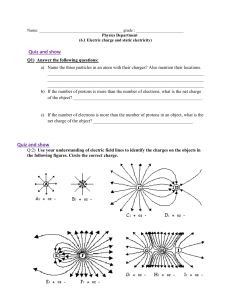
INSTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICITY BASIC CONCEPT OF ELECTRICITY Electricity is a term used to describe the energy produced when electric charges are caused to move from one object to another. 1 Differentiate static electricity from electric current; 2 Define current, voltage, and resistance; 3 Differentiate conductors from insulators PROPERTIES OF ELECTRON Charge is basically a property of electrons and protons. They have the same magnitude of charge but their charge is opposite in sign. Protons have a positive charge, while electrons have negative charge. In most objects around you, these charges are in equal amount. ELECTRICITY • It is the movement or flow of electrons in a conductor. • Is a present phenomenon which can be determined by its effects. a) The iron produces heat b) Air conditioner makes surrounding either cold or hot c) Bulb produces light. Suppose you rub a plastic comb on your hair, the atoms in your hair holds their electrons more loosely than the atoms in your hair hold theirs. As a result, electrons are transferred from the atoms in your hair to the atoms on the plastic comb. Since your hair loses electrons, it becomes positively charged, while the plastic comb that gains electrons becomes negatively charged. EXPERIMENT TIME Rubbing neutral objects together allows electron to move from one object to another. All charged objects exert an electric force on each other. Objects with the same type of charge repel one another, while the objects with opposite charges attract one another. Since your hair and the comb have opposite charges, they will be attracted to one another. An electric charge on an object that causes to attract or repel other objects is called static electricity. EXPERIMENT TIME Rubbing neutral objects together allows electron to move from one object to another. QUALITIES/ FACTORS VOLTAGE- (Electromotive force), The amount of pressure which enables or pushes the electrons to flow in a conductor. CURRENT- The amount of the flow of electrons in a conductor. RESISTANCE- Amount of opposition which limits or opposed the flow of electron OHMS LAW The amount of current in flowing in any circuit is directly proportional to the voltage or electromotive force and inversely proportional to resistance. TABLE OF SPECIFICATION 1. Proton is ________ a. Neutral b. Positively charged c. Negatively charged d. Either positive or negative 2. In a neutral atom, _______ a. Electrons and protons are equal and with the same charge b. Electrons and protons are equal but with different charges c. Electrons are greater in number than protons d. Protons are greater in number than electrons 3. When atom gains an electron, it becomes a. Neutral b. Positively charged c. Negatively charged d. Will not be affected 4. Objects with the same type of charge a. Repel one another b. Attract one another c. Do not affect each other d. Exert force on each other 5. The movement of electric charges is known as_______? a. Electrical resistance b. Electric current c. Electric power d. Voltage 6. Electrons moves through materials which called _______ a. Conductors b. Generators c. Insulators d. Transformers 7. Electric current is measured using the unit _______ a. Ampere b. Ohm c. Volt d. Watt 8. Sources of voltage or EMF include _______? a. Conductors and Insulators b. Batteries and Generators c. Generators and Motors d. Wires and Cables 9. Voltage is measured using_______? a. Electric meter b. Ohmmeter c. Ammeter d. Voltmeter 10. Electrical Resistance describe the force that _______? a. Pulls the electric charges b. Pushes the electric charges through the insulators c. Pushes the electric charges through conductors d. Oppose the flow of electric charges in conductors 1. How much current flows in a fluorescent lamp with a resistance of 20 ohms and connected in a 200 volts power source? 1. 2. 3. 4. Given Formula Solution/Substitution Final Answer 2. What is the applied voltage to a 100 amps bulb with resistance of 10 ohms. 1. 2. 3. 4. Given Formula Solution/Substitution Final Answer 3. What is the Resistance or the amount of opposition to a incandescent bulb with a current flow of 20 amps and connected to a 400 volts 1. 2. 3. 4. Given Formula Solution/Substitution Final Answer TABLE OF SPECIFICATION FORMULA NAMED AFTER SYMBOL FACTORS/ QUALITY UNIT OF MEASUREMENT VOLTAGE VOLTS 13. _______________ CURRENT AMPERES 14. _______________ RESISTANCE OHMS 15. _______________ E I R 1. Proton is ________ a. Neutral b. Positively charged c. Negatively charged d. Either positive or negative 2. In a neutral atom, _______ a. Electrons and protons are equal and with the same charge b. Electrons and protons are equal but with different charges c. Electrons are greater in number than protons d. Protons are greater in number than electrons 3. When atom gains an electron, it becomes a. Neutral b. Positively charged c. Negatively charged d. Will not be affected 4. Objects with the same type of charge a. Repel one another b. Attract one another c. Do not affect each other d. Exert force on each other 5. The movement of electric charges is known as_______? a. Electrical resistance b. Electric current c. Electric power d. Voltage 6. Electrons moves through materials which called _______ a. Conductors b. Generators c. Insulators d. Transformers 7. Electric current is measured using the unit _______ a. Ampere b. Ohm c. Volt d. Watt 8. Sources of voltage or EMF include _______? a. Conductors and Insulators b. Batteries and Generators c. Generators and Motors d. Wires and Cables 9. Voltage is measured is using_______? a. Electric meter b. Ohmmeter c. Ammeter d. Voltmeter 10. Electrical Resistance describe the force that _______? a. Pulls the electric charges b. Pushes the electric charges through the insulators c. Pushes the electric charges through conductors d. Oppose the flow of electric charges in conductors TABLE OF SPECIFICATION