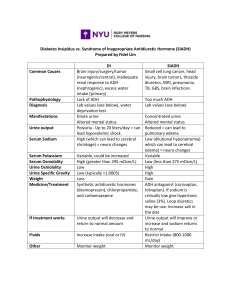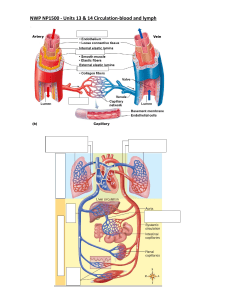
Pathophysiology Deficiency of ADH or the kidneys inability to respond to ADH. Key remembering o Diabetes insipidus o Decreased ADH o Diuresis Types of Diabetes Insipidus Nephrogenic o The posterior pituitary gland is doing its job and releasing ADH, there’s a problem with the kidneys, and it is not responding appropriately to the signal and reabsorbing more water. o The Kidneys do not respond to ADH o Which results in inability to conserve (reabsorb) water. Primary o There’s a defect in the hypothalamus or posterior pituitary o Resulting in lack of ADH Secondary o Results from tumors or tumor near the hypothalamus or pituitary o Head tumor or Metastatic tumors o Infection o Surgery Drug Related o Drugs such as: Lithium and Demeclocycline interferes with the kidney response to ADH Signs and Symptoms Large amount of Diluted Urine Polydipsia (excessive thirst) Severe Dehydration Pt at risk for Hypovolemic Shock Hypernatremia (increase sodium) Risk Factors Hypernatremia Severe dehydration Putting pt on fluid restriction to decrease urine output can cause worsening dehydration and hypernatremia Diagnostic 24 hours urine Test o Less than 2 Liters I n24 hours without hypernatremia rules out Diabetes Insipidus (DI) Vasopressin Challenge Test (DDAVP) o Osmolality measures the concentration o Normal Value: 700-1400 The higher the value, the more concentrated the urine Primary or Secondary: the osmolality will increase with admin of DDAVP (urine will be more concentrated Fluid Deprivation Test o Withholding fluids for 8-12 hours util 35% of body wt is lost o Contraindication if pt is hypernatremia o Inability to increase specific gravity and osmolality of urine is characteristic of Diabetes Insipidus Labs Serum Osmolality o Will be increased in DI (concentration) o Normal Value: 288-291 o Critical Value: >295 Urine Specific Gravity o Will be decreased in DI (diluted) o Normal Value: 1.015-1.03 o Critical Value: 1.001 to 1.005 Serum Sodium o Normal value: 135-145 o Critical Value: > 145 Assessment- Recognize Cues Most of the manifestations are related to dehydration and extreme thirst Make sure Nasal passage is clear for meds Monitor VS, labs, and maintain Fluid Volume Daily wts Ask about o Recent surgery o Head trauma o Drug used (Lithium) Extremely large amounts of diluted urine output o Greater than 4L/day and up to 30L/day S/S of fluid volume deficit o Weight loss, Poor skin turgor, Dry mucous membranes, Tachycardia, and Hypotension Management Desmopressin (DDAVP) o Synthetic Vasopressin o Used to control fluid balance o Do Not have the same impact as the natural ADH o Used with caution in pt existing CV due to vasoconstrictive properties o Administer: intranasally or sublingual 10 mcg/spray Dose is 1-6 sprays a day depending on severity o Given IM If unable to give Intranasally Thiazide Diuretics o For Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus o It decreases polyuria and increase osmolality Mild Sodium Restriction o To help maximize the effectiveness of Thiazide Diuretics NSAID Sulfonylureas o Diabinese