Uploaded by
Derek Brian Boron Pinlac
IT Fundamentals: Definitions, Hardware, Software, History
advertisement

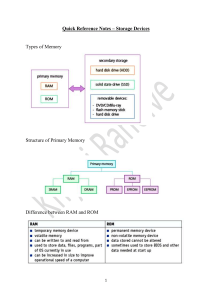
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY DEFINED • • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY • • • • information technology is the use of any computer, storage, networking and other physical device to create, process, store, secure and exchange all forms of electronic data. focuses on the information processing from the collection, to the processing, and the sharing of information deals with the methods and tools used in the information processing. Computer literacy is also known as digital literacy and it’s the ability to find, evaluate, and compose clear information through writing and other media on various digital platforms. • PERIPHERAL DEVICES • non- essential hardware components that usually connect to the system externally. (e.g. keyboard, mouse, microphone, web cam, etc.) • houses the electronic components to process data. o Motherboard- the main circuit board of the system unit. The motherboard is central to any computer system. o Processor- The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of the computer. It controls what the computer does and is responsible for performing calculations and data processing. o Memory- – Electronic component that store instructions waiting to be executed and data needed by those instructions. 2 TYPES OF INTERNAL MEMORY. ROM (Read Only Memory) o used to permanently store instructions that tell the computer how to boot (startup) also known as BIOS (Basic input/output system) operating system. o Information stored in ROM is known as READ ONLY o ROM is fast memory o ROM is Non-Volatile memory. RAM (Random Access Memory) o RAM is used to temporarily store information that is currently in use by the computer. SYSTEM UNIT WHY STUDY I.T.? • • • • we use these technologies in our everyday lives, and we need to further understand how these hardware and software are working. computer skills are needed regardless of setting and field you become self-sufficient whether you use it for research, communications or time management and in the years to come you’ll have a strong base to support the furtherance of your knowledge. avoid unfamiliar situations and modernize our skills to stay relevant in a dynamic work environment. • COMPUTER • is a machine, a collection of parts that work together. • is a collection of parts, a computer combined with hardware and software used to perform desired tasks. COMPUTER SYSTEM • COMPONENTS OF COMPUTER HARDWARE • the tangible, physical computer equipment and devices which provide support for major functions of the computer system o INPUT DEVICES • used to enter data or instructions into a computer system. o manual input devices need to be operated by a human to input data (e.g. keyboard, mouse, microphone, scanner, numeric keypad, light pen, STORAGE DEVICES webcam, touch screen, digital camera, web cam) automatic input devices can input data on their own (e.g. bar-code reader, magnetic stripe reader, chip and pin reader, magnetic ink character recognition, optical mark/character reader) pieces of hardware that send this usable information out of the computer. o • used to convey information from the computer system to one or more people. Output devices send information out temporarily and permanently: temporary output device (monitors, speakers, projectors) and permanent output devices (printers, plotter). • • • can be read from and written to and so the information stored in RAM can change all the time o RAM is a fast memory. Data can be written to and read from RAM very quickly. o generally measured in GB o RAM is Volatile Memory and stores date ‘nonpermanently’. o The more RAM the faster it can perform. Holds data, instructions and information permanently for future use. Magnetic Storage Device - one of the most popular types of storage used. Optical Storage Device – uses lasers and lights as its mode of saving and retrieving data. OUTPUT DEVICES • • Flash Memory Device – is now replacing magnetic storage device as it is economical, more functional and dependable. Online and Cloud Storage – is now becoming widespread as people access data from different devices. COMMUNICATION DEVICES • • Enables a computer to send and receive data, instructions, and information to and from one or more computers. Bluetooth devices, Infrared devices, Modem (over phone line), Network card (using Ethernet), Smartphone, Wi-Fi devices (using a Wi-Fi router) SOFTWARE • • • • • SYSTEMS SOFTWARE includes the programs that are dedicated to managing the computer itself (e.g. operating system, file management utilities, and disk operating system (or DOS). • end-user programs that execute specific tasks like (report generation, spreadsheet management, running games, sending • • • consists of individual facts or pieces of USERS information that are used by the computer system to produce information JACQUARD LOOM • • the operator of a computer is known as ‘peopleware’, other books call them liveware, or human ware. commands the computer system to execute EARLY ELECTRONIC COMPUTERS (20TH CENTURY) on instructions • • • • • • • • • • COLOSSUS • • • • • combination of hardware and software that is designated to perform a highly specific function examples are washing machine, camera, phones, microwaves, airplanes, automobiles, and calculators. EVOLUTION OF COMPUTERS ANALYTICAL ENGINE • has a central processing unit (CPU) as a microprocessor. also known as personal computers (PC) used for word processing, managing databases or spreadsheets, graphics and general office applications. EMBEDDED COMPUTER • MECHANICAL COMPUTERS (19TH CENTURY) emails, and online research among other functions) DATA has the most of the features and capabilities of a large computer but more compact in size. used for process control and performing financial and administrative tasks, such as word processing and accounting. Some machines were designed for medical laboratory and teaching aids. MICROCOMPUTER • APPLICATION SOFTWARE PASCALINE • referred to the large cabinets called “main frames” that housed the central processing unit and main memory of early computers. contains the large memory, huge storage space, multiple high-grade processors, so it has ultra-processing power compare to standard computer systems. used in moderate data processing, banking, and insurance. It handles bulk data processing, statistics, and analysis them. MINICOMPUTERS • known as the series of related instructions that make the computer perform tasks. tells the computer what to do. The term ‘program’ or ‘application’ refers to ABACUS any piece of software. • • allowed users to perform basic arithmetic operations through