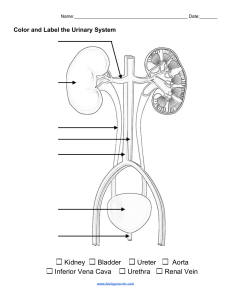
Renal Problems Test: Nephrology & Nursing Interventions
advertisement

TEST 1 - RENAL PROBLEMS 1 1. Which of the following symptoms do you expect to see in a patient diagnosed with acute pyelonephritis? 1. Jaundice and flank pain 2. Costovertebral angle tenderness and chills 3. Burning sensation on urination 4. Polyuria and nocturia 2. You have a patient that might have a urinary tract infection (UTI). Which statement by the patient suggests that a UTI is likely? 1. “I pee a lot.” 2. “It burns when I pee.” 3. “I go hours without the urge to pee.” 4. “My pee smells sweet.” 3. Which instructions do you include in the teaching care plan for a patient with cystitis receiving phenazopyridine (Pyridium). 1. If the urine turns orange-red, call the doctor. 2. Take phenazopyridine just before urination to relieve pain. 3. Once painful urination is relieved, discontinue prescribed antibiotics. 4. After painful urination is relieved, stop taking phenazopyridine. 4. Which patient is at greatest risk for developing a urinary tract infection (UTI)? 1. A 35 y.o. woman with a fractured wrist 2. A 20 y.o. woman with asthma 3. A 50 y.o. postmenopausal woman 4. A 28 y.o. with angina 5. You have a patient that is receiving peritoneal dialysis. What should you do when you notice the return fluid is slowly draining? 1. Check for kinks in the outflow tubing. 2. Raise the drainage bag above the level of the abdomen. 3. Place the patient in a reverse Trendelenburg position. 4. Ask the patient to cough. 6. What is the appropriate infusion time for the dialysate in your 38 y.o. patient with chronic renal failure? 1. 15 minutes 2. 30 minutes 3. 1 hour 4. 2 to 3 hours 7. A 30 y.o. female patient is undergoing hemodialysis with an internal arteriovenous fistula in place. What do you do to prevent complications associated with this device? 1. Insert I.V. lines above the fistula. 2. Avoid taking blood pressures in the arm with the fistula. 3. Palpate pulses above the fistula. 4. Report a bruit or thrill over the fistula to the doctor. 8. Your patient becomes restless and tells you she has a headache and feels nauseous during hemodialysis. Which complication do you suspect? 1. Infection 2. Disequilibrium syndrome 3. Air embolus 4. Acute hemolysis 9. Your patient is complaining of muscle cramps while undergoing hemodialysis. Which intervention is effective in relieving muscle cramps? 1. Increase the rate of dialysis 2. Infuse normal saline solution 3. Administer a 5% dextrose solution 4. Encourage active ROM exercises 10. Your patient with chronic renal failure reports pruritus. Which instruction should you include in this patient’s teaching plan? 1. Rub the skin vigorously with a towel 2. Take frequent baths 3. Apply alcohol-based emollients to the skin 4. Keep fingernails short and clean 11. Which intervention do you plan to include with a patient who has renal calculi? 1. Maintain bed rest 2. Increase dietary purines 3. Restrict fluids 4. Strain all urine 12. An 18 y.o. student is admitted with dark urine, fever, and flank pain and is diagnosed with acute glomerulonephritis. Which would most likely be in this student’s health history? 1. Renal calculi 2. Renal trauma 3. Recent sore throat 4. Family history of acute glomerulonephritis 13. Which drug is indicated for pain related to acute renal calculi? 1. Narcotic analgesics 2. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) 3. Muscle relaxants 4. Salicylates 14. Which of the following causes the majority of UTI’s in hospitalized patients? 1. Lack of fluid intake 2. Inadequate perineal care 3. Invasive procedures 4. Immunosuppression 15. Clinical manifestations of acute glomerulonephritis include which of the following? 1. Chills and flank pain 2. Oliguria and generalized edema 3. Hematuria and proteinuria 4. Dysuria and hypotension 16. You expect a patient in the oliguric phase of renal failure to have a 24 hour urine output less than: 1. 200ml 2. 400ml 3. 800ml 4. 1000ml 17. The most common early sign of kidney disease is: 1. Sodium retention 2. Elevated BUN level 3. Development of metabolic acidosis 4. Inability to dilute or concentrate urine 18. A patient is experiencing which type of incontinence if she experiences leaking urine when she coughs, sneezes, or lifts heavy objects? 1. Overflow 2. Reflex 3. Stress 4. Urge 19. Immediately post-op after a prostatectomy, which complications requires priority assessment of your patient? 1. Pneumonia 2. Hemorrhage 3. Urine retention 4. Deep vein thrombosis 20. The most indicative test for prostate cancer is: 1. A thorough digital rectal examination 2. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) 3. Excretory urography 4. Prostate-specific antigen 21. A 22 y.o. patient with diabetic nephropathy says, “I have two kidneys and I’m still young. If I stick to my insulin schedule, I don’t have to worry about kidney damage, right?” Which of the following statements is the best response? 1. “You have little to worry about as long as your kidneys keep making urine.” 2. “You should talk to your doctor because statistics show that you’re being unrealistic.” 3. “You would be correct if your diabetes could be managed with insulin.” 4. “Even with insulin, kidney damage is still a concern.” 22. A patient diagnosed with sepsis from a UTI is being discharged. What do you plan to include in her discharge teaching? 1. Take cool baths 2. Avoid tampon use 3. Avoid sexual activity 4. Drink 8 to 10 eight-oz glasses of water daily 23. You’re planning your medication teaching for your patient with a UTI prescribed phenazopyridine (Pyridium). What do you include? 1. “Your urine might turn bright orange.” 2. “You need to take this antibiotic for 7 days.” 3. “Take this drug between meals and at bedtime.” 4. “Don’t take this drug if you’re allergic to penicillin.” 24. Which finding leads you to suspect acute glomerulonephritis in your 32 y.o. patient? 1. Dysuria, frequency, and urgency 2. Back pain, nausea, and vomiting 3. Hypertension, oliguria, and fatigue 4. Fever, chills, and right upper quadrant pain radiating to the back 25. What is the priority nursing diagnosis with your patient diagnosed with end-stage renal disease? 1. Activity intolerance 2. Fluid volume excess 3. Knowledge deficit 4. Pain 26. A patient with ESRD has an arteriovenous fistula in the left arm for hemodialysis. Which intervention do you include in his plan of care? 1. Apply pressure to the needle site upon discontinuing hemodialysis 2. Keep the ehad of the bed elevated 45 degrees 3. Place the left arm on an arm board for at least 30 minutes 4. Keep the left arm dry 27. Your 60 y.o. patient with pyelonephritis and possible septicemia has had five UTIs over the past two years. She is fatigued from lack of sleep, has lost weight, and urinates frequently even in the night. Her labs show: sodium, 154 mEq/L; osmolarity 340 mOsm/L; glucose, 127 mg/dl; and potassium, 3.9 mEq/L. Which nursing diagnosis is priority? 1. Fluid volume deficit related to osmotic diuresis induced by hyponatremia 2. Fluid volume deficit related to inability to conserve water 3. Altered nutrition: Less than body requirements related to hypermetabolic state 4. Altered nutrition: Less than body requirements related to catabolic effects of insulin deficiency 28. Which sign indicated the second phase of acute renal failure? 1. Daily doubling of urine output (4 to 5 L/day) 2. Urine output less than 400 ml/day 3. Urine output less than 100 ml/day 4. Stabilization of renal function 29. Your patient had surgery to form an arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis. Which information is important for providing care for the patient? 1. The patient shouldn’t feel pain during initiation of dialysis 2. The patient feels best immediately after the dialysis treatment 3. Using a stethoscope for auscultating the fistula is contraindicated 4. Taking a blood pressure reading on the affected arm can cause clotting of the fistula 30. A patient with diabetes mellitus and renal failure begins hemodialysis. Which diet is best on days between dialysis treatments? 1. Low-protein diet with unlimited amounts of water 2. Low-protein diet with a prescribed amount of water 3. No protein in the diet and use of a salt substitute 4. No restrictions 31. After the first hemodialysis treatment, your patient develops a headache, hypertension, restlessness, mental confusion, nausea, and vomiting. Which condition is indicated? 1. Disequilibrium syndrome 2. Respiratory distress 3. Hypervolemia 4. Peritonitis 32. Which action is most important during bladder training in a patient with a neurogenic bladder? 1. Encourage the use of an indwelling urinary catheter 2. Set up specific times to empty the bladder 3. Encourage Kegel exercises 4. Force fluids 33. A patient with diabetes has had many renal calculi over the past 20 years and now has chronic renal failure. Which substance must be reduced in this patient’s diet? 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3. Protein 4. Vitamin C 34. What is the best way to check for patency of the arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis? 1. Pinch the fistula and note the speed of filling on release 2. Use a needle and syringe to aspirate blood from the fistula 3. Check for capillary refill of the nail beds on that extremity 4. Palpate the fistula throughout its length to assess for a thrill 35. You have a paraplegic patient with renal calculi. Which factor contributes to the development of calculi? 1. Increased calcium loss from the bones 2. Decreased kidney function 3. Decreased calcium intake 4. High fluid intake 36. What is the most important nursing diagnosis for a patient in end-stage renal disease? 