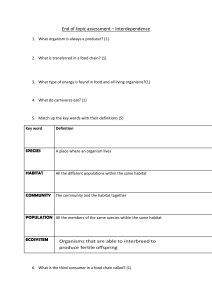
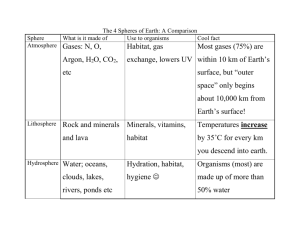
Ms Daly BW 5 Habitat Study Ecology • • Ecology is the study of plants and animals in relation to the environment A Community is where all the animals and plants in a particular area live Producer • Producer makes its own food e.g. Green plants Consumers • • • Herbivores are animals that feed on plants e.g. cattle, sheep, deer Carnivores are animals that feed on other animals (flesh meat) e.g. fox Omnivores are animals that feed on plants and animals e.g. humans, badger Food Chain • • Food chain is a list of organisms in the order in which one is eaten by the other A food chain always begins with a producer (plant – can make its own food) Food Web • Food web is a group of interconnected food chains Competition Competition occurs when organisms fight for something in short supply. Plants: compete for water, space, light. Animals: food, shelter, mates, territory Adaptation An adaptation is a structure or way of life an organism has that helps it survive better in its habitat. ● ● ● Nettles have stings to keep away herbivores. Primroses flower early before the leaves grow on trees shading them. Foxes have a brown coat for camouflage, snails have a shell for protection against being eaten by birds. Ms Daly ● ● BW 5 Habitat Study Fish have gills to absorb oxygen underwater and fins to swim. Frogs have webbed feet to swim. Interdependence ● ● Interdependence is the way different organisms rely on each other. Insects depend on plants for food, plants depend on insects for pollination. Fewer bees would result in less pollination which could reduce the crop of fruits such as apples. Habitat Study A habitat is a place where an organism lives. ● ● ● A robin lives in a nest in a tree A Rabbit lives in a burrow in the ground A Blackberry plant lives in the hedgerow Steps in a habitat study 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Map your area Identify Abiotic Factors Qualitative Study - Identify flora and fauna present using a key Quantitative Study - Estimate the number of flora and fauna present Write up findings (1) MAP Draw a map of the grassland habitat including the following. Grass, Trees, Hedges, Walls and Fences (2) Identify Abiotic Factors These are non living factors that affect organisms in their habitats. Ms Daly BW 5 Habitat Study Abiotic Factor Method of Measuring Air Temperature Use a thermometer in the air Soil Temperature Soil thermometer Soil PH PH meter Light Intensity Light Meter (3) Qualitative Study Identify what plants and animals are present using a KEY identification tool Plants are easy to observe but animals must be captured carefully to observe them. Ms Daly BW 5 Habitat Study (4) Quantitative Study - It would be impossible to count all the plants and animals present so we take a random sample to give us an estimation of the overall numbers. - It is random to avoid bias and inaccurate results. - There are two methods a Quadrat or A Line Transect Quadrat Ms Daly BW 5 Habitat Study ● A square frame used to estimate plant numbers. ● Used to measure how frequently a plant species occurs in a habitat. ● Throw at random 10 times Count plants as follows: % Frequency = Number of quadrats in which ‘plant x’ found x 100 Total number of quadrats Line Transect ● A rope marked out at regular intervals across a habitat. ● It is used to investigate the distribution of organisms. ● Each interval is called a station - the type of plant or animal found touching each station are recorded.