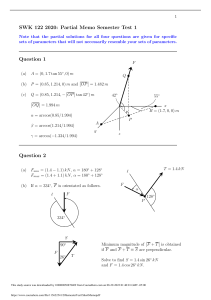
ONM4201 May 2021 Quiz 4 Quiz date: To be announced on BlackBoard Instructions: Each quiz will have 5 questions where each worth 20 points. 3 questions will be randomly selected from this assignment (excluding supplement questions). 2 question will be added that is not listed in this assignment. You will have approximately 25 minutes to answer all 5 questions. 1. List the following a. 2 assumptions that makes it unnecessary to keep Safety Stock (C7) 1) Demand is known, constant and deterministic 2) Lead time is known, constant and deterministic b. 4 obstacles of coordination in a Supply Chain that could cause Bullwhip (C7) Obstacles on Info sharing and Demand forecasting Pricing Obstacles Operation Related Obstacles Shortage Gaming Obstacles c. 3 scenarios enabling distortion of demand due to information sharing (C7) Scenarios enabling distortion of demand due to information sharing include: Supply chain members not sharing actual customer demand Demand data shared is delayed or data not Time Series Willingness of entities to share information due to Relationship Structure d. 3 supply chain’s operation or policy related approaches in mitigating Bullwhip Effect (C7) Many approaches to mitigate, however, using supply chain’s operations to mitigate may include: Controlling replenishment lead time Reducing delivery batch sizes Rationing of distribution e. 2 possible impact if a Supply Chain adopts long term rationing (C7) If Manufacturer or Distributer adopt long term rationing, tradeoff of this decision includes Entity exiting the supply chain Steady decline of the entire supply chain surplus 2. Define or Describe the followings a. Safety Stock (C7) Safety Stock is additional stock that an entity may keep to reduce the probability of stockout, which is stock on-hand (number of stock currently have) is not enough to meet current demand b. Stockout (C7) Stockout, or Out-Of-Stock (OOS) event, happens when the inventory is exhausted. Stockouts can happen at any stage of the supply chain. c. Bullwhip effect (C7) This study source was downloaded by 100000871520044 from CourseHero.com on 09-11-2023 04:58:51 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/113897981/ONM4201-2021-May-Q4-Quesdocx/ Bullwhip effect is a distribution channel phenomenon in which demand forecasts yield supply chain inefficiencies. It refers to increasing swings in inventory in response to shifts in consumer demand as one moves further up the supply chain. d. Rationing (C7) Rationing means control or limited distribution of the product to each buyer in terms of order quantity and delivery lead time e. Shortage Gaming (C7) Shortage Gaming means buyer order more than they need during period of rationing f. Quantity Discount (C7) Quantity discount is an incentive offered to a buyer that results in a decreased cost per unit of goods or materials when purchased in greater numbers. g. Minimum Delivery batch size (C7) Delivery batch size means the minimum number of unit that a seller is willing to transported the buyer, within a shipment. - This means that seller will not ship 1 bottle of beer to buyer, if the delivery batch size is set at 10k bottles 1. Discuss with example, tradeoff of keeping safety stock (C7) Keeping safety stock allows to avoid stock-out which increases the product availability and thus the probability of less customer will experience stock out will be lower. However, this will increase the inventory holding costs. For example, if the demand rate for Carlsberg suddenly increases, from 100 bottle per day to 1000 per day, the entities are able to meet the demand then Carlsberg cannot immediate delviery beer and customer need to wiat long waiting period. In contrast, if the safety stock is not being used for a long period, the rental cost which is also the holding cost to place this stock will increase as well. Thus, there is a trade off of keeping safety stock. 