1. Risk for injury 2. Fluid volume excess 3. Altered nutrition: less than body requirements 4. Activity intolerance 37. Frequent PVCs are noted on the cardiac monitor of a patient with end-stage renal disease. The priority intervention is: 1. Call the doctor immediately 2. Give the patient IV lidocaine (Xylocaine) 3. Prepare to defibrillate the patient 4. Check the patient’s latest potassium level 38. A patient who received a kidney transplant returns for a follow-up visit to the outpatient clinic and reports a lump in her breast. Transplant recipients are: 1. At increased risk for cancer due to immunosuppression caused by cyclosporine (Neoral) 2. Consumed with fear after the life-threatening experience of having a transplant 3. At increased risk for tumors because of the kidney transplant 4. At decreased risk for cancer, so the lump is most likely benign 39. You’re developing a care plan with the nursing diagnosis risk for infection for your patient that received a kidney transplant. A goal for this patient is to: 1. Remain afebrile and have negative cultures 2. Resume normal fluid intake within 2 to 3 days 3. Resume the patient’s normal job within 2 to 3 weeks 4. Try to discontinue cyclosporine (Neoral) as quickly as possible 40. You suspect kidney transplant rejection when the patient shows which symptoms? 1. Pain in the incision, general malaise, and hypotension 2. Pain in the incision, general malaise, and depression 3. Fever, weight gain, and diminished urine output 4. Diminished urine output and hypotension 41. Your patient returns from the operating room after abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Which symptom is a sign of acute renal failure? 1. Anuria 2. Diarrhea 3. Oliguria 4. Vomiting 42. Which cause of hypertension is the most common in acute renal failure? 1. Pulmonary edema 2. Hypervolemia 3. Hypovolemia 4. Anemia 43. A patient returns from surgery with an indwelling urinary catheter in place and empty. Six hours later, the volume is 120ml. The drainage system has no obstructions. Which intervention has priority? 1. Give a 500ml bolus of isotonic saline 2. Evaluate the patient’s circulation and vital signs 3. Flush the urinary catheter with sterile water or saline 4. Place the patient in the shock position, and notify the surgeon 44. You’re preparing for urinary catheterization of a trauma patient and you observe bleeding at the urethral meatus. Which action has priority? 1. Irrigate and clean the meatus before catheterization 2. Check the discharge for occult blood before catheterization 3. Heavily lubricate the catheter before insertion 4. Delay catheterization and notify the doctor 45. What change indicates recovery in a patient with nephritic syndrome? 1. Disappearance of protein from the urine 2. Decrease in blood pressure to normal 3. Increase in serum lipid levels 4. Gain in body weight 46. Which statement correctly distinguishes renal failure from prerenal failure? 1. With prerenal failure, vasoactive substances such as dopamine (Intropin) increase blood pressure 2. With prerenal failure, there is less response to such diuretics as furosemide (Lasix) 3. With prerenal failure, an IV isotonic saline infusion increases urine output 4. With prerenal failure, hemodialysis reduces the BUN level 47. Which criterion is required before a patient can be considered for continuous peritoneal dialysis? 1. The patient must be hemodynamically stable 2. The vascular access must have healed 3. The patient must be in a home setting 4. Hemodialysis must have failed 48. Polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) is used in renal failure to: 1. Correct acidosis 2. Reduce serum phosphate levels 3. Exchange potassium for sodium 4. Prevent constipation from sorbitol use 49. Your patient has complaints of severe right-sided flank pain, nausea, vomiting and restlessness. He appears slightly pale and is diaphoretic. Vital signs are BP 140/90 mmHg, Pulse 118 beats/min., respirations 33 breaths/minute, and temperature, 98.0F. Which subjective data supports a diagnosis of renal calculi? 1. Pain radiating to the right upper quadrant 2. History of mild flu symptoms last week 3. Dark-colored coffee-ground emesis 4. Dark, scant urine output 50. Immunosuppression following Kidney transplantation is continued: 1. For life 2. 24 hours after transplantation 3. A week after transplantation 4. Until the kidney is not anymore rejected Answers and Rationales 1. B. Costovertebral angle tenderness, flank pain, and chills are symptoms of acute pyelonephritis. Jaundice indicates gallbladder or liver obstruction. A burning sensation on urination is a sign of lower urinary tract infection. 2. B. A common symptom of a UTI is dysuria. A patient with a UTI often reports frequent voiding of small amounts and the urgency to void. Urine that smells sweet is often associated with diabetic ketoacidosis. 3. D. Pyridium is taken to relieve dysuria because is provides an analgesic and anesthetic effect on the urinary tract mucosa. The patient can stop taking it after the dysuria is relieved. The urine may temporarily turn red or orange due to the dye in the drug. The drug isn’t taken before voiding, and is usually taken 3 times a day for 2 days. 4. C. Women are more prone to UTI’s after menopause due to reduced estrogen levels. Reduced estrogen levels lead to reduced levels of vaginal Lactobacilli bacteria, which protect against infection. Angina, asthma and fractures don’t increase the risk of UTI. 5. A. Tubing problems are a common cause of outflow difficulties, check the tubing for kinks and ensure that all clamps are open. Other measures include having the patient change positions (moving side to side or sitting up), applying gentle pressure over the abdomen, or having a bowel movement. 6. A. Dialysate should be infused quickly. The dialysate should be infused over 15 minutes or less when performing peritoneal dialysis. The fluid exchange takes place over a period ranging from 30 minutes to several hours. 7. B. Don’t take blood pressure readings in the arm with the fistula because the compression could damage the fistula. IV lines 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. shouldn’t be inserted in the arm used for hemodialysis. Palpate pulses below the fistula. Lack of bruit or thrill should be reported to the doctor. B. Disequilibrium syndrome is caused by a rapid reduction in urea, sodium, and other solutes from the blood. This can lead to cerebral edema and increased intracranial pressure (ICP). Signs and symptoms include headache, nausea, restlessness, vomiting, confusion, twitching, and seizures. B. Treatment includes administering normal saline or hypertonic normal saline solution because muscle cramps can occur when the sodium and water are removed to quickly during dialysis. Reducing the rate of dialysis, not increasing it, may alleviate muscle cramps. D. Calcium-phosphate deposits in the skin may cause pruritus. Scratching leads to excoriation and breaks in the skin that increase the patient’s risk of infection. Keeping fingernails short and clean helps reduce the risk of infection. D. All urine should be strained through gauze or a urine strainer to catch stones that are passed. The stones are then analyzed for composition. Ambulation may help the movement of the stone down the urinary tract. Encourage fluid to help flush the stones out. C. The most common form of acute glomerulonephritis is caused by goup A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infection elsewhere in the body. A. Narcotic analgesics are usually needed to relieve the severe pain of renal calculi. Muscle relaxants are typically used to treat skeletal muscle spasms. NSAIDS and salicylates are used for their anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties and to treat less severe pain. C. Invasive procedures such as catheterization can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract. A lack of fluid intake could cause concentration of urine, but wouldn’t necessarily cause infection. C. Hematuria and proteinuria indicate acute glomerulonephritis. These finding result from increased permeability of the glomerular membrane due to the antigen-antibody reaction. Generalized edema is seen most often in nephrosis. B. Oliguria is defined as urine output of less than 400ml/24hours. B. Increased BUN is usually an early indicator of decreased renal function. C. Stress incontinence is an involuntary loss of a small amount of urine due to sudden increased intra-abdominal pressuer, such as with coughing or sneezing. B. Hemorrhage is a potential complication. Urine retention isn’t a problem soon after surgery because a catheter is in place. Pneumonia may occur if the patient doesn’t cough and deep breathe. Thrombosis may occur later if the patient doesn’t ambulate. D. An elevated prostate-specific antigen level indicates prostate cancer, but it can be falsely elevated if done after the prostate gland is manipulated. A digital rectal examination should be done as part of the yearly screening, and then the antigen test is done if the digital exam suggests cancer. MRI is used in staging the cancer. D. Kidney damage is still a concern. Microavascular changes occur in both of the patient’s kidneys as a complication of the diabetes. Diabetic nephropathy is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease. The kidneys continue to produce urine until the end stage. Nephropathy occurs even with insulin management. D. Drinking 2-3L of water daily inhibits bacterial growth in the bladder and helps flush the bacteria from the bladder. The patient should be instructed to void after sexual activity. A. The drug turns the urine orange. It may be prescribed for longer than 7 days and is usually ordered three times a day after meals. Phenazopyridine is an azo (nitrogenous) analgesic; not an antibiotic. C. Mild to moderate HTN may result from sodium or water retention and inappropriate rennin release from the kidneys. Oliguria and fatigue also may be seen. Other signs are proteinuria and azotemia. B. Fluid volume excess because the kidneys aren’t removing fluid and wastes. The other diagnoses may apply, but they don’t take priority. A. Apply pressure when discontinuing hemodialysis and after removing the venipuncture needle until all the bleeding has stopped. Bleeding may continue for 10 minutes in some patients. B. 28. A. Daily doubling of the urine output indicates that the nephrons are healing. This means the patient is passing into the second phase (dieresis) of acute renal failure. 