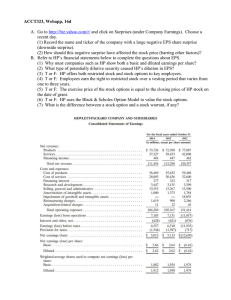
CHAPTER 19: EARNINGS PER SHARE EPS - BASIC - EPS provides a measure of how much earnings was generated for each share of common stock held by outsiders. o Reported by the company at earnings announcement. o Forecasted by security analysts. o Compared price per share to get “Price-Earning” P/E ratio. Basic EPS = Net Income−Preferred Dividends Weighted average number of common shares outstanding EPS – DILUTED: - - Company with “complex” capital structures also report Diluted EPS. o Complex capital structures include securities that can be converted into stock at the investor’s discretion. Convertible debt, stock options and warrants. o Some of the value of these convertible securities is tied to the value of common stock; thus investors holding these securities are “indirect” stockholders. Diluted EPS provides EPS assuming everything that could convert to a share of stock actually did so. Net Income−Preferred Divident+Adj.for convertibles Diluted EPS = Weighted avg number of common shares outstanding+Adj.for convertibles EPS – CONVERTIBLE DEBT - - - Convertible debt can be exchanged for common stock Diluted EPS is computed under the assumption that the convertible debt had been exchanged for common stock at the start of the period. o This is called the “if converted” method. Numerator of EPS: Net income is increased by the after-tax interest expense on the convertible bond. o If debt had converted, there would have been no interest expense, so it is added back to Net Income. Denominator of EPS: number of shares is increased as if the debt was converted to common shares at the beginning of the period. EPS – STOCK OPTIONS: - - “in-the-money” stock options give the holder the right to acquire a share of common stock at a pre-specified price. Diluted EPS is computed under the assumption that a faction of the option had converted to common shares. o This is called “treasury stock” method. Numerator of EP: no adjustment necessary - Denominator of EPS: number of shares is increased by a fraction of each outstanding option. o Number of additional shares = number of options x conversion fraction o Conversion fraction = Avg.Stock price−exercise price Avg.Stock Price DILUTED EPS – COMPLICATIONS - Diluted EPS must always be less than or equal to Basic EPS o Diluted EPS is set equal to Basic EPS in years where a firm has a loss from continuing operations to common stockholders. o If diluted EPS would be greater than Basic EPS after a convertible is added to the calculation, the convertible is considered “antidilutive” and is excluded from computation of Diluted EPS. o Options are considered “antidilutive” when the exercise price is greater than the market price (when option is “out of the money”).