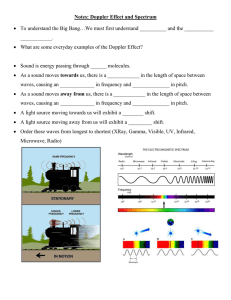
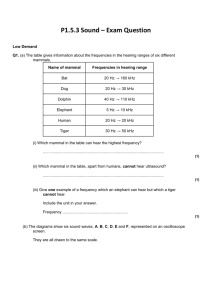
SOUND WAVES Sound waves are produced by vibrating sources. They are longitudinal waves in nature and as such need a medium in order to be transmitted from one place to another. Bell-jar experiment The bell-jar experiment can be used to show if this is possible. An electric bell is suspended with rubber bands inside a bell jar. The rubber bands reduce sound transmission by the wires so that sound is only transmitted through the glass. When the circuit is complete the bell rings. A vacuum pump is then used to remove the air from the bell jar. from the bell jar which shows that sound needs a medium for its propagation. Relative order of the speed of sound in gases, liquids and solids. Sound travels fastest in solids, followed by liquids then gases. This is because the particles of matter are far apart in gases but closely packed in solids. Material Iron steel Water Air(mixture of gases) Hydrogen Carbon dioxide Speed (m/s) 5000 4500 1500 330 1350 280 Reflection of Sound Reflected sound is called an echo. Multiple reflection of sound may produce an effect called reverberation. It occurs when too many echoes mix up to produce a dull unclear sound. Diffraction of Sound Waves You can hear around corners even if you can’t see the speaker. This is because the waves can bend (diffract) around corners. Audible Frequency Audible frequency refers to the range of frequencies which can be heard by an organism. Each animal species has its own audible frequency. Examples are shown below. The sound heard decreases as the air is pumped from the bell-jar even though the hammer is still seen striking the gong. Eventually no sound is heard even though the hammer is still striking the gong. This happens when all the air has been removed 1|Physics Notes - Sound Animal Human Beings Dogs Bats Dolphins Elephants Audible Frequency 20 Hz – 20 kHz 20 kHz – 100 kHz 20 Hz – 200 kHz 20 Hz – 200 KHz 5 Hz – 100 kHz Ultrasonic Sound (Ultrasound or sonar) This refers to sound which has a frequency which is above the audible frequency for a particular organisms. For human beings any sound above 20 kHz is ultrasound. This means that we can not hear sound which is above 20 kHz even though it can be heard by other animals or detected electronically. Ultrasound waves can be concentrated to form a narrow beam which has many uses. They can be used 1. To study the development of a foetus inside its mother or determining the sex of an unborn baby without operation. 2. To clean jewellery and equipment. The equipment/jewellery is placed in a bath of a special liquid. The ultrasound will shake the dirt off the equipment/jewellery. This is the technique that is used to clean clothes. 3. By dentist to clean tartar coating from your teeth, helping you prevent gum disease. 4. By ships to measure the depth of the sea using expression 2d s . t Where s = speed of sound waves d = depth of ocean t = time taken by wave to travel distance 2d. 2d = distance travelled by wave In order to measure the sea depth, ultra sound beams are sent from the ship to the sea bottom or floor. The time taken for the wave to move from the ship to the sea bottom and back to the ship is then measured. This time is then used along with the speed of sound in water to calculate the sea depth. 2|Physics Notes - Sound Example: The ultra sound wave above took 0.84 seconds to travel to sea floor and back to ship. If the speed of sound in sea water is 1500 m/s calculate depth, d. 2d s Solution: t st d 2 1500 x 0.84 d 2 d = 630 metres. This method is known as echo sounding and can also be used to calculate the distance between large buildings/structures. 5. Used for navigation by submarines to locate other submarines. 6. To locate shoal of fish as shown below in the diagram. Noise Pollution Unpleasant sounds are called noise. An area that has a high degree of noise is said to be polluted by noise. These situations can be in a densely populated town or part of the town, airports, studios, road traffic etc. Noise can damage ears, cause tiredness and make someone lose concentration. There are ways in which unwanted noise can be reduced. By building quieter engines or building airports far away from the residential area. In cars exhaust systems can be fitted with silencers. At home sound absorbing materials such as curtains, carpets, windows can be used. The further the noise is, the weaker it is. People who are exposed to high level of noise can wear ear protectors. Classwork 1. A man standing between two hills claps his hand. He receives the first echo after 2.25s. The speed of sound in air is 330 m/s. (a) find the distance between the man and the nearer hill. A high-pitched note has a high frequency but a short wavelength. Loudness and Amplitude Loudness of a sound depends on the amplitude of the wave. The larger the amplitude the louder the sound note. Quality of a sound note. The same note on different instrument sounds different even if the frequency is the same. We say they differ in quality (Timbre). This difference is brought by the fact that no instrument other than a tuning fork or a signal generator can produce a note of one frequency (a pure note). (b) Calculate the time taken by the second echo to reach the man if the distance between the man and the further hill is 512 m. 2. A man fires a gun and hears the echo from a cliff after 4 seconds. How far away is the cliff? (Speed of sound = 340 m/s) Notes of the same frequency (pitch) but different quality. Acoustics 3 A sonar pulse sent out by a boat arrives back after 3 seconds. If the speed of sound in water 1500 m/s, how deep is the water? Characteristics of Sound The notes from a musical instrument can vary in three ways: Pitch Loudness Quality Frequency and Pitch Pitch of a sound note depends on its frequency. The higher the frequency, the higher the pitch and the lower the frequency, the lower the pitch. 3|Physics Notes - Sound When a band is playing in a hall, the sound the audience hears depends partly on how the hall itself affects the sound waves. That is the acoustics of the hall. A large empty hall, with hard walls, floors, and ceiling usually sounds ‘echoey’. Sound waves are reflected from the surfaces and mixes with the original sound making the sound to be unheard and dull. This may take several seconds before the sound can die away. This effect is called reverberation. In a hall, some materials such as carpets, curtains and even the audience reduce reverberation by absorbing the sound. Some halls have specially designed sound absorbers suspended in ceilings.