29. D. Pressure on the fistula or the extremity can decrease blood flow and precipitate clotting, so avoid taking blood pressure on the affected arm. 30. B. The patient should follow a low-protein diet with a prescribed amount of water. The patient requires some protein to meet metabolic needs. Salt substitutes shouldn’t be used without a doctor’s order because it may contain potassium, which could make the patient hyperkalemic. Fluid and protein restrictions are needed. 31. A. Disequilibrium occurs when excess solutes are cleared from the blood more rapidly than they can diffuse from the body’s cells into the vascular system. 32. B. Instruct the patient with neurogenic bladder to write down his voiding pattern and empty the bladder at the same times each day. 33. C. Because of damage to the nephrons, the kidney can’t excrete all the metabolic wastes of protein, so this patient’s protein intake must be restricted. A higher intake of carbs, fats, and vitamin supplements is needed to ensure the growth and maintenance of the patient’s tissues. 34. D. The vibration or thrill felt during palpation ensures that the fistula has the desired turbulent blood flow. Pinching the fistula could cause damage. Aspirating blood is a needless invasive procedure. 35. A. Bones lose calcium when a patient can no longer bear weight. The calcium lost from bones form calculi, a concentration of mineral salts also known as a stone, in the renal system. 36. B. Kidneys are unable to rid the body of excess fluids which results in fluid volume excess during ESRD. 37. D. The patient with ESRD may develop arrhythmias caused by hypokalemi. Call the doctor after checking the patient’s potassium values. Lidocaine may be ordered if the PVCs are frequent and the patient is symptomatic. 38. A. Cyclosporine suppresses the immune response to prevent rejection of the transplanted kidney. The use of cyclosporine places the patient at risk for tumors. 39. A. The immunosuppressive activity of cyclosporine places the patient at risk for infection, and steroids can mask the signs of infection. The patient may not be able to resume normal fluid intake or return to work for an extended period of time and the patient may need cyclosporine therapy for life. 40. C. Symptoms of rejection include fever, rapid weight gain, hypertension, pain over the graft site, peripheral edema, and diminished urine output. 41. C. Urine output less than 50ml in 24 hours signifies oliguria, an early sign of renal failure. Anuria is uncommon except in obstructive renal disorders. 42. B. Acute renal failure causes hypervolemia as a result of overexpansion of extracellular fluid and plasma volume with the hypersecretion of rennin. Therefore, hypervolemia causes hypertension. 43. B. A total UO of 120ml is too low. Assess the patient’s circulation and hemodynamic stability for signs of hypovolemia. A fluid bolus may be required, but only after further nursing assessment and a doctor’s order. 44. D. Bleeding at the urethral meatus is evidence that the urethra is injured. Because catheterization can cause further harm, consult with the doctor. 45. A. With nephrotic syndrome, the glomerular basement membrane of the kidney becomes more porous, leading to loss of protein in the urine. As the patient recovers, less protein is found in the urine. 46. C. Prerenal failure is caused by such conditions as hypovolemia that impairs kidney perfusion; giving isotonic fluids improves urine output. Vasoactive substances can increase blood pressure in both conditions. 47. A. Hemodynamic stability must be established before continuous peritoneal dialysis can be started. 48. C. In renal failure, patients become hyperkalemic because they can’t excrete potassium in the urine. Polystyrene sulfonate acts to excrete potassium by pulling potassium into the bowels and exchanging it for sodium. 49. D. Patients with renal calculi commonly have blood in the urine caused by the stone’s passage through the urinary tract. The urine appears dark, tests positive for blood, and is typically scant. 50. A. For life. TEST 2 - GENITOURINARY SYSTEM 1. The nurse is aware that the following findings would be further evidence of a urethral injury in a male client during rectal examination? 1. A low-riding prostate 2. The presence of a boggy mass 3. Absent sphincter tone 4. A positive Hemoccult 2. When a female client with an indwelling urinary (Foley) catheter insists on walking to the hospital lobby to visit with family members, nurse Rose teaches how to do this without compromising the catheter. Which client action indicates an accurate understanding of this information? 1. The client sets the drainage bag on the floor while sitting down. 2. The client keeps the drainage bag below the bladder at all times. 3. The client clamps the catheter drainage tubing while visiting with the family. 4. The client loops the drainage tubing below its point of entry into the drainage bag. 3. A female client has just been diagnosed with condylomata acuminata (genital warts). What information is appropriate to tell this client? 1. This condition puts her at a higher risk for cervical cancer; therefore, she should have a Papanicolaou (Pap) smear annually. 2. The most common treatment is metronidazole (Flagyl), which should eradicate the problem within 7 to 10 days. 3. The potential for transmission to her sexual partner will be eliminated if condoms are used every time they have sexual intercourse. 4. The human papillomavirus (HPV), which causes condylomata acuminata, can’t be transmitted during oral sex. 4. A male client with bladder cancer has had the bladder removed and an ileal conduit created for urine diversion. While changing this client’s pouch, the nurse observes that the area around the stoma is red, weeping, and painful. What should nurse Katrina conclude? 1. The skin wasn’t lubricated before the pouch was applied. 2. The pouch faceplate doesn’t fit the stoma. 3. A skin barrier was applied properly. 4. Stoma dilation wasn’t performed. 5. The nurse is aware that the following laboratory values supports a diagnosis of pyelonephritis? 1. Myoglobinuria 2. Ketonuria 3. Pyuria 4. Low white blood cell (WBC) count 6. A female client with chronic renal failure (CRF) is receiving a hemodialysis treatment. After hemodialysis, nurse Sarah knows that the client is most likely to experience: 1. hematuria. 2. weight loss. 3. increased urine output. 4. increased blood pressure. 7. Nurse Lea is assessing a male client diagnosed with gonorrhea. Which symptom most likely prompted the client to seek medical attention? 1. Rashes on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet 2. Cauliflower-like warts on the penis 3. Painful red papules on the shaft of the penis 4. Foul-smelling discharge from the penis 8. Nurse Agnes is reviewing the report of a client’s routine urinalysis. Which value should the nurse consider abnormal? 1. Specific gravity of 1.03 2. Urine pH of 3.0 3. Absence of protein 4. Absence of glucose 9. A male client is scheduled for a renal clearance test. Nurse Maureen should explain that this test is done to assess the kidneys’ ability to remove a substance from the plasma in: 1. 1 minute. 2. 30 minutes. 3. 1 hour. 4. 24 hours. 10. A male client in the short-procedure unit is recovering from renal angiography in which a femoral puncture site was used. When providing postprocedure care, the nurse should: 1. keep the client’s knee on the affected side bent for 6 hours. 2. apply pressure to the puncture site for 30 minutes. 3. check the client’s pedal pulses frequently. 4. remove the dressing on the puncture site after vital signs stabilize. 11. A female client is admitted for treatment of chronic renal failure (CRF). Nurse Juliet knows that this disorder increases the client’s risk of: 1. water and sodium retention secondary to a severe decrease in the glomerular filtration rate. 2. a decreased serum phosphate level secondary to kidney failure. 3. an increased serum calcium level secondary to kidney failure. 4. metabolic alkalosis secondary to retention of hydrogen ions. 12. Because of difficulties with hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis is initiated to treat a female client’s uremia. Which finding signals a significant problem during this procedure? 1. Potassium level of 3.5 mEq/L 2. Hematocrit (HCT) of 35% 3. Blood glucose level of 200 mg/dl 4. White blood cell (WBC) count of 20,000/mm3 13. For a male client in the oliguric phase of acute renal failure (ARF), which nursing intervention is most important? 1. Encouraging coughing and deep breathing 2. Promoting carbohydrate intake 3. Limiting fluid intake 4. Providing pain-relief measures 14. A female client requires hemodialysis. Which of the following drugs should be withheld before this procedure? 1. Phosphate binders 2. Insulin 3. Antibiotics 4. Cardiac glycosides 15. A client comes to the outpatient department complaining of vaginal discharge, dysuria, and genital irritation. Suspecting a sexually transmitted disease (STD), Dr. Smith orders diagnostic tests of the vaginal discharge. Which STD must be reported to the public health department? 1. Chlamydia 2. Gonorrhea 3. Genital herpes 4. Human papillomavirus infection 16. A male client with acute pyelonephritis receives a prescription for co-trimoxazole (Septra) P.O. twice daily for 10 days. Which finding best demonstrates that the client has followed the prescribed regimen? 1. Urine output increases to 2,000 ml/day. 2. Flank and abdominal discomfort decrease. 3. Bacteria are absent on urine culture. 