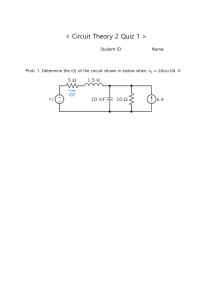
variable. 9. Two areas of application of the concepts covered in this chapter are the TV picture tube and electricity billing procedure. REVIEW QUESTIONS 1.1 One millivolt is one millionth of a volt. (a) True (b) False 1.2 The prefix micro stands for: (a) 106 (b) 103 (c) 10−3 1.3 (d) 10−6 The voltage 2,000,000 V can be expressed in powers of 10 as: (a) 2 mV (b) 2 kV (c) 2 MV (d) 2 GV 1.4 A charge of 2 C flowing past a given point each second is a current of 2 A. (a) True (b) False 1.5 A 4-A current charging a dielectric material will accumulate a charge of 24 C after 6 s. (a) True (b) False 1.6 Voltage is measured in: (a) Watts (c) Volts | ▲ | ▲ 1.7 The unit of current is: (a) Coulomb (c) Volt 1.8 The voltage across a 1.1 kW toaster that produces a current of 10 A is: (a) 11 kV (b) 1100 V (c) 110 V (d) 11 V 1.9 Which of these is not an electrical quantity? (a) charge (b) time (c) voltage (d) current (e) power 1.10 The dependent source in Fig. 1.19 is: (a) voltage-controlled current source (b) voltage-controlled voltage source (c) current-controlled voltage source (d) current-controlled current source io vs + ! 6io (b) Ampere (d) Joule Figure 1.19 (b) Amperes (d) Joules per second For Review Question 1.10. Answers: 1.1b, 1.2d, 1.3c, 1.4a, 1.5a, 1.6b, 1.7c, 1.8c, 1.9b, 1.10d. e-Text Main Menu| Textbook Table of Contents |Problem Solving Workbook Contents amounts of electrons: (a) 6.482 × 1017 (b) 1.24 × 1018 19 (c) 2.46 × 10 (d) 1.628 1020Concepts CHAPTER 1 ×Basic 0 0 Figure 1.20 2 4 6 8 2 4 For Prob. 1.6. 10 12 6 23 Find the energy absorbed by the element in 2 s. t (ms) 8 t (s) 1.11 !50 Find the current flowing through an element if the charge flow is given by: CHAPTER 1 Basic Concepts 23 (a) q(t) = (t + 2) mC PROBLEMS Figure 1.21 For Prob. 1.7. 1.7 The charge flowing in a wire is plotted in Fig. 1.21. (b) q(t) = (5t 2 + 4t − 3) C Sketch the corresponding current. −4t q (C) Section 1.3 Charge(c) and Current q(t) = 10e pC P R O B L E M S (d) q(t) = 20 cos 50π t nC 1.8 The current flowing past a point in a device is shown 50 1.1 How many coulombs are represented by these in Fig. 1.22. Calculate the total charge through the −2t q (C) point. = 5e and sinCurrent 100t µC amounts of electrons: Section 1.3 (e) q(t) Charge 17 18 (a) 6.482 × 10 (b) 1.24 × 10 0 | 1.1 1.3 How many represented by these Find coulombs the chargeare q(t) flowing through a device| if the | 2 50 4 19 20 8 t (s) 6 (c) 2.46 × 10amounts (d) i (mA) of electrons: current is: 1.628 × 10 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 q(t) (mC) Figure 1.20 80 q(t) (mC) 80 For Prob. 1.6. 0 Figure 1.23 1.11 5 The voltage v across a device and the current i 2 through 3 it4are 5 t (s) 1 v(t) = 5 cos 2t V, For Prob. 0 1.9.1 2 3 4 i(t) = 10(1 − e−0.5t ) A 5 t (s) | ▲ Calculate: Sections 1.4 and 1.5 Voltage, Power, and (a) theFor total charge 1.7 The charge flowing in a wire is plotted in Fig. 1.21. Figure 1.23 Prob. 1.9. in the device at t = 1 s Energy Sketch the corresponding current. (b) the power consumed by the device at t = 1 s. Sections 1.4 and 1.5draws the Voltage, 1.10 A certain electrical element currentPower, and i(t) = 10 cos 4t A at a voltage v(t)Energy = 120 cos 4t V. 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 t (ms) Find the energy absorbed by the element in 2 s. 1.10 A certain electrical element draws the current 1.11 The voltage vi(t) across a device and currentv(t) i = 120 cos 4t V. = 10 cos 4t A at the a voltage Figure 1.20 For Prob. 1.6. 