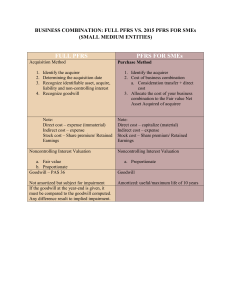
Accounting for Business Combination Von Zerick M. Casero, CPA, CTT Accountant in Public Practice Balagot and Co. CPAs Part-time Accounting Instructor STI - Koronadal General Class Rules and Grading System General Class Rules 1. Proper Attire and Video Conferencing Etiquette • Dress appropriately • Find a well-lit and quiet space • Minimizing distractions in the background • Engaging with the camera and showing respect during discussions General Class Rules 2. Attendance Policy • Online classes do not require mandatory attendance • However, regular attendance is encouraged and will be rewarded General Class Rules 3. Muting, Video, and Excusing Yourselves • Students must mute themselves upon admission to the class • Students should keep their video on during class • Leave a message in the chatbox when you want to excuse yourselves General Class Rules 4. Respect and Politeness • Students must show respect and politeness to professors and peers General Class Rules 5. Communication Channels • Students can communicate concerns, queries, or clarifications via text or messenger General Class Rules 6. Lab Activities and Grades • A grade of INC will be given for missed lab activities, lab reports, or project requirements. General Class Rules 7. Make-Up Exams and Excuses • Missed exams, recitations, quizzes, etc., without a valid excuse, receive a grade of zero. General Class Rules 8. Make-Up Exams and Excuses • Missed exams, recitations, quizzes, etc., without a valid excuse, receive a grade of zero. • Valid excuses allow for special exams and quizzes General Class Rules 9. Submission of Requirements • Students should complete assigned exercises and submit requirements by the agreed date. Valid excuses allow for special exams and quizzes • Google Classroom will be used as the submission platform General Class Rules 10. Preparing for Classes • Students should read assigned topics before attending class Grading System Class Participation (Recitation, Quizzes, etc.) 10% Task Performance (Long Quiz, Activities, Group Works, etc.) 50% Major Examination (Midterm, Finals) 40% TOTAL 100% Accounting for Business Combination Learning Objectives Assess whether a transaction is a business combination Recognize acquired assets and liabilities and compute goodwill or gain from bargain purchase under IFRS 3 Business Combination IFRS 3 A transaction or other event in which an acquirer obtains control of one or more businesses Transactions sometimes referred to as 'true mergers' or 'mergers of equals' are also business combinations An entity's purchase of a controlling interest in another unrelated operating entity is also a business combination Business IFRS 3 An integrated set of activities and assets that is capable of being conducted and managed for the purpose of providing a return in the form of dividends, lower costs, or other economic benefits directly to investors or other owners, members, or participants. Business Input Process Output Method of Accounting for Business Combination Acquisition Method 1. Identify the acquirer 2. Determine the acquisition date 3. Recognize and measure the identifiable net assets 4. Recognize and measure goodwill or gain from bargain purchase Identifying the Acquirer Acquirer – obtains control of the acquiree Identifying the Acquirer IFRS 10 – an investor controls and investee if and only if all of the following exist: 1. Power over investee 2. Exposure or rights to variable returns 3. Ability to use its power over the investee Identifying the Acquirer – Power over Investee Power arises from Rights Voting Appoint, reassign, or remove Direct Other rights Identifying the Acquirer – Power over Investee Acquisition of Control (Legal Perspective) Acquisition of Net Assets Stock acquisition Determine the Acquisition Date The date : When the investor obtains control of the acquiree On which the acquirer legally transfers the consideration, acquires the assets, and assumes the liabilities of the acquiree. Recognize and Measure the Identifiable Net Assets and Non-Controlling Interest Recognition Principle – asset and liabilities Measurement Principle: Identifiable net assets – Fair value NCI – Fair value or proportionate share basis Recognize Goodwill or Gain from Bargain Purchase Consideration Transferred ₱ XXX Non-controlling Interest XXX Acquisition-date fair value of previously held equity XXX Less: Fair value of Net Identifiable Assets Goodwill (Gain on bargain purchase) XXX (XXX) XXX Consideration Transferred Assets transferred by the acquirer Liabilities incurred by acquirer to former owners of the acquiree Equity interests issued by the acquirer Contingent considerations (if any) Cost and Expenses of Business Combination 1. Directly Attributable Costs – Professional fees, legal advisers, consultants 2. Indirect Acquisition Costs – General and administrative expenses 3. Cost of Issuing Securities – Transaction costs such as stamp duties, underwriter cost, brokerage fees. Cost and Expenses of Business Combination 1. Directly Attributable Costs – Expensed 2. Indirect Acquisition Costs – Expensed 3. Cost of Issuing Securities – Debit to Additional Paid-in Capital/Share Premium Sample Problem 1 ABC Company’s board of directors decided to acquire the net assets of DEF Corporation and GHI Company on January 1, 2021 ABC DEF GHI Current Assets 1,375,000 390,000 260,000 Non-Current Assets 3,125,000 2,550,000 1,700,000 325,000 210,000 140,000 2,748,500 1,780,200 1,186,800 176,500 169,800 113,200 1,250,000 780,000 520,000 Liabilities Ordinary share Capital Share Premium Retained Earnings Sample Problem 1 ABC Company will issue 22,500 of its ordinary shares in exchange for the net assets of DEF and 11,200 ordinary shares in exchange for the net assets of GHI. The fair value of ABC shares is P150. The following are the fair values of DEF and GHI DEF Current Assets Non-Current Assets GHI 450,000 230,000 2,150,000 1,975,000 Sample Problem 1 The following are the expenses incurred during the acquisition Legal Fees for the contract of business combination 8,000 Audit fee for SEC Registration of share issue 9,000 Accountant’s fee for pre-acquisition audit 10,000 Broker’s fee 4,000 Printing cost of shares certificates 5,000 Other direct acquisition costs 7,000 Internal secretarial, general, and allocated expenses 9,000 Documentary stamp tax on the new shares 2,000 Sample Problem 1 Requirements: 1. Record the acquisition of DEF and GHI and related transactions in the books of ABC 2. Prepare the Statement of Financial Position of ABC after the merger. Sample Problem 1 Sample Problem 1 Sample Problem 1 Sample Problem 1 Sample Problem 1 End