4. The red blood cell (RBC) count is normal. 17. A 26-year-old female client seeks care for a possible infection. Her symptoms include burning on urination and frequent, urgent voiding of small amounts of urine. She’s placed on trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim) to treat possible infection. Another medication is prescribed to decrease the pain and frequency. Which of the following is the most likely medication prescribed? 1. nitrofurantoin (Macrodantin) 2. ibuprofen (Motrin) 3. acetaminophen with codeine 4. phenazopyridine (Pyridium) 18. A triple-lumen indwelling urinary catheter is inserted for continuous bladder irrigation following a transurethral resection of the prostate. In addition to balloon inflation, the nurse is aware that the functions of the three lumens include: 1. Continuous inflow and outflow of irrigation solution. 2. Intermittent inflow and continuous outflow of irrigation solution. 3. Continuous inflow and intermittent outflow of irrigation solution. 4. Intermittent flow of irrigation solution and prevention of hemorrhage. 19. Nurse Claudine is reviewing a client’s fluid intake and output record. Fluid intake and urine output should relate in which way? 1. Fluid intake should be double the urine output. 2. Fluid intake should be approximately equal to the urine output. 3. Fluid intake should be half the urine output. 4. Fluid intake should be inversely proportional to the urine output. 20. After trying to conceive for a year, a couple consults an infertility specialist. When obtaining a history from the husband, nurse Jenny inquires about childhood infectious diseases. Which childhood infectious disease most significantly affects male fertility? 1. Chickenpox 2. Measles 3. Mumps 4. Scarlet fever 21. A male client comes to the emergency department complaining of sudden onset of sharp, severe pain in the lumbar region, which radiates around the side and toward the bladder. The client also reports nausea and vomiting and appears pale, diaphoretic, and anxious. The physician tentatively diagnoses renal calculi and orders flat-plate abdominal X-rays. Renal calculi can form anywhere in the urinary tract. What is their most common formation site? 1. Kidney 2. Ureter 3. Bladder 4. Urethra 22. A female client with acute renal failure is undergoing dialysis for the first time. The nurse in charge monitors the client closely for dialysis equilibrium syndrome, a complication that is most common during the first few dialysis sessions. Typically, dialysis equilibrium syndrome causes: 1. confusion, headache, and seizures. 2. acute bone pain and confusion. 3. weakness, tingling, and cardiac arrhythmias. 4. hypotension, tachycardia, and tachypnea. 23. Dr. Marquez prescribes norfloxacin (Noroxin), 400 mg P.O. twice daily, for a client with a urinary tract infection (UTI). The client asks the nurse how long to continue taking the drug. For an uncomplicated UTI, the usual duration of norfloxacin therapy is: 1. 3 to 5 days. 2. 7 to 10 days. 3. 12 to 14 days. 4. 10 to 21 days. 24. Nurse Joy is providing postprocedure care for a client who underwent percutaneous lithotripsy. In this procedure, an ultrasonic probe inserted through a nephrostomy tube into the renal pelvis generates ultra–high-frequency sound waves to shatter renal calculi. The nurse should instruct the client to: 1. limit oral fluid intake for 1 to 2 weeks. 2. report the presence of fine, sandlike particles through the nephrostomy tube. 3. notify the physician about cloudy or foul-smelling urine. 4. report bright pink urine within 24 hours after the procedure. 25. A client is frustrated and embarrassed by urinary incontinence. Which of the following measures should nurse Bea include in a bladder retraining program? 1. Establishing a predetermined fluid intake pattern for the client 2. Encouraging the client to increase the time between voidings 3. Restricting fluid intake to reduce the need to void 4. Assessing present elimination patterns 26. After having transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), a Mr. Lim returns to the unit with a three-way indwelling urinary catheter and continuous closed bladder irrigation. Which finding suggests that the client’s catheter is occluded? 1. The urine in the drainage bag appears red to pink. 2. The client reports bladder spasms and the urge to void. 3. The normal saline irrigant is infusing at a rate of 50 drops/minute. 4. About 1,000 ml of irrigant have been instilled; 1,200 ml of drainage have been returned. 27. Nurse Mary is inserting a urinary catheter into a client who is extremely anxious about the procedure. The nurse can facilitate the insertion by asking the client to: 1. initiate a stream of urine. 2. breathe deeply. 3. turn to the side. 4. hold the labia or shaft of penis. 28. A female adult client admitted with a gunshot wound to the abdomen is transferred to the intensive care unit after an exploratory laparotomy. Which assessment finding suggests that the client is experiencing acute renal failure (ARF)? 1. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level of 22 mg/dl 2. Serum creatinine level of 1.2 mg/dl 3. Serum creatinine level of 1.2 mg/dl 4. Urine output of 400 ml/24 hours 29. A 55-year old client with benign prostatic hyperplasia doesn’t respond to medical treatment and is admitted to the facility for prostate gland removal. Before providing preoperative and postoperative instructions to the client, Nurse Gerry asks the surgeon which prostatectomy procedure will be done. What is the most widely used procedure for prostate gland removal? 1. Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) 2. Suprapubic prostatectomy 3. Retropubic prostatectomy 4. Transurethral laser incision of the prostate 30. A female client with suspected renal dysfunction is scheduled for excretory urography. Nurse January reviews the history for conditions that may warrant changes in client preparation. Normally, a client should be mildly hypovolemic (fluid depleted) before excretory urography. Which history finding would call for the client to be well hydrated instead? 1. Cystic fibrosis 2. Multiple myeloma 3. Gout 4. Myasthenia gravis 31. Nurse Karen is caring for a client who had a cerebrovascular accident (CVA). Which nursing intervention promotes urinary continence? 1. Encouraging intake of at least 2 L of fluid daily 2. Giving the client a glass of soda before bedtime 3. Taking the client to the bathroom twice per day 4. Consulting with a dietitian 32. When examining a female client’s genitourinary system, Nurse Sandy assesses for tenderness at the costovertebral angle by placing the left hand over this area and striking it with the right fist. Normally, this percussion technique produces which sound? 1. A flat sound 2. A dull sound 3. Hyperresonance 4. Tympany 33. A male client with chronic renal failure has a serum potassium level of 6.8 mEq/L. What should nurse Olivia assess first? 1. Blood pressure 2. Respirations 3. Temperature 4. Pulse 34. Nurse Harry is aware that the following is an appropriate nursing diagnosis for a client with renal calculi? 1. Ineffective tissue perfusion 2. Functional urinary incontinence 3. Risk for infection 4. Decreased cardiac output 35. A male client develops acute renal failure (ARF) after receiving I.V. therapy with a nephrotoxic antibiotic. Because the client’s 24-hour urine output totals 240 ml, Nurse Billy suspects that the client is at risk for: 1. cardiac arrhythmia. 2. paresthesia. 3. dehydration. 4. pruritus. 36. After undergoing transurethral resection of the prostate to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia, a male client returns to the room with continuous bladder irrigation. On the first day after surgery, the client reports bladder pain. What should Nurse Anthony do first? 1. Increase the I.V. flow rate. 2. 3. 4. Notify the physician immediately. Assess the irrigation catheter for patency and drainage. Administer meperidine (Demerol), 50 mg I.M., as prescribed. 37. When performing a scrotal examination, Nurse Payne finds a nodule. What should the nurse do next? 1. Notify the physician. 2. Change the client’s position and repeat the examination. 3. Perform a rectal examination. 4. Transilluminate the scrotum. 38. A male client who has been treated for chronic renal failure (CRF) is ready for discharge. Nurse Billy should reinforce which dietary instruction? 1. “Be sure to eat meat at every meal.” 2. “Monitor your fruit intake, and eat plenty of bananas.” 3. “Increase your carbohydrate intake.” 4. “Drink plenty of fluids, and use a salt substitute.” 39. Nurse Gil is aware that the following statements describing urinary incontinence in the elderly is true? 1. Urinary incontinence is a normal part of aging. 2. Urinary incontinence isn’t a disease. 3. Urinary incontinence in the elderly can’t be treated. 4. Urinary incontinence is a disease. 40. The client underwent a transurethral resection of the prostate gland 24 hours ago and is on continuous bladder irrigation. Nurse Yonny is aware that the following nursing interventions is appropriate? 1. Tell the client to try to urinate around the catheter to remove blood clots. 2. Restrict fluids to prevent the client’s bladder from becoming distended. 3. Prepare to remove the catheter. 4. Use aseptic technique when irrigating the catheter. 41. A female client with a urinary tract infection is prescribed co-trimoxazole (trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole). Nurse Dolly should provide which medication instruction? 1. “Take the medication with food.” 2. “Drink at least eight 8-oz glasses of fluid daily.” 3. “Avoid taking antacids during co-trimoxazole therapy.” 4. “Don’t be afraid to go out in the sun.” 42. A male client is admitted for treatment of glomerulonephritis. On initial assessment, Nurse Miley detects one of the classic signs of acute glomerulonephritis of sudden onset. Such signs include: 1. generalized edema, especially of the face and periorbital area. 2. green-tinged urine. 