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 t (ms) through it areFind the energy absorbed by the element in 2 s. | v(t) = 5 cos 2t V, i(t) = 10(1 − e−0.5t ) A Calculate: (a) the total charge in the device at t = 1 s (b) the power consumed by the device at t = 1 s. e-Text Main Menu Textbook Table of Contents |Problem Solving Workbook Contents 17 18 (a) flowing 6.482 10= (b) (a) × i(t) 3 A, = 11.24 10 0 !50 Find the current through an q(0) element ifCthe× 10 20 19 2 4 8 t (s) 6 2.46 ×i(t) 10 = (2t + 5) (d) (b) mA,1.628 q(0) × = 10 0 charge flow is(c) given by: (c) i(t) = 20 cos(10t + π/6) µA, q(0) = 2 µC (a) q(t) + 2)the mC !50 1.2 = (t Find current flowing through an element if the Figure 1.21 For Prob. 1.7. 2 (d) i(t)C= 10e−30t sin 40t A, q(0) = 0 (b) q(t) = (5tcharge + 4tflow − 3) is given by: 0 2 t (ms) 1 −4t (c) q(t) = 10e pC (a) q(t) = current (t + 2) flowing mC 1.4 The through a device 1.8 is The current flowing past a For point in a1.7. device is shown Figure 1.21 Prob. (d) q(t) = 20(b) cosq(t) 50πt i(t) = 6π− t A. the total charge flow Figure For Prob. 1.8. the =nC (5t52 sin + 4t 3) Calculate C in Fig. 1.22. Calculate the1.22 total charge through −2t the pC device from t = 0 to t = 10 ms. point. (e) q(t) = 5e(c) q(t) sinthrough 100t µC−4t = 10e 1.8 The current flowing past a point in a device is shown 1.9 The current through an element is shown in Fig. (d)q(t) q(t) = 20 cos 50πt nC 1.5 Determine the total chargeifflowing into an element Find the charge flowing through a device the in Fig. 1.22. Calculate the total charge through the 1.23. Determine the total charge that passed through for=05e <−2t t< s when sin2100t µCthe current entering its i (mA) current is: (e) q(t) point. −2t the element at: positive terminal is i(t) = e mA. (a) i(t) q(0) 1 C q(t) flowing through a device if the 10 1.3 = 3 A, Find the=charge (a) t = 1 s (b) t = 3 s (c) t = 5 s (b) i(t) = (2t + 5) mA, q(0) =entering 0 1.6 The a certain element is shown in i (mA) current is: charge 1.20. Find= the (c) i(t) = 20(a) cos(10t + 3π/6) µA, q(0) = 2 µCat: i(t)Fig. = A, q(0) 1 Ccurrent 10 i (A) −30t (a) t = 1 ms (b) (c) t = 10 ms (d) i(t) = 10e sin 40t A, q(0) = 0 (b) i(t) = (2t + 5) mA, q(0)t = = 60 ms 0 2 t (ms) 1 10 (c) i(t)through = 20 cos(10t + is π/6) µA, q(0) = 2 µC The current flowing a device (d) A. i(t)Calculate = 10e−30t 40tcharge A, q(0) =0 i(t) = 5 sin 6πt thesin total flow Figure 1.22 For Prob. 1.8. 5 0 2 t (ms) 1 through the device from t = 0 to t = 10 ms. 1.4 The current flowing through a device is q(t) (mC) an element is shown = charge 5 sin 6πt A. Calculate the total charge1.9 flow The current through Determine thei(t) total flowing into an element Figure 1.22 For Prob. 1.8. in Fig. 4 5 t (s) 1.23. Determine the total0charge1 that 2passed3through 80 from t = its 0 to t = 10 ms. for 0 < t < 2through s when the device current entering the element at: positive terminal is i(t) = e−2t mA. The current throughFor an Prob. element is shown in Fig. 1.5 Determine the total charge flowing into an element (a) t 1.9 Figure = 1 s 1.23.(b)Determine t = 31.23 s the total (c) tcharge =1.9. 5 s that passed through for 0 <at certain < 2 s when theiscurrent its The charge entering element shownentering in the element positive terminal Fig. 1.20. Find the current at: is i(t) = e−2t mA. Sections 1.4at: and 1.5 Voltage, Power, and i (A) (a) t = 1 s (b) t = 3 sEnergy (c) t = 5 s (a) t 1.6 = 1 ms The (b) t = 6 ms (c) t = 10 ms charge entering a certain element is shown in 10 Fig. 1.20. Find the current at: 1.10 A certain electrical element draws the current i (A) (a) t = 1 ms (b) t = 6 ms (c) t = 10 ms i(t) = 10 cos 4t A at a voltage v(t) = 120 cos 4t V. 5 10 Find the energy absorbed by the element in 2 s. 