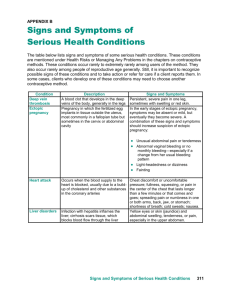
Surigao Education Center Km. 2, 8400 Surigao City College of Allied Medical Sciences Nursing Department A Case Study of Ectopic Pregnancy Submitted by: Group 2 ARCAYA, CHRISTINE MAE C. CABALLES, NELSAN C. ESTRELLA, KIRK PATRICK D. DAYTOC, LENEN FAITH A. PEROCHO, SHANTAL SHEEN E. RAVELO, JOYCE CLAIRE L. SARIM, LAMBERTO A. Jr. SAGA, CHRISTINE C. TECSON, CHRISTINE S. VALLE, KAILA P. VASQUEZ, KRISTINE P. Submitted to: Cheryl Porpayas – Alvarado, RN March 4, 2023 Surigao Education Center Km. 2, 8400 Surigao City College of Allied Medical Sciences Nursing Department TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction and Definition Signs and Symptoms Anatomy and Physiology Pathophysiology Diagram Narrative Management Medical Surgical Nursing Considerations Prevalence Prognosis Surigao Education Center Km. 2, 8400 Surigao City College of Allied Medical Sciences Nursing Department I. INTRODUCTION For many women, pregnancy is a time of excitement and delight. A new life begins to take root and prepare to enter this world. A healthy pregnancy is essential for both the mother and the unborn child. But occasionally, a pregnancy might not be healthy. Either a normal or an ectopic pregnancy is possible. In a healthy pregnancy, the fertilized egg attaches itself to the lining of the uterus. While they get ready for the baby, expecting parents are enjoying this joyful moment. They prepare for the new family by making arrangements. However, each pregnancy is different, and a lot for prenatal care along with consultations with the OBGYN can make it better. Pregnancy begins with a fertilized egg. In a healthy pregnancy, the fertilized egg attaches itself to the lining of the uterus. In an ectopic pregnancy, the egg attaches itself somewhere outside the uterus — usually to the inside of a fallopian tube. The most common site is the ampullary portion of the tube, where over 80% of ectopic pregnancies occur. Nontubal ectopic pregnancies are rare, with abdominal pregnancies accounting for 1.4% and ovarian and cervical sites accounting for 0.2%. Some ectopic pregnancies implant in the cervix (< 1%), in previous cesarean delivery scars, or in a rudimentary uterine horn. In the absence of modern prenatal care, abdominal pregnancies can present at an advanced stage (>28 wk) and have the potential for catastrophic rupture and bleeding. The term "ectopic pregnancy" comes from the Greek word "ektopos," which means "out of place." In this condition, the gestation grows and takes its blood supply from the location of the aberrant implantation. Only the uterine cavity is intended to expand and support fetal development, thus as the gestation grows, there is a risk of organ rupture. Ectopic pregnancy may result in severe bleeding, infertility, or even death. II. SIGNS and SYMPTOMS You may not notice any symptoms at first. However, some women who have an ectopic pregnancy have the usual early signs or symptoms of pregnancy — a missed period, breast tenderness and nausea. Sharp abdominal pain. A pregnant woman with possible ectopic pregnancy might move suddenly, and as a result, the anterior uterine support might be pulled and cause pain in the abdomen. Vaginal spotting. This would rarely occur in conjunction with the pain, but this may be a sign that the ectopic pregnancy is nearing its rupture. Sharp, stabbing pain at the lower quadrant. This is one of the symptoms which tell that the ectopic pregnancy has already ruptured. Vaginal bleeding. Bleeding occurs after the ectopic pregnancy has ruptured. Tearing of the blood vessels and its destruction is the cause of the bleeding, and the amount would not be determined fully because some products of conception and blood might be expelled into the pelvic cavity. Extreme lightheadedness or fainting Shoulder pain Syncope. Loss consciousness for a short period of time. Amenorrhea Low hgb/hct, hCG, progesterone level Surigao Education Center Km. 2, 8400 Surigao City College of Allied Medical Sciences Nursing Department III. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Female Pelvic Anatomy To have an understanding of the disease process, Anatomy and Physiology provides the necessary information about the normal function of certain body components, its structure and function. The relationship between anatomy and physiology are that they will always correlate with each other anatomy being the study of the actual physical organs and their structure as well as their relationship to each other. While physiology studies how those organs work to function the whole body as organ systems. The female reproductive system is a collection of organs that cooperate to allow for fertilization, pregnancy, and childbirth. Moreover, it creates progesterone and estrogen, which are female sex hormones. The system contains of tissues and organs that are found both inside and outside the body. The fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina are among the internal organs. During Sexual Intercourse, sperm cells travel through the vagina to the uterus and fallopian tubes. In the fallopian tube, the sperm meets the egg that was released from the ovary during ovulation to form a zygote. Then the zygote travels down the fallopian tube, where it becomes a morula. Once it reaches the uterus, the morula becomes a blastocyst. The blastocyst then burrows into the uterine lining — a process called implantation. Basic Structure