3. moderate to severe hypotension. 4. polyuria. 43. A client reports experiencing vulvar pruritus. Which assessment factor may indicate that the client has an infection caused by Candida albicans? 1. Cottage cheese–like discharge 2. Yellow-green discharge 3. Gray-white discharge 4. Discharge with a fishy odor 44. A 24-year old female client has just been diagnosed with condylomata acuminata (genital warts). What information is appropriate to tell this client? 1. This condition puts her at a higher risk for cervical cancer; therefore, she should have a Papanicolaou (Pap) smear annually. 2. The most common treatment is metronidazole (Flagyl), which should eradicate the problem within 7 to 10 days. 3. The potential for transmission to her sexual partner will be eliminated if condoms are used every time they have sexual intercourse. 4. The human papillomavirus (HPV), which causes condylomata acuminata, can’t be transmitted during oral sex. 45. Nurse Vic is monitoring the fluid intake and output of a female client recovering from an exploratory laparotomy. Which nursing intervention would help the client avoid a urinary tract infection (UTI)? 1. Maintaining a closed indwelling urinary catheter system and securing the catheter to the leg 2. Limiting fluid intake to 1 L/day 3. Encouraging the client to use a feminine deodorant after bathing 4. Encouraging the client to douche once a day after removal of the indwelling urinary catheter 46. Nurse Eve is caring for a client who had a cerebrovascular accident (CVA). Which nursing intervention promotes urinary continence? 1. Encouraging intake of at least 2 L of fluid daily 2. Giving the client a glass of soda before bedtime 3. Taking the client to the bathroom twice per day 4. Consulting with a dietitian 47. A female client with an indwelling urinary catheter is suspected of having a urinary tract infection. Nurse Angel should collect a urine specimen for culture and sensitivity by: 1. disconnecting the tubing from the urinary catheter and letting the urine flow into a sterile container. 2. wiping the self-sealing aspiration port with antiseptic solution and aspirating urine with a sterile needle. 3. draining urine from the drainage bag into a sterile container. 4. clamping the tubing for 60 minutes and inserting a sterile needle into the tubing above the clamp to aspirate urine. 48. Nurse Grace is assessing a male client diagnosed with gonorrheA. Which symptom most likely prompted the client to seek medical attention? 1. Rashes on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet 2. Cauliflower-like warts on the penis 3. Painful red papules on the shaft of the penis 4. Foul-smelling discharge from the penis 49. Nurse Erica is planning to administer a sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) enema to a client with a potassium level of 5.9 mEq/L. Correct administration and the effects of this enema would include having the client: 1. retain the enema for 30 minutes to allow for sodium exchange; afterward, the client should have diarrhea. 2. retain the enema for 30 minutes to allow for glucose exchange; afterward, the client should have diarrhea. 3. retain the enema for 60 minutes to allow for sodium exchange; diarrhea isn’t necessary to reduce the potassium level. 4. retain the enema for 60 minutes to allow for glucose exchange; diarrhea isn’t necessary to reduce the potassium level. 50. When caring for a male client with acute renal failure (ARF), Nurse Fatrishia expects to adjust the dosage or dosing schedule of certain drugs. Which of the following drugs would not require such adjustment? 1. acetaminophen (Tylenol) 2. gentamicin sulfate (Garamycin) 3. cyclosporine (Sandimmune) 4. ticarcillin disodium (Ticar) Answers and Rationales 1. Answer B. When the urethra is ruptured, a hematoma or collection of blood separates the two sections of urethra. This may feel like a boggy mass on rectal examination. Because of the rupture and hematoma, the prostate becomes high riding. A palpable prostate gland usually indicates a nonurethral injury. Absent sphincter tone would refer to a spinal cord injury. The presence of blood would probably correlate with GI bleeding or a colon injury. 2. Answer B. To maintain effective drainage, the client should keep the drainage bag below the bladder; this allows the urine to flow by gravity from the bladder to the drainage bag. The client shouldn’t lay the drainage bag on the floor because it could become grossly contaminated. The client shouldn’t clamp the catheter drainage tubing because this impedes the flow of urine. To promote drainage, the client may loop the drainage tubing above — not below — its point of entry into the drainage bag. 3. Answer A. Women with condylomata acuminata are at risk for cancer of the cervix and vulva. Yearly Pap smears are very important for early detection. Because condylomata acuminata is a virus, there is no permanent cure. Because condylomata acuminata can occur on the vulva, a condom won’t protect sexual partners. HPV can be transmitted to other parts of the body, such as the mouth, oropharynx, and larynx. 4. Answer B. If the pouch faceplate doesn’t fit the stoma properly, the skin around the stoma will be exposed to continuous urine flow 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. from the stoma, causing excoriation and red, weeping, and painful skin. A lubricant shouldn’t be used because it would prevent the pouch from adhering to the skin. When properly applied, a skin barrier prevents skin excoriation. Stoma dilation isn’t performed with an ileal conduit, although it may be done with a colostomy if ordered. Answer C. Pyelonephritis is diagnosed by the presence of leukocytosis, hematuria, pyuria, and bacteriuria. The client exhibits fever, chills, and flank pain. Because there is often a septic picture, the WBC count is more likely to be high rather than low, as indicated in option D. Ketonuria indicates a diabetic state. Answer B. Because CRF causes loss of renal function, the client with this disorder retains fluid. Hemodialysis removes this fluid, causing weight loss. Hematuria is unlikely to follow hemodialysis because the client with CRF usually forms little or no urine. Hemodialysis doesn’t increase urine output because it doesn’t correct the loss of kidney function, which severely decreases urine production in this disorder. By removing fluids, hemodialysis decreases rather than increases the blood pressure. Answer D. Symptoms of gonorrhea in men include purulent, foul-smelling drainage from the penis and painful urination. Rashes on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet are symptoms of the secondary stage of syphilis. Cauliflower-like warts on the penis are a sign of human papillomavirus. Painful red papules on the shaft of the penis may be a sign of the first stage of genital herpes. Answer B. Normal urine pH is 4.5 to 8; therefore, a urine pH of 3.0 is abnormal. Urine specific gravity normally ranges from 1.002 to 1.035, making this client’s value normal. Normally, urine contains no protein, glucose, ketones, bilirubin, bacteria, casts, or crystals. Red blood cells should measure 0 to 3 per high-power field; white blood cells, 0 to 4 per high-power field. Urine should be clear, its color ranging from pale yellow to deep amber. Answer A. The renal clearance test determines the kidneys’ ability to remove a substance from the plasma in 1 minute. It doesn’t measure the kidneys’ ability to remove a substance over a longer period. Answer C. After renal angiography involving a femoral puncture site, the nurse should check the client’s pedal pulses frequently to detect reduced circulation to the feet caused by vascular injury. The nurse also should monitor vital signs for evidence of internal hemorrhage and should observe the puncture site frequently for fresh bleeding. The client should be kept on bed rest for several hours so the puncture site can seal completely. Keeping the client’s knee bent is unnecessary. By the time the client returns to the short-procedure unit, manual pressure over the puncture site is no longer needed because a pressure dressing is in place. The nurse shouldn’t remove this dressing for several hours — and only if instructed to do so. Answer A. A client with CRF is at risk for fluid imbalance — dehydration if the kidneys fail to concentrate urine, or fluid retention if the kidneys fail to produce urine. Electrolyte imbalances associated with this disorder result from the kidneys’ inability to excrete phosphorus; such imbalances may lead to hyperphosphatemia with reciprocal hypocalcemia. CRF may cause metabolic acidosis, not metabolic alkalosis, secondary to inability of the kidneys to excrete hydrogen ions. Answer D. An increased WBC count indicates infection, probably resulting from peritonitis, which may have been caused by insertion of the peritoneal catheter into the peritoneal cavity. Peritonitis can cause the peritoneal membrane to lose its ability to filter solutes; therefore, peritoneal dialysis would no longer be a treatment option for this client. Hyperglycemia occurs during peritoneal dialysis because of the high glucose content of the dialysate; it’s readily treatable with sliding-scale insulin. A potassium level of 3.5 mEq/L can be treated by adding potassium to the dialysate solution. An HCT of 35% is lower than normal. However, in this client, the value isn’t abnormally low because of the daily blood samplings. A lower HCT is common in clients with chronic renal failure because of the lack of erythropoietin. Answer C. During the oliguric phase of ARF, urine output decreases markedly, possibly leading to fluid overload. Limiting oral and I.V. fluid intake can prevent fluid overload and its complications, such as heart failure and pulmonary edema. Encouraging coughing and deep breathing is important for clients with