2. In accordance to EOQ model, list the TWO (2) assumptions that would render stockout to be impossible to occur. Justify your conclusion. Support your justification with appropriate diagram (C7) The assumptions that would render stockout to be impossible to occur: 1) Demand is known, constant and deterministic: refer to diagram A, with a constant demand, the store can order future stocks with the accurate amount needed and the inventory will be sufficient to supply their customers because there is no sudden increase in sales. However, reere to diagram B, if the demand is not constant 2) Lead time is known, constant and deterministic: The buyer can more rely on the ROP since the lead time is constant, and buyer enable to refill their stock exactly on the day they run out of stock, thus there will be no stockout happen. Diagram A (need improve) This study source was downloaded by 100000871520044 from CourseHero.com on 09-11-2023 04:58:51 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/113897981/ONM4201-2021-May-Q4-Quesdocx/ 3. Jackie claims that Optimal Order Quantity place by a buyer is not equal to the Demand experience by the buyer. Do you agree? Justify your conclusion using the EOQ model (C7) I do not agree because the basis for the EOQ formula assumes that consumer demand is constant. The calculation also assumes that both ordering and holding costs remain constant. For example, the demand rate increase the optimal quantity also increases. 4. Determine the Optimal Order Quantity and ROP with SS for the following set of conditions. Assume that there are 12 months per year and 30 days per month. (C7) Demand Holding Cost Unit Cost Ordering cost Lead Time Safety stock Set A 10,000 unit per month $8 per unit 1 month $10 per unit $250 per order 3 days 10 units Set B 2,000 unit per month $10 for 2 units per year $5 per unit $100 per order 4 days 20 units Set C 20,000 unit per year $8 per unit for 4 months $2 per unit $1000 per order 5 days 0 units This study source was downloaded by 100000871520044 from CourseHero.com on 09-11-2023 04:58:51 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/113897981/ONM4201-2021-May-Q4-Quesdocx/ Set D 12,000 unit per year $6 per unit for 2 months $5 per unit $80 per order 4 days 30 units 5. Draw an “Oder Quantity vs Time” diagram that highlights bullwhip effect occurring in 3 consecutive order cycle. Assume that the supply chain member type include; End Customer, Retailer, Distributer, Producer, Tier1 Supplier and Tier2 Supplier (C7) 6. From perspective of Supply Chain Surplus, is Bullwhip Effect a “good thing” or “bad thing”? Explain your conclusion with TWO (2) factors related to Supply Chain Surplus (C7) I think it is bad thing. Because, supply chain members did not work together & did not share information so it cause Bullwhip effect. For example: Let’s consider a retailer sells on average 10 ice creams per day in the summer season. Following a heatwave the retailer's sales increase to 30 units per day, in order to meet this new demand, the retailer increases their demand forecast and places an increased order on the wholesaler to 40 units per day in order to meet the new customer demand levels and to buffer any potential further increase in demand, this creates the first wave in the exaggerated demand being driven down the supply chain. The wholesaler noticing this increase in demand from the retailer may then also build an incremental increase into their forecast so generating a larger order on the ice cream manufacturer, rather than ordering 40 units to be manufactured, the wholesaler may order 60 units from the This study source was downloaded by 100000871520044 from CourseHero.com on 09-11-2023 04:58:51 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/113897981/ONM4201-2021-May-Q4-Quesdocx/ manufacturer, this will further exaggerate the demand down the supply chain and so creates a second wave of demand increase. The manufacturer also feeling the increase in demand from the wholesalers may also react to the increase by increasing their manufacturing run to 80 units, this creates a third wave in the exaggeration of demand. The retailer may run out of stock during the heatwave whilst the manufacturer is producing new stock and may take the option of switching to an alternative brand to meet customer demand, this will then create a false demand situation as sales appear to slump to next to nothing so the retailer may then not place further demand for the original ice cream brand even though the manufacturer has increased their production runs. Alternatively, if the weather changes and the end consumers slow down on purchasing ice creams, this could result in an overstock situation across the supply chain as each tier of the supply chain has reacted to the heatwave sales and increased their demand. Hence, its a bad thing since increasing the Supply Chain Cost in the sense that this may drive holding cost to increase for supply chain entities (retaielr, prodcue, suppler) When the demand is high, product cost icnrease, if Producer or supplier try to reduce the gap between order quantity and production capasity by haveing more overtime or buy new equipment or buy raw materila from entity who are not part of the member of SC causing excess