Ovaries - are the female gonads — the primary female reproductive organs. These glands perform three crucial tasks: they secrete hormones, they protect the eggs a female is born with, and they release eggs for potential fertilization. Uterus - also called womb, an inverted pear-shaped muscular organ of the female reproductive system, located between the bladder and the rectum. It functions to nourish and house a fertilized egg until the fetus, or offspring, is ready to be delivered. Fallopian Tube - also called oviduct or uterine tube, either of a pair of long narrow ducts located in the human female abdominal cavity that transport male sperm cells to the egg, provide a suitable environment for fertilization, and transport the egg from the ovary, where it is produced, to the central channel (lumen) of the uterus. Cervix - The lower, narrow part of the uterus (womb) located between the bladder and the rectum. Cervix has three main functions such as producing cervical mucus during the most fertile phase of the menstrual cycle, which helps sperm travel from the vagina into the uterus, opening during labor to allow the baby to pass through the birth canal, and protecting the uterus from bacteria and other foreign objects. Surigao Education Center Km. 2, 8400 Surigao City College of Allied Medical Sciences Nursing Department Endometrium - also known as the mucosal layer or membrane is the innermost layer of the uterus. It is composed of the epithelial layer and cell-rich connective tissue layer (lamina propria). The main function of the endometrium is to prepare the optimal environment for the implantation of the embryo. In addition, this layer prevents the adhesions between the opposed walls of the myometrium and maintains the patency of the uterine cavity. Vagina - The vagina is a muscular canal lined with nerves and mucus membranes. It connects the uterus and cervix to the outside of the body, allowing for menstruation, intercourse, and childbirth. Sites of Ectopic Pregnancy IV. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY PREDISPOSING FACTORS - Age above 35 years old - Pelvic Inflammatory disease PRECIPATING FACTORS - Previous ectopic pregnancy - History of infertility Surigao Education Center Km. 2, 8400 Surigao City College of Allied Medical Sciences Nursing Department Implantation of developing blastocyte outside the uterine Penetration of ovum Tubal distention into muscular wall of Tubal rupture fallopian tube. Embryo releases human Pregnancy Maternal blood Intra-abdominal cannot extrudes hemorrhage survive through without the fimbrae of chorionic gonadotropin (-hCG), which supports corpus luteum to Syncope fallopian tubes hypotensi Level of Progesterone maintains Embryo of the endometrial lining trophoblasti Lower preventing it from c death abdominal pain Shock Hemoperitoneum Missed Period Transvaginal Ultrasound Sloughing of Cessation of human decidua out of the chorionic uterus through the gonadotropin (- Vaginal Low -hCG Positive -hCG, Discriminatory but rising <35% zone: -hCG over 2 days >2000 + absence of Legend: MECHANISM SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS COMPLICATIONS LAB FINDINGS LABORATORIES Surigao Education Center Km. 2, 8400 Surigao City College of Allied Medical Sciences Nursing Department NARRATIVE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY The major risk factor that contributes to Ectopic Pregnancy are pelvic inflammatory disease, older than 35 years old, and cigarette smoking. other factors that may provoke women's risk of ectopic pregnancy are, previous ectopic pregnancy, and history of infertility. The pathologic process starts with the implantation of blastocyte outside the main cavity of the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube. Then the embryo develop, embryo releases human chorionic gonadotropin ( -hCG), which supports corpus luteum to continue producing progesterone. The progesterone maintains the endometrial lining preventing it from shedding that results to missed period. When blastocyst implant outside the uterine body, the ovum begins to penetrate into the muscular wall of the fallopian tube. As the fertilized egg continues to grow inside the fallopian tube, it can cause tube rupture which results to intra-abdominal hemorrhage, symptoms of this are life-threatening event includes syncope, hypotension, and level of consciousness. Due to the presence of blood within the presence of blood within the periteoneal cavity it causes hemoperitoneum which result a mother experiencing lower abdominal pain. Without the nutrients and the proper support of fertilized egg needed, the pregnancy cannot survive on its own which leads to the embryo of trophoblastic death. Sloughing of decidua out of the uterus through the vagina that leads to vaginal bleeding. If left untreated, it will cause life threatening complications. Surigao Education Center Km. 2, 8400 Surigao City College of Allied Medical Sciences Nursing Department V. MANAGEMENT 1. Medical treatment A. Start IV/BT as prescribed B. Administer drugs: Methotrexate- This drug stops cells from growing, which ends the pregnancy. Mifepristone- is a steroidal anti-progesterone drug, the main principle of its treatment of ectopic pregnancy is: blocking the secretion of progesterone to shrink corpus luteum, causing cells degeneration, decidua, and chorion decrease. Leucovorin – is also called folinic acid. It’s very similar, but not the