Classical Breeding vs Genetic Engineering: Techniques & Analysis
advertisement

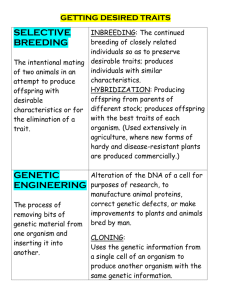
Identify identify examples of crops and animals that have been improved through classical breeding and genetic engineering. Explain explain the advantages and disadvantages of classical breeding and genetic engineering techniques. • • • Classical breeding has been used for thousands of years to improve crops and livestock, and it is still a vital tool in modern agriculture. traditional method of breeding plants and animals that involves selecting for desired traits over several generations. This method relies on the natural mechanisms of inheritance and genetic recombination, as well as controlled breeding between individuals with desired traits. newer technique that involves modifying the DNA of an organism in order to introduce or remove specific traits. This is typically achieved by using recombinant DNA technology to insert or delete specific genes in the organism's genome. Classical breeding has been used Classical breeding has been better suited to specific to produce wheat varieties that environments, have higher milk used to improve the yield, disease resistance, and drought are resistant to pests and or meat yields, and are more tolerance of corn diseases and have higher yields. disease-resistant. resistant to herbicides, reducing the need for chemical weed control. longer shelf lives and improved resistance to pests and diseases longer shelf lives and improved resistance to pests and diseases. • Natural process: Classical breeding relies on natural mechanisms of inheritance and genetic recombination, and can be used to enhance desirable traits naturally within a population. • Cost-effective: Classical breeding does not require expensive equipment or sophisticated technical knowledge, making it an accessible and cost-effective approach. • Well-established: Classical breeding has been used for thousands of years, and there is a wealth of knowledge and experience in this area. • Time-consuming: Classical breeding can take several generations and a significant amount of time to achieve the desired traits. • Limited precision: Classical breeding can be imprecise and result in traits that are not completely predictable or controllable. • Limited genetic diversity: Classical breeding can result in a loss of genetic diversity, especially if breeding is restricted to a limited number of individuals or populations • Precision: Genetic engineering allows for precise control over the traits of an organism, making it quicker and more precise in achieving desired results. • Rapid results: Genetic engineering can produce results in a much shorter time than classical breeding, making it useful for timesensitive applications. • Expanded genetic diversity: Genetic engineering allows for the introduction of genetic material from other species or organisms, increasing genetic diversity and potential for new traits. • Costly: Genetic engineering requires specialized equipment and expertise, making it a more expensive method than classical breeding. • Regulatory hurdles: Genetic engineering is often heavily regulated due to concerns over safety, ethical considerations, and public perception. • Potential risks: There are concerns over the potential risks and ethical implications of genetic engineering, such as unintended effects on the environment and human health.