various respiratory disorders. Promoting carbohydrate intake may be helpful in ARF but 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. doesn’t take precedence over fluid limitation. Controlling pain isn’t important because ARF rarely causes pain. Answer D. Cardiac glycosides such as digoxin should be withheld before hemodialysis. Hypokalemia is one of the electrolyte shifts that occur during dialysis, and a hypokalemic client is at risk for arrhythmias secondary to digitalis toxicity. Phosphate binders and insulin can be administered because they aren’t removed from the blood by dialysis. Some antibiotics are removed by dialysis and should be administered after the procedure to ensure their therapeutic effects. The nurse should check a formulary to determine whether a particular antibiotic should be administered before or after dialysis. Answer B. Gonorrhea must be reported to the public health department. Chlamydia, genital herpes, and human papillomavirus infection aren’t reportable diseases. Answer C. Co-trimoxazole is a sulfonamide antibiotic used to treat urinary tract infections. Therefore, absence of bacteria on urine culture indicates that the drug has achieved its desired effect. Although flank pain may decrease as the infection resolves, this isn’t a reliable indicator of the drug’s effectiveness. Co-trimoxazole doesn’t affect urine output or the RBC count. Answer D. Phenazopyridine may be prescribed in conjunction with an antibiotic for painful bladder infections to promote comfort. Because of its local anesthetic action on the urinary mucosa, phenazopyridine specifically relieves bladder pain. Nitrofurantoin is a urinary antiseptic with no analgesic properties. While ibuprofen and acetaminophen with codeine are analgesics, they don’t exert a direct effect on the urinary mucosa. Answer A. When preparing for continuous bladder irrigation, a triple-lumen indwelling urinary catheter is inserted. The three lumens provide for balloon inflation and continuous inflow and outflow of irrigation solution. Answer B. Normally, fluid intake is approximately equal to the urine output. Any other relationship signals an abnormality. For example, fluid intake that is double the urine output indicates fluid retention; fluid intake that is half the urine output indicates dehydration. Normally, fluid intake isn’t inversely proportional to the urine output. Answer C. Mumps is the most significant childhood infectious disease affecting male fertility. Chickenpox, measles, and scarlet fever don’t affect male fertility. Answer A. The most common site of renal calculi formation is the kidney. Calculi may travel down the urinary tract with or without causing damage and may lodge anywhere along the tract or may stay within the kidney. The ureter, bladder, and urethra are less common sites of renal calculi formation. Answer A. Dialysis equilibrium syndrome causes confusion, a decreasing level of consciousness, headache, and seizures. These findings, which may last several days, probably result from a relative excess of interstitial or intracellular solutes caused by rapid solute removal from the blood. The resultant organ swelling interferes with normal physiologic functions. To prevent this syndrome, many dialysis centers keep first-time sessions short and use a reduced blood flow rate. Acute bone pain and confusion are associated with aluminum intoxication, another potential complication of dialysis. Weakness, tingling, and cardiac arrhythmias suggest hyperkalemia, which is associated with renal failure. Hypotension, tachycardia, and tachypnea signal hemorrhage, another dialysis complication. Answer B. For an uncomplicated UTI, norfloxacin therapy usually lasts 7 to 10 days. Taking the drug for less than 7 days wouldn’t eradicate such an infection. Taking it for more than 10 days isn’t necessary. Only a client with a complicated UTI must take norfloxacin for 10 to 21 days. Answer C. The client should report the presence of foul-smelling or cloudy urine. Unless contraindicated, the client should be instructed to drink large quantities of fluid each day to flush the kidneys. Sandlike debris is normal due to residual stone products. Hematuria is common after lithotripsy. Answer D. The guidelines for initiating bladder retraining include assessing the client’s intake patterns, voiding patterns, and reasons for each accidental voiding. Lowering the client’s fluid intake won’t reduce or prevent incontinence. The client should actually be encouraged to drink 1.5 to 2 L of water per day. A voiding schedule should be established after assessment. 26. Answer B. Reports of bladder spasms and the urge to void suggest that a blood clot may be occluding the catheter. After TURP, urine normally appears red to pink, and normal saline irrigant usually is infused at a rate of 40 to 60 drops/minute or according to facility protocol. The amount of retained fluid (1,200 ml) should correspond to the amount of instilled fluid, plus the client’s urine output (1,000 ml + 200 ml), which reflects catheter patency. 27. Answer B. When inserting a urinary catheter, facilitate insertion by asking the client to breathe deeply. Doing this will relax the urinary sphincter. Initiating a stream of urine isn’t recommended during catheter insertion. Turning to the side or holding the labia or penis won’t ease insertion, and doing so may contaminate the sterile field. 28. Answer D. ARF, characterized by abrupt loss of kidney function, commonly causes oliguria, which is demonstrated by a urine output of 400 ml/24 hours. A serum creatinine level of 1.2 mg/dl isn’t diagnostic of ARF. A BUN level of 22 mg/dl or a temperature of 100.2° F (37.8° C) wouldn’t result from this disorder. 29. Answer A. TURP is the most widely used procedure for prostate gland removal. Because it requires no incision, TURP is especially suitable for men with relatively minor prostatic enlargements and for those who are poor surgical risks. Suprapubic prostatectomy, retropubic prostatectomy, and transurethral laser incision of the prostate are less common procedures; they all require an incision. 30. Answer B. Fluid depletion before excretory urography is contraindicated in clients with multiple myeloma, severe diabetes mellitus, and uric acid nephropathy — conditions that can seriously compromise renal function in fluid-depleted clients with reduced renal perfusion. If these clients must undergo excretory urography, they should be well hydrated before the test. Cystic fibrosis, gout, and myasthenia gravis don’t necessitate changes in client preparation for excretory urography. 31. Answer A. By encouraging a daily fluid intake of at least 2 L, the nurse helps fill the client’s bladder, thereby promoting bladder retraining by stimulating the urge to void. The nurse shouldn’t give the client soda before bedtime; soda acts as a diuretic and may make the client incontinent. The nurse should take the client to the bathroom or offer the bedpan at least every 2 hours throughout the day; twice per day is insufficient. Consultation with a dietitian won’t address the problem of urinary incontinence. 32. Answer B. Percussion over the costovertebral angle normally produces a dull, thudding sound, which is soft to moderately loud with a moderate pitch and duration. This sound occurs over less dense, mostly fluid-filled matter, such as the kidneys, liver, and spleen. In contrast, a flat sound occurs over highly dense matter such as muscle; hyperresonance occurs over the air-filled, overinflated lungs of a client with pulmonary emphysema or the lungs of a child (because of a thin chest wall); and tympany occurs over enclosed structures containing air, such as the stomach and bowel. 33. Answer D. An elevated serum potassium level may lead to a life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia, which the nurse can detect immediately by palpating the pulse. The client’s blood pressure may change, but only as a result of the arrhythmia. Therefore, the nurse should assess blood pressure later. The nurse also can delay assessing respirations and temperature because these aren’t affected by the serum potassium level. 34. Answer C. Infection can occur with renal calculi from urine stasis caused by obstruction. Options A and D aren’t appropriate for this diagnosis, and retention of urine usually occurs, rather than incontinence. 35. Answer A. As urine output decreases, the serum potassium level rises; if it rises sufficiently, hyperkalemia may occur, possibly triggering a cardiac arrhythmia. Hyperkalemia doesn’t cause paresthesia (sensations of numbness and tingling). Dehydration doesn’t occur during this oliguric phase of ARF, although typically it does arise during the diuretic phase. In a client with ARF, pruritus results from increased phosphates and isn’t associated with hyperkalemia. 