same as folic acid. Folic acid is an over-the-counter dietary supplement for low folate levels, whereas leucovorin is only available by prescription, and it treats side effects from methotrexate and other anti-folate medications. Dactinomycin- is a type of antibiotic that is only used in cancer chemotherapy. It works by slowing or stopping the growth of cancer cells in your body. 2. Surgical treatment Salpingostomy- is the creation of an opening into the fallopian tube, but the tube itself is not removed in this procedure. Salpingectomy - is the surgical removal of a fallopian tube. Oophorectomy - is surgery to remove one or both of your ovaries. VI. NURSING CONSIDERATIONS Ask the patient if she has allergy to any medicine. Consider the patient feelings. Monitor medicine intake that's not appropraited for the patient talking benzodiazepines - drugs such as Xanax or Valium- within 90 days before conception raises the risk of life threathing condition known as ectopic pregnancy. Patient with confirmed ectopic pregnancy should avoid using intrauterine device as contraception since this can increase the chance of ectopic pregnancy. Women undergoing medical management should avoid alcoholic beverages, NSAIDs, vitamins containing folic acid, sexual intercourse, sun exposure due to risk of Methotrexate dermatitis, and ultrasound and pelvic examinations during Methotrexate therapy surveillance. VI. PREVALENCE Ectopic pregnancies occur at a rate of 1%-2% in the general population and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality and 2%-5% among individuals who have used assisted reproductive technologies. Fewer than 10% of ectopic pregnancies are estimated to involve implantation outside the fallopian tube, (Universal health care law, 2023). Hospital ng Maynila Medical Center, Manila, Philippines, the incidence of ovarian ectopic pregnancy is one in 7000 to 40 000, but most rupture in the first trimester and only a few survive to term. An untreated ovarian pregnancy is a medical emergency as it may cause fatal intraabdominal bleeding. This paper reports a rare case of a term unruptured ovarian pregnancy in a 35year old Gravida 2 Para 1 (1–0–0-1) at 40 weeks and 6 days age of gestation (Patricia Nevira V. Suarez, MD, Soccoro Caguiat MD, 2020). According to Yan-Yan Fan and Yi-Nan Liu, 2021, At least 90% of all Ectopic pregnancy are located in the fallopian tube, and 80% of these are located in the ampullary segment of the tube, the Surigao Education Center Km. 2, 8400 Surigao City College of Allied Medical Sciences Nursing Department prevalence of EP was 7.93% among all gynecological admissions. The majority of these patients were aged 25–34 y and had a past history of abortion (61%) and uterine cavity surgery (38.6%), and a significant number were nulliparous (549, 43.1%). Bleeding accompanied by abdominal pain were the most common presenting complaints (65.2%). The present study revealed that a significant proportion of nulliparous women have an EP. VII. PROGNOSIS Ectopic pregnancies carry high rates of morbidity and mortality if not recognized and treated promptly. According to World Health Organization (2007), 5 % of maternal deaths in developed countries are from ectopic pregnancy. These deaths declined markedly from 19801992 due to improved diagnosis and management. In a review of deaths from ectopic pregnancy in Michigan, 44 % of the women who died were either found dead at home or were dead on arrival at the emergency department. In a review of 206 cases of ectopic pregnancy in the Philippines, the mortality was 7.28 %. Patients with a relatively low beta hCG level will likely have a better prognosis regarding treatment success with single-dose methotrexate. The further the ectopic pregnancy has advanced, the less likely single-dose methotrexate therapy will suffice. The patients that present in extremis or with hemodynamically instability have more risk of deterioration such as from hemorrhagic shock or other perioperative complications. Prognosis will thus hinge on early recognition and timely intervention. Fertility outcomes with tubal conservation surgeries remain debatable as some data suggests no si gnificant difference in intrauterine pregnancy rates when comparing salpingectomy versus conservative tubal management. Surigao Education Center Km. 2, 8400 Surigao City College of Allied Medical Sciences Nursing Department REFERENCE https://www.topdoctors.co.uk/medical-dictionary/ectopic-pregnancy#1 https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ectopic-pregnancy/symptoms-causes/syc20372088 https://www.google.com/search?q=ECTOPIC+PREGNANCY&client=firefox-bd&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwj15JWthrr9AhULhVYBHeuwArkQ_AUoAX oECAIQAw&biw=1366&bih=682&dpr=1#imgrc=r6EgsT6OH0Wv2M https://www.google.com/search?q=PATHOPHYSiology+of+ectopic+pregnancy&client=firefoxbd&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjIsI_Wh7r9AhVTpVYBHWyPBrkQ_AUoA XoECAEQAw&biw=1366&bih=682&dpr=1#imgrc=GoUbxNYvWqSMyM https://www.slideshare.net/NikitaSharma346/ectopic-pregnancy-228932794 https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/ectopicpregnancy/treatment/#:~:text=The%20main%20treatment%20options%20are,with%20the%20aff ected%20fallopian%20tube https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/women-s-health-issues/complications-of-pregnancy/ectopicpregnancy https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8684394/