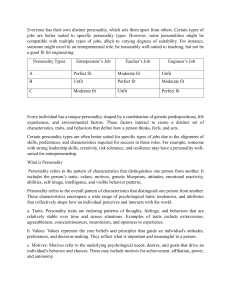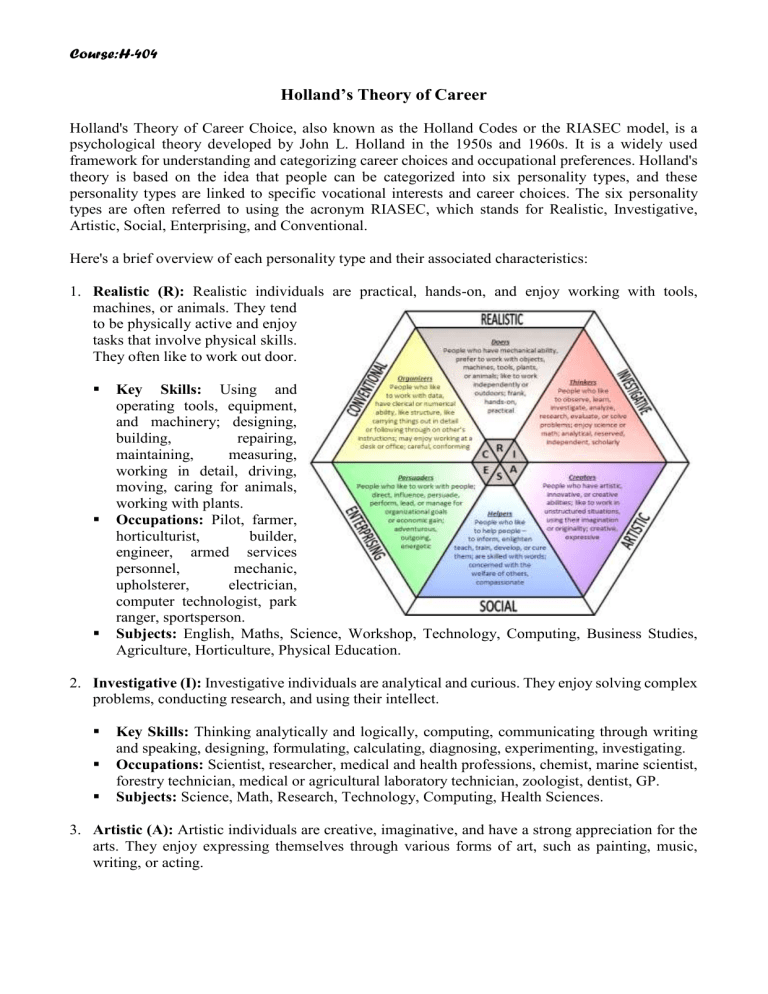
Course:H-404 Holland’s Theory of Career Holland's Theory of Career Choice, also known as the Holland Codes or the RIASEC model, is a psychological theory developed by John L. Holland in the 1950s and 1960s. It is a widely used framework for understanding and categorizing career choices and occupational preferences. Holland's theory is based on the idea that people can be categorized into six personality types, and these personality types are linked to specific vocational interests and career choices. The six personality types are often referred to using the acronym RIASEC, which stands for Realistic, Investigative, Artistic, Social, Enterprising, and Conventional. Here's a brief overview of each personality type and their associated characteristics: 1. Realistic (R): Realistic individuals are practical, hands-on, and enjoy working with tools, machines, or animals. They tend to be physically active and enjoy tasks that involve physical skills. They often like to work out door. Key Skills: Using and operating tools, equipment, and machinery; designing, building, repairing, maintaining, measuring, working in detail, driving, moving, caring for animals, working with plants. Occupations: Pilot, farmer, horticulturist, builder, engineer, armed services personnel, mechanic, upholsterer, electrician, computer technologist, park ranger, sportsperson. Subjects: English, Maths, Science, Workshop, Technology, Computing, Business Studies, Agriculture, Horticulture, Physical Education. 2. Investigative (I): Investigative individuals are analytical and curious. They enjoy solving complex problems, conducting research, and using their intellect. Key Skills: Thinking analytically and logically, computing, communicating through writing and speaking, designing, formulating, calculating, diagnosing, experimenting, investigating. Occupations: Scientist, researcher, medical and health professions, chemist, marine scientist, forestry technician, medical or agricultural laboratory technician, zoologist, dentist, GP. Subjects: Science, Math, Research, Technology, Computing, Health Sciences. 3. Artistic (A): Artistic individuals are creative, imaginative, and have a strong appreciation for the arts. They enjoy expressing themselves through various forms of art, such as painting, music, writing, or acting. Course:H-404 Key Skills: Expressing artistically or physically, communicating through speaking, writing, and singing, performing, designing, presenting, planning, composing, playing, dancing. Occupations: Artist, illustrator, photographer, signwriter, composer, singer, instrument player, dancer, actor, reporter, writer, editor, hairdresser, fashion designer. Subjects: English, Social Studies, Music, Drama, Art, Graphic Design, Computing, Business Studies, Languages. 4. Social (S): Social individuals are outgoing, empathetic, and enjoy helping others. They are drawn to careers that involve interpersonal interactions and a focus on human relationships, such as teaching, counseling, or healthcare professions. Key Skills: Communicating through writing and speaking, caring and supporting, training, meeting, greeting, assisting, teaching, informing, interviewing, coaching. Occupations: Teacher, nurse, counselor, police officer, social worker, salesperson, customer service representative, secretary, waiter. Subjects: English, Social Studies, Math, Science, Health, Physical Education, Art, Computing, Business Studies, Languages. 5. Enterprising (E): Enterprising individuals are ambitious, assertive, and enjoy taking on leadership roles. They are often entrepreneurial and thrive in competitive environments. Key Skills: Selling, promoting, and persuading, developing ideas, public speaking, managing, organizing, leading, computing, planning. Occupations: Salesperson, lawyer, politician, accountant, business owner, executive or manager, travel agent, music or sports promoter. Subjects: English, Math, Business Studies, Accounting, Economics, Social Studies, Drama, Computing, Languages. 6. Conventional (C): They prefer working indoors and tasks that involve organizing and being accurate, following procedures, working with data or numbers, and planning work and events. Key Skills: Computing and keyboarding, recording and keeping records, paying attention to detail, meeting and greeting, doing calculations, handling money, organizing, arranging, working independently. Occupations: Secretary, receptionist, office worker, librarian, bank clerk, computer operator, stores and dispatch clerk. Subjects: English, Math, Business Studies, Accounting, Economics, Computing. According to Holland's theory, individuals tend to be most satisfied and successful in careers that align with their dominant personality types. They are also more likely to stay in their chosen careers if they match their personality preferences. Moreover, the theory suggests that individuals can be a combination of two or more of these personality types, resulting in a more complex career profile. Holland's Theory of Career Choice has been widely used in career counseling and vocational guidance to help individuals better understand their interests and make informed career decisions. It provides a useful framework for career exploration and development, as it helps people identify careers that are a good fit for their personality and interests.