! 10/01/2023