the manipulation of beads on rods. roots dating back to around 2400 BCE in ancient Mesopotamia and China. invented by Blaise Pascal in 1642, mechanical calculator capable of performing addition and subtraction gears and wheels to handle numerical computations. designed by Charles Babbage in the 1830s, laid the groundwork for modern computing. it featured basic arithmetic operations, loops, and conditional branching. in the early 1800s, Joseph-Marie Jacquard developed Jacquard Loom a loom that used punched cards to control the weaving patterns, effectively introducing COMPUTER TYPES AND VARIETIES the concept of programming through for big amount of computing power cloud computing and the use of digital systems leading edge of data processing capability, with respect to calculation speed usually used on a large-scale operation like industrial function, space exploration, weather forecasting, and nuclear testing. (high-performance computing) which crunch numbers and data, while mainframes focus on transaction processing. SUPERCOMPUTER punched cards. • • • during World War II, British engineer Tommy Flowers developed Colossus, world's first programmable electronic digital computer used to break encrypted German codes and played a crucial role in the Allied victory. MAINFRAME COMPUTER • ELECTRONIC NUMERICAL INTEGRATOR AND COMPUTER (ENIAC) like Pets.com and Webvan, which eventually burst in the early 2000s. ADVANCEMENTS IN THE 21ST CENTURY TRENDS IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SMARTPHONES QUANTUM COMPUTING ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND MACHINE LEARNING • • Completed in 1945 first general-purpose electronic computer • used vacuum tubes for computation. • the introduction of the iPhone in 2007 revolutionized mobile computing, leading to a proliferation of smartphones and tablets. • provide scalable and on-demand computing resources over the internet, enabling businesses and individuals to access data and applications from anywhere. such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure led to breakthroughs in natural language processing, image recognition, autonomous vehicles, and more. perform complex calculations exponentially faster than traditional computers. IBM and Google CLOUD COMPUTING INTERNET OF THINGS UNIVAC I AUGMENTED REALITY • • • developed by J. Presper Eckert and John Mauchly in 1951, first commercially available computer used for scientific and business applications. • THE BIRTH OF MODERN COMPUTING (1950S-1960S) • • • • VIRTUAL REALITY • TRANSISTORS • • • • • • • • In 1947, the invention of transistors by John BLOCKCHAIN TECHNOLOGY Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley at Bell Labs revolutionized computing Replaced bulky vacuum tubes, making computers smaller, faster, and more reliable. Introduced in 1964 offered compatibility across models, setting a new standard for computer architecture. In the late 1960s, the U.S. Department of Defense's Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) created ARPANET, the precursor to the modern internet allowed computers to communicate with AUTOMATION each other for the first time. • • • • • in 1975, became one of the first commercially successful microcomputers, Bill Gates and Paul Allen to develop software for it. introduced in 1977, first mass-produced, user-friendly personal computers, significant impact on the home computing market. • • • • • • • launched in 1981, became the industry standard, accelerates the adoption of personal computers in businesses and homes • in 1989, Tim Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web, the internet accessible to non-technical users transforms the way we access and share information. in late 1990s, a surge of internet-based companies, leading to the dot-com bubble, • • • IBM 360 into our real-world environments. examples:pokemon go, historical ARPANET information, location based. A complete immersion experience that shuts out the physical world examples : vr in military, sports, mental health, education digital information (the “block”) stored in THE RISE OF MICROCOMPUTERS (1970S-1980S) ALTAIR 880 a public database (the “chain”) • example: cryptocurrency APPLE II • • INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTIONS • • • simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think like humans and mimic their actions examples: self-driving cars, chatbots/ virtual assistants, facial recognition, and language translators made up of devices that allows them to communicate from their environments. examples: smart home, smart farming, and smart wearables blending of interactive digital elements – like dazzling visual overlays, buzzy haptic feedback, or other sensory projections – • • the technique of making a system operate automatically. examples: robotic process automation, big IBM PC data, automated decision making, test automation A period of development in the latter half of the 18th century, where there is change THE INTERNET ERA (1990S) WORLD WIDE WEB from one economy to another. involves technological, socioeconomic, and cultural aspects which transforms the way in which a society carries out the DOT COM BUBBLE INVENTION • • • o o o o o o o o o o • o o • production and distribution of goods. discovery of new products and processes. the commercialization and improvement of the existing products. started in England during the late 18th century, concentrated in Britain and initially focused on textile manufacturing. Significant evolutions: Cort’s puddling; rolling process for making iron, Crompton’s mule for spinning cotton, Watt steam engine Products / Services – Vegetables, Coal, Iron, Discovery of chemicals Transportation – Railroads, Basic farming Production System – Manual Labor to mechanical Communication - Printed materials Significant evolution: Development of electricity, Internal-combustion engine, Railway, Chemical industry Products / Services – electricity, chemicals, petroleum, steel Transportation – automobiles, aircrafts Production System – machine-aided equipment Communication – telephone, telegraph Started with the development of transistors and the rise of electronics and digital technology. Products / Services – Internet, rise of electronics, source of energy: nuclear power Production System – Automation Klaus Schwab described the fourth industrial revolution as an era of technological revolution that is blurring the lines between the physical, digital and biological spheres. INOVATION FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION - 1765 SECOND INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION - 1870 THIRD INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION - 1969 FOURTH INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION – 2000