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 t (ms) ▲ 1.2 ▲ ▲ 1.2 The voltage v across a device and the current i through it are e-Text Main Menu| Textbook Table of Contents |Problem Solving Workbook Contents v(t) = 5 cos 2t voltage V, = 10(1 − e−0.5t A current i 1.11 The vi(t) across a device and) the 6A 12 V + ! 1A 3A 0 1 3 4 t (s) 24 Figure 1.24 30 V PART 1 DC Circuits For Prob. 1.13. + Vo ! + ! + ! 28 V – + 6A 5Io 3A The current entering the positive terminal of a 1.16 Determine Io in the circuit of Fig. 1.27. Section 1.6 1.12 Circuit Elements device is i(t) = 3e−2t A and the voltage across the Figure 1.28 For Prob. 1.17. 1.14 Figure 1.25 shows five elements. If devicea iscircuit v(t) =with 5 di/dt V. 12 V p1 = −205 W, p = 60 W, p = 45 W, p = 30 W, + ! 4 delivered 5to the device between (a) 2Find the charge calculate the power received t =p03 and t = 2or s. delivered by Section 1.7 Applications Io 5A element 3. (b) Calculate the power absorbed. + 1.18 It takes eight photons to strike the surface of a + + (c) Determine 20 V 2 4 the energy absorbed in 3 s. 20 Vone electron. If 8 V ! photodetector in order to emit 1.13 Figure 1.24 shows the current through and the 4 × 1011 photons/second strike! the surface of the! voltage across a device. Find the total energy photodetector, calculate the amount of current flow. 1 3 5 absorbed by the device for the period of 0 < t < 4 s. 1.19 Find the power rating of the following electrical3 A i (mA) appliances in your household: 50 Figure 1.27 For (b) Prob.Radio 1.16. set (a) Lightbulb Figure 1.25 For Prob. 1.14. (c) TV set (d) Refrigerator Find Vo in the circuit of Fig. 1.28. (e)1.17 Personal computer (f ) PC printer 1.15 Find the power absorbed by each of the elements in (g) Microwave oven (h) Blender Fig. 1.26. 0 I = 10 A 30 V + ! 2 10 V + v!(V) 10 p2 + 14 A + 20 V 0! p1 Figure 1.24 8V ! 4 t (s) 4A 1.20 p4 p5 + 12 V 3 4 !t (s) 0.4I p3 1 For Prob. 1.13. ▲ | ▲ | ! Vo A 1.2-kW toaster takes roughly 4!minutes to heat – + four slices of 6 Abread. Find the cost of operating the toaster once per day for 1 month (30 days). Assume energy costs 9 cents/kWh. 1.6Prob. 1.15. Circuit Elements FigureSection 1.26 For 1.14 Io = 2 A A 1.5-kW electric heater is connected to a 120-V source. + ! 28 V (a) How much current does the heater draw? 12 V 1 A 6A ! (b) If the heater is on for+ 45 minutes, how much energy is consumed in kilowatt-hours (kWh)? + ! 3A 28 for V 45 (c) Calculate the cost of operating the heater + minutes if energy costs 10 cents/kWh. + 30 V 1.21 3A Figure 1.28 Figure 1.25 shows a circuit with five elements. If p1 = −205 W, p2 = 60 W, p4 = 45 W, p5 = 30 W, calculate the power p3 received or delivered by element 3. 5Io 3A For Prob. 1.17. Workbook Contents e-Text Main Menu| Textbook Table of ContentsSection |Problem 1.7 Solving Applications 2 1 Figure 1.25 1.15 4 3 1.18 It takes eight photons to strike the surface of a photodetector in order to emit one electron. If 4 × 1011 photons/second strike the surface of the photodetector, calculate the amount of current flow. 1.19 Find the power rating of the following electrical appliances in your household: (a) Lightbulb (b) Radio set (c) TV set (d) Refrigerator (e) Personal computer (f ) PC printer (g) Microwave oven (h) Blender 5 For Prob. 1.14. Find the power absorbed by each of the elements in Fig. 1.26.