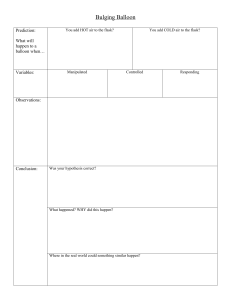
Be SMART 1. Who was the English scientist who made accurate observations on the relationship of pressure and volume? Robert Boyle 2. What is the formula or equation used in solving problem involving Boyle’s Law? 3. According to Boyle’s Law, as the pressure exerted on a gas is increased, the volume will ______________________. 4. In the equation for Boyle’s Law, V2 stands for ___________. FINAL VOLUME 5. What is the value equal to the standard pressure? 1 atm 6. A 2.75 L sample of dry air in a cylinder exerts a pressure of 3 atm at 30 ˚C. without changing the temperature, a piston is moved until the pressure in the cylinder is reduced to 1 atm. What is the final volume of the gas? Activity No. 2 TEAM + PEA + RATE + TURE TEMPERATURE GAS + LAW GAS LAW BALL + LUME VOLUME AT + MOIST + PEAR ATMOSPHERE PRESS + SURE PRESSURE Objectives: Investigate the relationship between volume and temperature at constant pressure. Materials: Erlenmeyer Flask, alcohol burner, small balloon and ice. Procedure: 1.Add a small amount of water to an Erlenmeyer Flask. 2.Place the flask on a hot burner. 3.Put the open end of a balloon over the opening of the flask. 4.Observe the expansion of the balloon. 5.Move the flask to an ice bath. 6.Observe the suction on the balloon. What is your observation on the activity? What do you think is the cause why the balloon expands? How could hot water be the reason to make the balloon inflated? What are the quantities involved in this experiment? How does the change in the temperature relate to the volume of gas in the balloon? What is Charles’ Law? Plot each coordinate point on the coordinate grid and connect the points using a line. A. (0,0) D. (6,8) B. (2,4) E. (8, 10) C. (4,6) “directly proportional” Example: A syringe contains 56.11 ml of gas at 311K. Determine the volume that the gas will occupy if the temperature is increased to 400K 1.A cylinder with a movable piston 3 contains 250 cm air at 10˚ C. If the pressure is kept constant, at what temperature would you 3 expect the volume to be 150cm ? 2. A tank contains 2.3 L of helium gas at 25˚ C. what will be the volume of the tank after heating it and its content to 40˚ C temperature at constant pressure? 3. A 20˚ C, the volume of chlorine 3 gas is 15dm . Compute for the resulting volume if the temperature is adjusted to 318K provided that the pressure remains the same. Bring out ¼ sheet of paper and answer the following questions. Write only the letter of the correct answer. 1. The relationship of which two variables are compared in Charles’ Law a. Pressure and volume b. Volume and temperature c. Temperature and pressure d. Volume and moles 2. Dionelle and Tristan are playing basketball outside in 82˚C weather. If they leave the ball outside and temperature drops about 53˚C, what will happen to the volume of the gas in the ball if the pressure remains constant? a.Volume will remain the same b.Volume will increase c.Volume will decrease d.Volume will double in size 3. At constant pressure, what happens to temperature of a gas when the volume doubles? a.The temperature also doubles b.The temperature decreases to half of its original volume c.The temperature doesn’t change. d.The temperature quadruples 4. Elisa and Jiesel want to play a game of beach volleyball If the beach ball has a volume of 400 L at a temperature of 500K, what will the temperature of the balloon be if the volume decreases to 176 L? a.176 L b.500K c.400L d.220K 5. Charles’ Law is an experimental gas law that describes how gases tend to expand when heated. The law states that if a quantity of gas is held _____________ pressure, there is a _______________relationship between its volume and the temperature. a.Constant- direct b.Higher- inverse c.Greater- constant d.Decreasing- double Bring Charles’ Law in action by giving solution to the problem below: BAKING. We can see Charles’ Law in our kitchen. Using a yeast as an ingredient, how is the law applied in delicious bakery products like bread and cakes? Rubric: 5 points- The student demonstrates a thorough understanding of the concept behind the task. 4 points- The student demonstrates an understanding of the concept behind the task. 3 points- The student demonstrates only a partial understanding of the concept behind the task. 2 points- The student demonstrates a very limited understanding of the concept behind the task. 1 point- The student provides a completely incorrect solution. 0 point- No response at all.