36. Answer C. Although postoperative pain is expected, the nurse should make sure that other factors, such as an obstructed irrigation catheter, aren’t the cause of the pain. After assessing catheter patency, the nurse should administer an analgesic, such as meperidine, as prescribed. Increasing the I.V. flow rate may worsen 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. the pain. Notifying the physician isn’t necessary unless the pain is severe or unrelieved by the prescribed medication. Answer D. A nurse who discovers a nodule, swelling, or other abnormal finding during a scrotal examination should transilluminate the scrotum by darkening the room and shining a flashlight through the scrotum behind the mass. A scrotum filled with serous fluid transilluminates as a red glow; a more solid lesion, such as a hematoma or mass, doesn’t transilluminate and may appear as a dark shadow. Although the nurse should notify the physician of the abnormal finding, performing transillumination first provides additional information. The nurse can’t uncover more information about a scrotal mass by changing the client’s position and repeating the examination or by performing a rectal examination. Answer C. In a client with CRF, unrestricted intake of sodium, protein, potassium, and fluid may lead to a dangerous accumulation of electrolytes and protein metabolic products, such as amino acids and ammonia. Therefore, the client must limit intake of sodium; meat, which is high in protein; bananas, which are high in potassium; and fluid, because the failing kidneys can’t secrete adequate urine. Salt substitutes are high in potassium and should be avoided. Extra carbohydrates are needed to prevent protein catabolism. Answer B. Urinary incontinence isn’t a normal part of aging nor is it a disease. It may be caused by confusion, dehydration, fecal impaction, restricted mobility, or other causes. Certain medications, including diuretics, hypnotics, sedatives, anticholinergics, and antihypertensives, may trigger urinary incontinence. Most clients with urinary incontinence can be treated; some can be cured. Answer D. If the catheter is blocked by blood clots, it may be irrigated according to physician’s orders or facility protocol. The nurse should use sterile technique to reduce the risk of infection. Urinating around the catheter can cause painful bladder spasms. Encourage the client to drink fluids to dilute the urine and maintain urine output. The catheter remains in place for 2 to 4 days after surgery and is only removed with a physician’s order. Answer B. When receiving a sulfonamide such as co-trimoxazole, the client should drink at least eight 8-oz glasses of fluid daily to maintain a urine output of at least 1,500 ml/day. Otherwise, inadequate urine output may lead to crystalluria or tubular deposits. For maximum absorption, the client should take this drug at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals. No evidence indicates that antacids interfere with the effects of sulfonamides. To prevent a photosensitivity reaction, the client should avoid direct sunlight during co-trimoxazole therapy. Answer A. Generalized edema, especially of the face and periorbital area, is a classic sign of acute glomerulonephritis of sudden onset. Other classic signs and symptoms of this disorder include hematuria (not green-tinged urine), proteinuria, fever, chills, weakness, pallor, anorexia, nausea, and vomiting. The client also may have moderate to severe hypertension (not hypotension), oliguria or anuria (not polyuria), headache, reduced visual acuity, and abdominal or flank pain. Answer A. The symptoms of C. albicans include itching and a scant white discharge that has the consistency of cottage cheese. Yellow-green discharge is a sign of Trichomonas vaginalis. Gray-white discharge and a fishy odor are signs of Gardnerella vaginalis. Answer A. Women with condylomata acuminata are at risk for cancer of the cervix and vulva. Yearly Pap smears are very important for early detection. Because condylomata acuminata is a virus, there is no permanent cure. Because condylomata acuminata can occur on the vulva, a condom won’t protect sexual partners. HPV can be transmitted to other parts of the body, such as the mouth, oropharynx, and larynx. Answer A. Maintaining a closed indwelling urinary catheter system helps prevent introduction of bacteria; securing the catheter to the client’s leg also decreases the risk of infection by helping to prevent urethral trauma. To flush bacteria from the urinary tract, the nurse should encourage the client to drink at least 10 glasses of fluid daily, if possible. Douching and feminine deodorants may irritate the urinary tract and should be discouraged. Answer A. By encouraging a daily fluid intake of at least 2 L, the nurse helps fill the client’s bladder, thereby promoting bladder retraining by stimulating the urge to void. The nurse shouldn’t give the client soda before bedtime; soda acts as a diuretic and may make the client incontinent. The nurse should take the client to the bathroom or offer the bedpan at least every 2 hours throughout the day; twice per day is insufficient. Consultation with a dietitian won’t address the problem of urinary incontinence. 47. Answer B. Most catheters have a self-sealing port for obtaining a urine specimen. Antiseptic solution is used to reduce the risk of introducing microorganisms into the catheter. Tubing shouldn’t be disconnected from the urinary catheter. Any break in the closed urine drainage system may allow the entry of microorganisms. Urine in urine drainage bags may not be fresh and may contain bacteria, giving false test results. When there is no urine in the tubing, the catheter may be clamped for no more than 30 minutes to allow urine to collect. 48. Answer D. Symptoms of gonorrhea in men include purulent, foul-smelling drainage from the penis and painful urination. Rashes on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet are symptoms of the secondary stage of syphilis. Cauliflower-like warts on the penis are a sign of human papillomavirus. Painful red papules on the shaft of the penis may be a sign of the first stage of genital herpes. 49. Answer A. Kayexalate is a sodium exchange resin. Thus the client will gain sodium as potassium is lost in the bowel. For the exchange to occur, Kayexalate must be in contact with the bowel for at least 30 minutes. Sorbitol in the Kayexalate enema causes diarrhea, which increases potassium loss and decreases the potential for Kayexalate retention. 50. Answer A. Because acetaminophen is metabolized in the liver, its dosage and dosing schedule need not be adjusted for a client with ARF. In contrast, the dosages and schedules for gentamicin and ticarcillin, which are metabolized and excreted by the kidney, should be adjusted. Because cyclosporine may cause nephrotoxicity, the nurse must monitor both the dosage and blood drug level in a client receiving this drug. TEST 3 - ACUTE RENAL FAILURE 1) The cause of ___________ failure is impaired blood supply to the kidney (Fluid Volume Deficit, hemorrhage, heart failure, shock) 1. prerenal 2. Intrarenal 3. Postrenal 4. perirenal 2) What electrolytes are in urine? 1. Na 2. K 3. Cl 4. HCO35. All of the above 3) Which diagnostic test would be monitored to evaluate glomerulat filtration rateand renal function? 1. Sreum creatinine and BUN 2. Urinalysis 3. Kidney biopsy 4. creatinine clearance 4) Marina with acute renal failure moves into the diuretic phase after one week of therapy. During this phase the client must be assessed for signs of developing: 1. Hypovolemia 2. renal failure 3. metabolic acidosis 4. hyperkalemia 5) true or false? Creatinine, phosphate, sulfates, and uric acid should not be present in urine because they signify renal failure. 1. True 2. False 6) The nurse is reviewing laboratory results on a client with acute renal failure. Which one of the following should be reported immediately? 1. Blood urea nitrogen 50 mg/dl 2. Hemoglobin of 10.3 mg/dl 3. Venous blood pH 7.30 4. Serum potassium 6 mEq/L 7)Nurse Liza is assigned to care for a client who has returned to the nursing unit after left nephrectomy. Nurse Liza’s highest priority would be… 1. Hourly urine output 2. Temperature 3. Able to turn side to side 4. Able to sips clear liquidQ. 8) The charge nurse assigned in the care for a client with acute renal failure and hypernatremia to you, a newly graduated RN. Which actions can you delegate to the nursing assistant? 1. Provide oral care every 3-4 hours 2. Monitor for indications of dehydration 3. Administer 0.45% saline by IV line 4. Assess daily weights for trends 9) __________ in BUN/Creatinine ratio indicate fluid volume excess,malnutrition and fluid volume excess or malnutrition ? 1. Increase 2. Decrease 10) The most serious electrolyte disorder associated with kidney disease is 1. hypermagnesemia 2. hyponatremia 3. hyperkalemia 4. metabolic acidosis 11) A client in acute renal failure is a candidate for continuous renal placement therapy (CRRT). The most common indication for use of CRRT is 1. azotemia 2. pericarditis 3. hyperkalemia 4. fluid overload 12) A history of infection specifically caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococci is associated with which of the following disorders? 1. Acute glomerulonephritis 2. Acute renal failure 3. Chronic renal failure 4. Nephrotic syndrome 13) The leading cause of ESRD is the client with a history of 1. hypotension 2. anemia 3. prostate cancer 4. diabetes Mellitus 14) The risk for __________________ is particularly high when ischemia and exposure to a nephrotoxin occur at the same time. 1. acute tubular necrosis or tubular necrosis 2. acute glomerulonephritis 3. chronic renal failure 4. UTI 15) What controls the amount of water absorption? 1. antidiuretic hormone (Vasopressin) 2. melanin 3. thyroxine 4. prolactin 16) What does urine mostly consist of? 1. H2O (Water) 2. NaCl (Salt) 3. Urea 4. KCl 17) How much water do normal kidneys excrete each day? 1. 3-4 liters 2. 5-6 liters 3. 1-2 liters 4. 7-8 liters 18) Chronic kidney disease is defined by Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (K/DOQI) as evidence of structural or functional kidney abnormalities (abnormal urinalysis, imaging studies, or histology) that persists for at least ______________ months, with or without a decreased GFR. 1. 1 2. 2 3. 3 4. 6 5. 12 19) What is the # 1 renal function test? 1. Renal Clearance/Creatinine Clearance 2. Osmolarity 3. Serum Creatinine 4. BUN 20) For a male client in the oliguric phase of acute renal failure (ARF), which nursing intervention is most important? 1. Encouraging coughing and deep breathing 2. Promoting carbohydrate intake 3. Limiting fluid intake 4. Providing pain-relief measures 21) How much salt do normal kidneys excrete each day? 1. 1-2 mg 2. 5 g 3. 3-4 g 4. 6-8 g 22) Which is a normal value of Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)? 1. 0.5-1.1 mg/dL 2. 5-20 mg/dL 3. 40-70 mg/dL 4. 