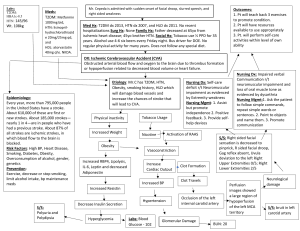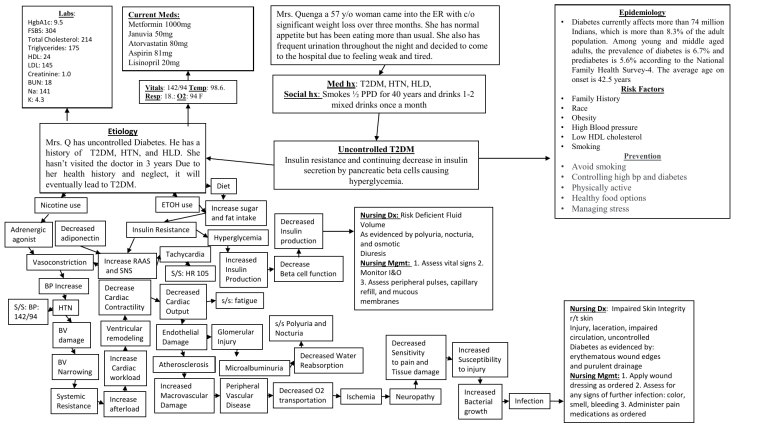
Labs: HgbA1c: 9.5 FSBS: 304 Total Cholesterol: 214 Triglycerides: 175 HDL: 24 LDL: 145 Creatinine: 1.0 BUN: 18 Na: 141 K: 4.3 ETOH use Nicotine use Decreased adiponectin Vasoconstriction BP Increase S/S: BP: 142/94 Insulin Resistance Increase RAAS and SNS HTN Decrease Cardiac Contractility BV damage Ventricular remodeling BV Narrowing Systemic Resistance Increase Cardiac workload Increase afterload Tachycardia S/S: HR 105 Decreased Cardiac Output Endothelial Damage • Med hx: T2DM, HTN, HLD, Social hx: Smokes ½ PPD for 40 years and drinks 1-2 mixed drinks once a month Vitals: 142/94 Temp: 98.6. Resp: 18.: O2: 94 F Etiology Mrs. Q has uncontrolled Diabetes. He has a history of T2DM, HTN, and HLD. She hasn’t visited the doctor in 3 years Due to her health history and neglect, it will eventually lead to T2DM. Adrenergic agonist Mrs. Quenga a 57 y/o woman came into the ER with c/o significant weight loss over three months. She has normal appetite but has been eating more than usual. She also has frequent urination throughout the night and decided to come to the hospital due to feeling weak and tired. Current Meds: Metformin 1000mg Januvia 50mg Atorvastatin 80mg Aspirin 81mg Lisinopril 20mg Uncontrolled T2DM Insulin resistance and continuing decrease in insulin secretion by pancreatic beta cells causing hyperglycemia. Diet Increase sugar and fat intake Hyperglycemia Increased Insulin Production • • • • • Nursing Dx: Risk Deficient Fluid Volume As evidenced by polyuria, nocturia, and osmotic Diuresis Nursing Mgmt: 1. Assess vital signs 2. Monitor I&O 3. Assess peripheral pulses, capillary refill, and mucous membranes Decreased Insulin production Decrease Beta cell function s/s: fatigue Glomerular Injury • • • • • • s/s Polyuria and Nocturia Atherosclerosis Microalbuminuria Increased Macrovascular Damage Peripheral Vascular Disease Decreased Water Reabsorption Decreased O2 transportation Ischemia Decreased Sensitivity to pain and Tissue damage Neuropathy Increased Susceptibility to injury Increased Bacterial growth Infection Epidemiology Diabetes currently affects more than 74 million Indians, which is more than 8.3% of the adult population. Among young and middle aged adults, the prevalence of diabetes is 6.7% and prediabetes is 5.6% according to the National Family Health Survey-4. The average age on onset is 42.5 years Risk Factors Family History Race Obesity High Blood pressure Low HDL cholesterol Smoking Prevention Avoid smoking Controlling high bp and diabetes Physically active Healthy food options Managing stress Nursing Dx: Impaired Skin Integrity r/t skin Injury, laceration, impaired circulation, uncontrolled Diabetes as evidenced by: erythematous wound edges and purulent drainage Nursing Mgmt: 1. Apply wound dressing as ordered 2. Assess for any signs of further infection: color, smell, bleeding 3. Administer pain medications as ordered