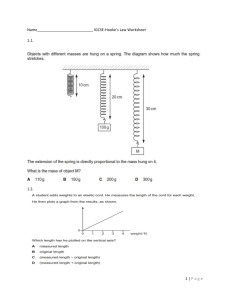
Chapter 1 Section 1: Periodic Motion Learning Objectives 1 Describe Simple Harmonic Motion 2 Calculate the energy stored in spring 3 Identify the factors affecting Pendulum’s period Key Vocabulary 1. Periodic Motion 2. Simple Harmonic Motion 3. Resonance Warmer Activity • From the following clip: • What is special about this motion !? Try to describe it with your own words • Do you know what we call such motion. Periodic Motion • Periodic motion occurs when objects move in a repetitive way along a particular path in a fixed interval of time. Which forms a beautiful repeated motion like a “harmony” . Simple Harmonic Motion • Recall wave characteristic: •Amplitude is the maximum displacement or distance reached by an object from the equilibrium position. •Period is the time needed for an object to complete one cycle. • Simple Harmonic Motion: Any system in which the force acting to restore an object to its equilibrium position (Net force = 0) is directly proportional to the displacement of the object. Activity (1): Spring – Mass Experiment • Perform the following experiment and write down your observations about S.H.M: https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/masses-andsprings/latest/masses-and-springs_en.html Mass on a spring system • Observations: • We can observe that spring force increase as displacement increase • Spring force always opposes motion (toward equilibrium position ( x=0 ) • The time needed across the min. & max. position (Period) is constant. • Restoring force: Is the force responsible for this kind of motion (S.H.M) and its always directed toward the equilibrium position (X=0) • And in this example, it’s the spring force where its directed opposite to the direction of motion to restore the normal position of the spring (toward equilibrium) causing a repetitive motion through fixed time interval Hooke’s Law • Based on the experiment we did of Mass-spring system: 1. Find the relation between Spring force – Displacement 2. What if you changed the spring to a stronger one !? Hooke’s Law • In Hooke’s Law: • K : represents the spring constant that depends on the stiffness of the spring and some other properties. • It represents the slope of the force magnitude Vs. displacement ( N/m) • Steeper slope will give a larger K. Which means that the spring is harder to stretch NEGATIVE SIGN means that spring force opposes motion Objects that obeys Hooke’s law called elastic objects Hooke’s Law valid for a certain limits, if the spring stretched further this limit. Then deformation will happen Elastic Potential Energy • Once we apply an external force to stretch or compress the spring, A WORK is done and stored as a potential energy in the spring. • This potential energy stored is called Elastic potential energy • Elastic potential energy = Area under the curve • P.E = (area of triangle) = ½ × Base × Height • Base = ∆x • Height = Force = kx (according to hook’s law) Elastic Potential Energy • Use the previous experiment then write-down your observation from the energy graph: We apply the law of conservation of energy: Potential Energy converted into Kinetic energy, and repeat. 1. Max. Potential Energy occurs at (max. compression or extension position) where at this instant velocity is ZERO ( K.E = 0 ) 2. Max. Kinetic Energy occurs at (max. velocity), when displacement is ZERO (Equilibrium) where elastic potential energy is equal to ZERO Activity (2) Activity 3 • Perform the following experiment: and answer the given questions https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/pendulumlab/latest/pendulum-lab_en.html • Q1) What is the location of Max. Potential Energy • Q2) Is it considered as periodic motion !! Explain !? • Q3) What happen to the time period once you: • Change the mass of the hanged ball • Change the Length of the rope • Manipulate the gravity value • Q4) What are the factors that affects the period of this pendulum ? Pendulum The component of the gravitational force in the direction of the pendulum’s circular path is a restoring force. • This force is Max. & Min. at the highest point on right and left (where velocity is zero) • At equilibrium point velocity is max. and the restoring force is zero. • Only for a small angles (less than 15) the force is proportional to the displacement from the equilibrium >>> simple harmonic motion • Masses are called Bob. Activity 4 Resonance • See the given video to visualize resonance: Resonance • Resonance: Is a force applied to a vibrating or oscillating object at a time interval equal to the period of oscillation • It cause an increment of the amplitude in the vibration • Resonance is a simple harmonic motion causes a larger displacement as energy added in small increments • Resonance can cause useful increase in amplitude or catastrophic result. • https://www.twig-world.com/film/resonance-1428/ Activity 5 • Apply your understanding of resonance using the following simulation: • https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/legacy/resonance Check your understanding Let's play: https://kahoot.it/challenge/0476052?challenge-id=86fdb651-f1b84548-859b-a7e0a8874730_1693727624340