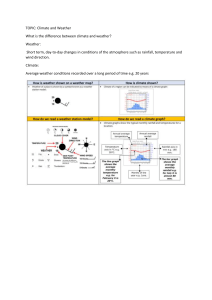
Difference between weather and climate Weather the condition in the air or atmosphere in the present, or at the moment. We call it the current state. When we use the word 'weather' we are talking about temperature, clouds, wind and rainfall. The weather can stay the same, or it can change quickly. We use the word climate when we talk about the weather in general. Climate is the average temperature, clouds, wind and rainfall conditions worked out over a minimum of 20 years. Climate allows us to have a good idea of what the weather conditions are likely to be like throughout a year. We can then say what we expect the temperature, winds and rainfall to be in a place in summer and winter. This does not mean that it will always be so. Sometimes a place will get warmer or colder temperatures than normal or more rainfall or less rainfall. Over the last few years, scientists have noticed that the world's climate is changing. Some places have more droughts than usual, while other places have more floods. Some places experience warmer temperatures, while others have cooler temperatures. This change in the world's climate is linked to global warming. This is often talked about in the newspapers and on television. Warm, mild and cold climatic regions of the world In warm climates, the temperature is high most of the year. It is usually above 25°C. In some hot places it often reaches 35°C. The highest recorded temperature in the world which is 57°C, in Libya. In mild climates the temperature is not too high or too low for most of the year. It usually stays between 10°C and 30°C. In cold climates, temperatures are low for most of the year. 1 It is usually below 10°C. In some very cold places the temperature drops to -20°C. The lowest recorded temperature in the world reaching -89°C in Antarctica. Temperatures in hot, mild and cold climates are not always the same at different times of the year. In January it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere and summer in the Southern Hemisphere. In July it is summer in the Northern Hemisphere and winter in the Southern Hemisphere. Wet and dry areas of the world The wetlands of the world are found near warm oceans. Hot oceans are found in the areas around the equator. Wet areas along the equator receive about 2,600 mm of rainfall per year. This is five times more than the average rainfall for South Africa. Dry areas are found inland, far away from the oceans. This is because winds that bring rainfall do not reach those areas. Dry areas are also found along cold oceans. Cold oceans do not give the air enough moisture. Dry areas receive between 25 mm and 250 mm of rainfall per year. Tropical rainforests are forests that are warm and wet. There is very little change in temperature - it is always hot. It rains all year round. Tropical rainforests are called the 'jewels of the earth' because half of the world's plant and animal species live in these forests. 2 There are still some plants and animals in these forests of which we know very little about. Rainforests absorb 4.8 billion tons of carbon dioxide each year. This makes them very important for the survival of the world. One of the most famous rainforests is the Amazon rainforest. Location on Earth Tropical rainforests are found along the low-lying areas of the equator. That's why they're hot and wet. These areas have very high rainfall, warm temperatures throughout the year and high humidity. Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. Humidity makes the air feel sticky. Climate: temperature and rainfall patterns The climate in rainforests is often humid because it is always warm and wet. We can use rainfall and temperature graphs to find out more about the climate of an area. The graphs show the rainfall and temperature of an area for each month of the year. Natural vegetation and wildlife in a rainforest Tropical rainforests are the perfect habitat for many different kinds of living things. There are plants that grow low on the ground, tall trees and plants that climb up against others and grow on others. This is because there is so much rain and it's always hot. The warm temperatures and good rainfall mean the vegetation grows easily. The wide variety and large numbers of trees and plants provide food, lots of fruit and seeds. 3 The vegetation also provides safety and places for different creatures to make their homes and nests. That's why there is so much wildlife in rainforests. It is estimated that almost half of the world's plant and animal species are found in the rainforests of the world. Two-thirds of all flowering plants can be found in these rainforests. The wildlife and vegetation have adapted to the hot, humid and wet conditions. The forests consist of many different types of trees and plants. The trees are called evergreen trees. These are trees that do not lose their leaves in winter. Different animals, birds and insects live in the different layers. The tall trees get a lot of sunlight and the short trees and vegetation are in the shade most of the time. Deforestation It is very sad that these rainforests are being cut down by people very quickly. This leads to deforestation. Deforestation occurs when trees are cut down and forests destroyed. Every minute of every day, large parts of the world's tropical forest are being cut down. The reason for this is that the land is used to grow crops and graze cattle. The wood of the trees is also used to make furniture and is also used in construction and mining industries. The forest land is also used for other things such as farming, mining or building towns. 