History of International Trade: Trade Routes & Development
advertisement

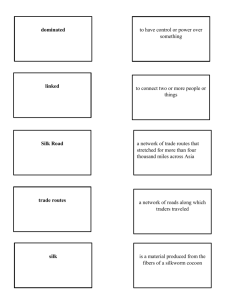
History of International Trade LESSON 1 Let’s guess… FORM GET GROUPS OF THREE MEMBERS. A PIECE OF PAPER. LIST DOWN FIVE COUNTRIES WHICH YOU THINK ARE TRADE PARTNERS OF THE PHILIPPINES. LIST DOWN FIVE EXPORT COMMODITIES OF THE PHILIPPINES. LET’S CHECK… Top Trading Partners of the Philippines 1. United States 2. Japan 3. Hong Kong 4. China 5. Germany 6. Holland 7. Singapore 8. South Korea Major Export Commodities of the Philippines Transport Equipment Garments Fruits Coconut Oil Petroleum Products Copper Products Electronic Products Learning Outcomes 1) Explain how international business and trade started and progressed 2) Determine the importance of International business and trade to entrepreneurship OUTLINE: HISTORY OF INTERNATIONAL TRADE ANCIENT TRADE ROUTES CLASSICAL MEDIEVAL TRADE ROUTES COLONIAL MODERN TRADE ROUTES TRADE ROUTES INTERNATIONAL TRADE What is Trade? Trade means exchange of goods, services, or both. Trade is also called commerce. Trading is greatly important to the global economy. Trade is a boon for human interaction, bringing cross-cultural contact to a whole new level. What is International Trade? THE EXCHANGE OF GOODS & SERVICES BETWEEN COUNTRIES. + JOBS + CONSUMPTION + THE FIGHT AGAINST POVERTY + ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES + NATURAL RESOURCES + FASHION Origin of Trade Trade originated in prehistoric times. It was the main facility of prehistoric people, who bartered goods and services from each other. Ancient Trade There is evidence of the exchange of obsidian and flint during the Stone Age. Ancient Trade Routes Materials used for creating jewelry were traded with Egypt since 3000 BCE. Historians believe, the first long-distance trade occurred between Mesopotamia and the Harappan civilization of Indus Valley around 3000 BC. Ancient Trade Routes In the absence of proper roads, the most efficient way to transport goods from one place to another was by sea. The first and most extensive trade networks were actually waterways like the Nile, the Tigris and the Euphrates in present-day Iraq and the Yellow River in China. Cities grew up in the fertile basins on the borders of those rivers and then expanded by using their watery highways to import and export goods. Ancient Trade Routes The domestication of camels around 1000 BC helped encourage trade routes over land, called caravans, and linked India with the Mediterranean. Classical Age Trade Routes THE SILK ROAD From the very beginning of Greek civilization to the fall of the Roman Empire in the 5th century, a financially worthwhile trade brought valuable spice to Europe from the Far East, including China. The Sogdians ruled the East-West trade route known as the Silk Road from the end 4th century AD to the 8th century AD. The Silk Road was originally opened up by Zhang Qian, and it gradually formed in the Han Dynasty (206 BC-220 AD). Trade Routes of the Middle Ages The fall of the Roman Empire, and the succeeding Dark Ages brought insecurity to Western Europe and a near end of the trade network. VIKING AND VARANGIAN TRADE ROUTES The Vikings and Varangians traded from the 8th to the 11th century as they sailed from and to Scandinavia. Vikings sailed to Western Europe. Varangians sailed to Russia. VARANGIAN TRADE ROUTES Trade Routes of the Middle Ages SRI VIJAYAN TRADE ROUTES Srivijaya empire was a maritime and commercial kingdom that flourished between the 7th and the 13th centuries, largely in what is now Indonesia. Srivijaya’s power was based on its control of international sea trade. It established trade relations not only with the states in the Malay Archipelago but also with China and India. Trade Routes of the Middle Ages OTTOMAN EMPIRE TRADE ROUTES The Ottoman Empire trade routes grew from the narrow streets of Anatolia (Turkey) to the Silk Road. The Ottomans most famously traded silk, furs, cotton, spices and tobacco. They also imported glassware, gunpowder and medicines. Colonial Trade Routes SPICE TRADE ROUTE Vasco da Gama restarted the European Spice trade in 1498. Earlier to his sailing around Africa, the flow of spice into Europe was controlled by Islamic powers, especially Egypt. It was monopolized by Spain and Portugal from 15th to 17th century. Colonial Trade Routes MANILA TO ACAPULCO GALLEON TRADE Manila galleon, Spanish sailing vessel that made an annual round trip (one vessel per year) across the Pacific between Manila and Acapulco, in present Mexico, during the period 1565–1815. The galleon brought porcelain, silk, ivory, spices, and myriad other exotic goods from China to Mexico in exchange for New World silver. Colonial Trade Routes BRITISH EAST INDIA COMPANY The British East India Company was a private corporation formed in December 1600 to establish a British presence in the lucrative Indian spice trade. Colonial Trade Routes DUTCH EAST INDIA COMPANY Dutch East India Company (Vereenigde Oost-Indische Compagnie) was a trading company founded in the Dutch Republic (present-day Netherlands) in 1602 to protect that state’s trade in the Indian Ocean and to assist in the Dutch war of independence from Spain. The company prospered through most of the 17th century as the instrument of the powerful Dutch commercial empire in the East Indies (present-day Indonesia). It was dissolved in 1799. Colonial Trade Routes FREE TRADE AGREEMENT BETWEEN FRANCE AND BRITAIN When he became emperor in 1852, Napoléon III found that leading industrialists staunchly defended protectionist trade laws, fearing that without them they would lose market share to foreign competition. After consolidating power, he assigned Michel Chevalier to undertake secret negotiations with the British to dramatically reduce trade barriers. The result, the Cobden-Chevalier Treaty of 1860, was "a watershed in the history of modern international trade." MODERN INTERNATIONAL TRADE GATT was designed by the UN in 1946 aimed to increase trade by tariff reduction. Later, World Trade Organization (WTO) was established in 1995, (global international organization dealing with the rules of trade between nations). Developments in Trade The invention of money has made trade simpler. Today traders generally negotiate through the medium of exchange, like money, which then makes buying separate from selling, or earning. Developments in Trade As transportation has become increasingly less expensive and telecommunications have improved, hence international trade has flourished. References: Dominick Salvatore, International Economics, John Wiley & Sons Inc., 2004. Krugman,Paul R. and Obstfeld, Maurice (2005).International Economics: Theory and Policy,7th edition, Boston: Addison-Wesley.