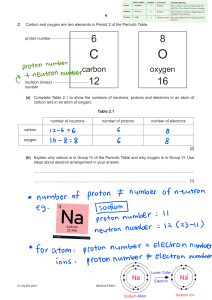
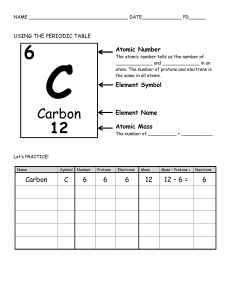
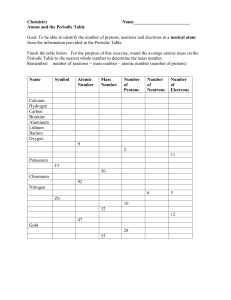
Name Date Chapter Test B Class Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table I. Testing Concepts Directions: Determine whether the italicized term makes each statement true or false. If the statement is true, write true in the blank at the left. If the statement is false, write in the blank the term that makes the statement true. 1. The central core of an atom is called the hub. 2. The chart showing the classifications of elements according to their properties and increasing atomic numbers is called the periodic table. 3. The mass of an electron is about equal to the mass of a proton. 4. Elements arranged in vertical columns in the periodic table are called periods. 5. The region around the nucleus occupied by the electrons is called the negative zone. 6. The symbol for chlorine is C. 7. The maximum number of electrons in the second energy level of an atom is 4. Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 8. Two isotopes of carbon are carbon-12 and carbon-14. These isotopes differ from one another by two electrons. 9. Nonmetals are poor conductors of heat and electricity. 10. Seven electrons in the outermost energy level is characteristic of a metal. 11. Quarks can be produced by bombarding protons with protons. 12. The number of protons in an atom is called the atomic mass. 13. The sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in an atom is the mass number. 14. The weighted average of the mass numbers of all the isotopes that occur in nature for a particular element is the average atomic number. 15. A diagram showing only outer energy level electrons is called a(n) periodic table. 16. Elements having three or fewer electrons in the outer energy level are classified as nonmetals. 17. The atomic masses of the elements are not whole value numbers because of the existence of quarks. 18. The identity of an element is determined by the number of protons. Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table 37 Name Date Class Chapter Test B (continued) 19. According to present atomic theory, the location of an electron in an atom is best represented by a probability cloud. 20. As you move from left to right in a row of the periodic table, metallic properties increase. Directions: In the blank at the left, write the letter of the term or phrase that correctly completes each statement. 21. Each energy level of an atom has a maximum number of ______ it can hold. a. neutrons b. quarks c. protons d. electrons 22. Dot diagrams are used to represent ______. a. the structure of the nucleus c. isotopes b. atomic number d. outer electrons 24. A chemical symbol represents the ______of an element. a. name b. structure c. reaction d. type 25. Horizontal rows of the periodic table are called ______. a. groups b. families c. clusters d. periods 26. Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called ______. a. metalloids c. transition elements b. radioactive d. isotopes 27. A particle that moves around the nucleus is a(n) ______. a. proton b. ion c. neutron d. electron 28. Elements in groups 3 through 12 are called ______. a. metalloids c. noble gases b. transition elements d. isotopes 29. The ______ is used to accelerate protons in the study of subatomic particles. a. Tevatron c. technology b. temanite d. television 30. A certain atom has 26 protons, 26 electrons, and 30 neutrons. Its mass number is ______. a. 26 b. 30 c. 52 d. 56 II. Understanding Concepts Skill: Concept Mapping 1. In a concept map of the atom, which term would appear closer to the top of the map: mass number or neutrons? 38 Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 23. Particles of matter that make up protons and neutrons are ______. a. electrons c. atoms b. isotopes d. quarks Name Date Class Chapter Test B (continued) Skill: Using a Table 2. Complete the following table. The atomic number of hydrogen is 1. Name Atomic mass Atomic number Number of protons Number of neutrons a. Hydrogen-1 b. Hydrogen-2 c. Hydrogen-3 3. Look at the table completed in question 2. What is unusual about the structure of hydrogen-1? Skill: Comparing and Contrasting Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 4. In what ways are protons and neutrons alike? How are they different? 5. How did Mendelev set up his periodic table? How was his first periodic table like the periodic table today? How is it different? 6. What is an isotope? How does it differ from the standard form of an element? Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table 39 Name Date Class Chapter Test B (continued) III. Applying Concepts Writing Skills Directions: Answer the following questions using complete sentences. 1. Explain why the periodic table is such a useful tool for both scientists and students. 2. Scientists often use mental pictures to explain their ideas. What do we call these mental pictures? Why are they useful? 4. Compare and contrast the masses of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 5. Explain why the elements in group 18 are stable. 40 Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 3. Suppose that you have just discovered a new element and have named it “neptunite.” While studying your new element you find that it has two isotopes. These are neptunite-220 and neptunite-250. What is the average atomic mass of your new element? (Assume that these two isotopes are present in equal amounts in nature.)