inventory, quality control issues and other inefficiencies. Forecasting accuracy decreases as we move upstream along the supply chain. Example 2 : a food wholesaler who regularly sells 1,000 cans of tuna to a customer each week. Then, this customer orders double the amount of tuna they normally do. You assume that demand is increasing and purchase 2,000 cans to ensure you don't run out. Seeing your increased purchase, your supplier may also increase the amount of tuna they stock, thus further amplifying the issue. On the other end of the spectrum, you can run into issues with too little supply. Let's say, in the scenario above, you didn't increase how much tuna you purchase. However, the demand on the customer side continued to increase. Immediately you'd run into an issue meeting demand. You then place a larger order with your supplier who also can't meet the demand, leading to a scarcity in cans of tuna. its a bad thing, because it reduce value for end customer avaialbility / stockout 7. Discuss TWO (2) possible barriers towards rationing agreement between seller and buyers. (C7) Information is not shared by buyers Information regarding buyers past sales and current inventory level is an important part of rationing. Because rationing limits order quantity in a specific period, suppliers need to know how much they can supply to buyers. For example, if KK mart wants to buy milk, and milk suppliers do not know KK mart`s past sales or current milk inventory level, they would probably put out a standard figure or an average figure based on other stores such as 7-eleven, 99 speedmart, etc…. However, this level of inventory may be too less for KK mart, hence, KK mart will order more than expected causing other buyers to have less than what they need. This study source was downloaded by 100000871520044 from CourseHero.com on 09-11-2023 04:58:51 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/113897981/ONM4201-2021-May-Q4-Quesdocx/ Shortage gaming Shortage gaming occurs when a company or buyer looks out for themselves by buying more than they need during the rationing period. This will cause the supplier`to recevied be lesser Q than the orders quantity which it placed . This will affect the entire supply chain as other companies may need to wait longer or will receive less inventory. For example, if 7-Eleven is Q* 10 units of chocolate and KK mart is supposed to buy 20 units, hence, Cadbury will produce 30 units. However, 7-Eleven engage in Shortage Gaming decides to buy 12 units (more then Q*) during the rationing period, this ends up leaving on 18 units for KK mart which is not enough. So, KK mart will either receive less chocolate or will have to wait a certain number of days while Cadbury produces more chocolate. 8. Explain with example, how “Shortage Gaming” could causes Bullwhip Effect. (C7) A “Shortage Gaming” would happen when buyer decides to buy more than what they need due to the rationing amount set by the seller. For example, if Tesco’s Optimal Order Quantity is 100 units of diapers and the distributor has set a rationing of 50%, that means the distributor will only give partial of the rationing set instead of full. Here, Tesco will only be able to get 50 units. Hence, to avoid getting only partial amount of goods, Tesco now will go for shortage gaming where they will place 200 units of diapers as their order. Since there is 50% rationing set by the distributor, Tesco will now be able to get 100 units which is the exact number of units needed by Tesco. Hence, order quantity under Shortage Gaming is more than the aggreagate Order Quantity fro all reatier will increase hence cases Bullwhip Effect . Supplement questions 1. “If demand is deterministic and constant then safety stock is not necessary”. Do you agree with this statement? Justify your conclusion. Support your justification with appropriate diagram. (C7) 2. Discuss with example, how Bullwhip Effect could propagate across each supply chain member types. (C7) 3. Explain with example, THREE (3) possibilities where “Information sharing and Demand forecasting” could causes Bullwhip Effect. (C7) 4. Identify (ONE) 1 benefit enjoyed by the producer and (ONE) 1 drawback experience by the buyer, when the producer set a very large minimum delivery batch size to its buyers. Explain how the producer’s benefit and the buyer’s drawback occur. (C7) This study source was downloaded by 100000871520044 from CourseHero.com on 09-11-2023 04:58:51 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/113897981/ONM4201-2021-May-Q4-Quesdocx/ Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)