4 Deserts are arid areas that receive less than 250 mm of rain per year. Some deserts are hot and others are cold. This unit is about the world's hot deserts. Location on Earth Check out the image below where the world's main hot deserts are found. Climate: temperature and rainfall patterns The temperature in warm deserts is usually between 20°C and 25°C. In some places the temperature can reach 50°C during the day and it can get very cold at night. Warm deserts get very little rain and there is often no rain for months. Natural vegetation and wildlife in a desert Due to the high temperatures and dry conditions of the Sahara desert, plant life is sparse and includes only about 500 species. These are mainly types of plants that are drought and heat resistant. Plants adapted to the heat and drought by: Grow long roots. With little leaves; and Storage of water in leaves and stems. The harsh conditions and dust storms in the Sahara desert affect what type of animals can survive there. In the central driest part of the desert there are only about 70 different animal species. Animals have adapted to the desert by: Hunt at night when it's cool. 5 Living underground during the day. By reducing the amount of water they lose from their bodies. With large ears with very small blood vessels - heat escapes from the blood vessels. It helps to cool their bodies. And also help them lose body heat. How people live in a desert The Tuareg The Tuareg of the Sahara keeps herds of sheep, goats and camels. They are nomadic and move from place to place as the seasons change. They eat the meat and drink the milk of their animals. They also use animal skins to make tents and other goods. The Australian natives The Australian natives lived in the Australian deserts. They were nomads. They knew when and where it would rain and moved to those areas. They did not own much, but always carried their hunting and gathering tools with them. About 200 years ago European settlers took over the country and this forced the Australian natives to change their way of life. The Oasis An oasis is a place in a desert where water is permanently present. People build settlements near oases and can even plant crops such as olives, figs and date palms. The date palm is a useful plant. The fruit can be eaten, the stem provides wood and some of the leaves can be made into rope, which is used in roofs of buildings. Desert dwellers even many years ago found ways to bring groundwater to the surface. For example, they dug wells or built water canals to divert water from the source to their crops. Today, people lay underground pipes, build modern pumps, or even use trucks to bring fresh water to areas where it is needed. 6 Coniferous forests cover about 15% of the earth's land surface. They form the world's largest forests, but often have fewer species of plants and animals than other forests. They are often found in areas where there are lakes. Location on Earth Here you can see the location on the map. Climate: temperature and rainfall patterns Coniferous forests grow in climatic regions where summers are short and winters are long and cold, with heavy snowfall. Natural vegetation and wildlife in a coniferous forest There is more wildlife in the temperate coniferous forests than in the warm deserts, but not as much as in the tropical rainforests. The forest vegetation and mosses provide food and shelter for animals, birds and insects. There are fewer reptiles as it is very cold in winter. The vegetation of temperate coniferous forests must cope with the long cold winters and the thin poor soils. The trees are evergreen and the most common are the spruce and pine. The pine tree, which is a common tree in coniferous forests, is shaped like a pyramid so that snow will not collect and break the branches. 7 The leaves are thin and needle-like so that the leaves can get sunlight lower in winter and snow will slide off the leaves. The leaves are not nutritious and are therefore not eaten by the animals. The leaves are covered with wax so that they do not lose too much water and protect them from the cold. Lynxes feed on small animals and birds found in the forests. They have long legs and fur on the soles of their feet so they can hunt in the snow. They have a thick light brown fur to keep them warm in winter and help hide in the shadows of the forests. They have a short tail so they do not lose too much heat. Human activities The forest land is poor, so it is not good for farming. Instead, large areas of temperate coniferous forests were cleared by logging. Stumps of wood are driven into rivers by sawmills. The soft wood is good for making paper, matches, furniture and houses. This is the most important way people make a living from the forests. A large number of forests are plantations. In plantation forests, areas with a single tree species are planted. These trees grow straight and fast which means they can be cut down sooner. Many coniferous forests are located near major industrial centers and urban areas where many people live. Forests are also being destroyed by air pollution from these industries and from heavy traffic. Population growth and the expansion of cities means many forests are cleared to make way for roads, towns and cities. Mining is another reason why forests are being cut down. In the summer people gather berries, nuts and fruit and fish and hunt animals. People ski on the snow slopes in winter. 8