250-500 mg/dL 23) When the kidneys cannot effectively regulate fluid and electrolyte balance and eliminate metabolic waste products, intake of these substances must be regulated. Fluid and Sodium intake are ________. 1. encouraged 2. limited 3. restricted 24) The nurse is caring for the client who has had a renal biopsy. Which of the following interventions would the nurse avoid in the care of the client after this procedure? 1. Encourage fluids to at least 3L in the first 24 hours 2. Administering narcotics as needed 3. Testing serial samples iwth dipsticks for occult blood 4. Ambulating the client in the room and hall for short distances 25) A female client is admitted with a diagnosis of acute renal failure. She is awake, alert, oriented, and complaining of severe back pain, nausea and vomiting and abdominal cramps. Her vital signs are blood pressure 100/70 mm Hg, pulse 110, respirations 30, and oral temperature 100.4°F (38°C). Her electrolytes are sodium 120 mEq/L, potassium 5.2 mEq/L; her urinary output for the first 8 hours is 50 ml. The client is displaying signs of which electrolyte imbalance? 1. Hyponatremia 2. Hyperkalemia 3. Hyperphosphatemia 4. Hypercalcemia 26) how many ml/hr of urine output is the normal minimum? 1. 30 2. 35 3. 40 4. 45 27) Signs and symptoms of acute kidney rejection that the nurse should teach the patient to observe for include 1. tachycardia and headache 2. fever and painful transplant site 3. severe hypotension and weight loss 4. recurrent urinary tract infections and oral yeast infections 28) ________ renal failure is a slow, insidious process of kidney destruction. It may go unrecognized for years as nephrons are destroyed and renal mass is reduced. 1. Chronic 2. Acute 29) The client with renal failure should be on which type of diet? 1. high protein, high carbohydrate, low calorie 2. adequate calorie intake, high carbohydrate, limited protein 3. Limited protein, low carbohydrate, adequate calorie intake 4. Low calorie, limited protein, low carbohydrate 30) A client suffering from acute renal failure has an unexpected increase in urinary output to 150ml/hr. The nurse assesses that the client has entered the second phase of acute renal failure. Nursing actions throughout this phase include observation for signs and symptoms of 1. Hypervolemia, hypokalemia, and hypernatremia. 2. Hypervolemia, hyperkalemia, and hypernatremia. 3. Hypovolemia, wide fluctuations in serum sodium and potassium levels. 4. Hypovolemia, no fluctuation in serum sodium and potassium levels. 31) _________ is the most frequent complication during hemodialysis. 1. hypertension 2. bleeding 3. Infection 4. Dialysis dementia 32) After 1 week a client with acute renal failure moves, into the diuretic phase. During this phase the client must be carefully assessed for signs of: 1. Hypovolemia 2. Hyperkalemia 3. Metabolic acidosis 4. Chronic renal failure 33) What is the #1 cause of death when kidneys fail? 1. hyperkalemia 2. hypokalemia 3. hypernatremia 4. hyponatremia 34) The nurse is reviewing laboratory results on a client with acute renal failure. Which one of the following should be reported IMMEDIATELY? 1. Blood urea nitrogen 50 mg/dl 2. Hemoglobin of 10.3 mg/dl 3. Venous blood pH 7.30 4. Serum potassium 6 mEq/L 35) When the kidneys have too few nephrons to excrete metabolic wastes and regulate fluid and electrolyte balance adequately, the client is said to have ____________, the final stage of Chronic Renal Failure. 1. End-stage renal disease (ESRD) 2. renal insufficiency 3. acute tubular necrosis 4. dialysis 36) _________ renal Failure is a rapid decline in renal function with an abrupt onset 1. acute 2. chronic 37) How do kidneys control Na+ levels and K+ levels? 1. The kidneys release renin, which controls angiotensin. The angiotensin controls aldosterone. Aldosterone controls the levels of Na+ and K+ 2. Kidneys release aldosterone which controls renin. Renin causes the release of angiotensin. Angiotensin controls the levels of Na+ and K+ 3. The kidneys release renin which controls K+. The kidneys release angiotensin which causes Na+ realease. 38) Anti-hypertensive therapy in patients with chronic renal disease is for? 1. Renal protection 2. Cardiovascular protection 3. Both renal and cardiovascular protection 4. None of the above 39) ____________ is a treatment for renal failure in which blood id continuously circulated (artery to vein or vein to vein) and filtered, allowing excess water and solutes to empty into a collecting device. Fluid may be replaced with a balanced electrolyte solution as needed during treatment. 1. Hemodialysis 2. Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis 3. Continuous cyclic peritoneal dialysis 4. Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy 40) __________ failure is caused by obstruction of urine flow. (urethral obstruction by enlarged prostate or tumor; ureteral or kidney pelvis obstruction by calculi) 1. prerenal 2. intrarenal 3. postrenal 4. perirenal 41) Agents that damage the kidney tissue are called: 1. nephrons 2. nephrotoxins 3. antibodies 4. enterotoxins 42) Which phase of Acute Renal Failure results in FVE and edema due to salt and water retention, hypertension, Azotemia, hyperkalemia, muscle weakness, nausea, diarrhea, and high serum creatinine and BUN levels? 1. initiation phase 2. maintenance phase 3. recovery phase 4. intrarenal phase 43) A patient rapidly progressing toward ESRD asks about the possibility of a kidney transplant. In responding to the patient, the nurse knows that contraindications to kidney transplantation include 1. hepatitis C infection 2. extensive vascular disease 3. coronary artery disease 4. refractory hypertension 44) Which of the following medications does not interfere with either creatinine secretion or the assay used to measure the serum creatinine? 1. Ibuprofen 2. Cimetidine 3. Trimethoprim 4. Cefoxitin 5. Flucytosine 45) A female client with acute renal failure is undergoing dialysis for the first time. The nurse in charge monitors the client closely for dialysis equilibrium syndrome, a complication that is most common during the first few dialysis sessions. Typically, dialysis equilibrium syndrome causes: 1. confusion, headache, and seizures. 2. acute bone pain and confusion. 3. weakness, tingling, and cardiac arrhythmias. 4. hypotension, tachycardia, and tachypnea. 46) Clients with chronic renal failure should notify the physician of any weight: 1. loss of 2 pounds over a 5 day period 2. gain of 2 pounds over a 2 day period 3. loss of 5 pounds over a 5 day period 4. gain of 5 pounds over a 2 day period 47) Nurse Tristan is caring for a male client in acute renal failure. The nurse should expect hypertonic glucose, insulin infusions, and sodium bicarbonate to be used to treat: 1. hypernatremia. 2. hypokalemia. 3. hyperkalemia. 4. hypercalcemia. 48) The client with ESRD tells the nurse that she hates the thought of being tied to the machine, but is also glad to start dialysis because she will be able to eat and drink what she wants. Based on this information, the nuse identifies the nursing diagnosis of 1. self-esteem disturbance related to dependence on dialysis 2. anxiety related to perceived threat to health status and role functioning 3. ineffective management of therapeutic regimen related to lack of knowledge of treatment plan 4. risk for imbalanced nutrition: more than body requirements, related to increased dietary intake 49) How acidic is urine compared to blood? 1. 100 times more acidic 2. 200 times less acidic 3. 1000 times more acidic 4. 2000 times more acidic 50) Impaired metabolic processes such as Hyperkalemia, Acidosis, Hyperlipidemia, Hyperuricemia, and malnutrition are some effects of ___________. 1. hematuria 2. oliguria 3. uremia 4. nephrotoxins 51) ________ failure is caused by Acute damage to renal tissue and nephrons or acute tubular necrosis: abrupt decline in tubular and glomerular function due to either prolonged ischemia and/or exposure to nephrotoxins. (Acute glomerulonephritis, malignant hypertension, ischemia; nephrotoxic drugs or substances; red blood cell destruction; muscle tissue breakdown due to trauma, heatstroke) 1. Prerenal 2. Intrarenal 3. Postrenal 4. Perirenal 52) Common early manifestations of kidney disease are loss of concentration and dilute urine and loss of ability to concentrate and dilute urine . 1. True 2. False 53) A client with acute renal failure is aware that the most serious complication of this condition is: 1. Constipation 2. Anemia 3. Infection 4. Platelet dysfunction 54) The nurse is performing an assessment on a client who has returned from the dialysis unit following hemodialysis. The client is complaining of a headache and nausea and is extremely restless. Which of the following is the most appropriate nursing action? 1. Notify the physician 2. Monitor the client 3. Elevate the head of the bed 4. Medicate the client for nausea 55) How much KCL do normal kidneys excrete each day? 1. 6-8 g 2. 1 g 3. 6-8 mg 4. 3 mg 56) Clients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) must empty their peritoneal cavity and replace the dialysate every __________ hours. 1. 24 2. 6-8 3. 4-6 4. 48 57) Which of these drugs is nephrotoxic? 1. Diuretics 2. ACE inhibitors 3. NSAIDs 4. Sodium bicarbonate/ Potassium bicarbonate 58) A client is admitted to the hospital and has a diagnosis of early stage chronic renal failure. Which of the following would the nurse expect to note on assessment of the client? 1. Polyuria 2. Polydipsia 3. Oliguria 4. Anuria 59) A client on peritoneal dialysis notices that the collecting bag of dialysate is cloudy, what is this an indication of? 1. The client needs to change their dialysate 2. The patient needs a kidney transplant 3. Medication was added to the dialysate 4. The patient is infected and experiencing peritonitis 60) End-stage renal disease is defined as GFR less than ________________ ml/min per 1.73m2. 1. 45 2. 30 3. 15 4. 10 5. 5 61) During the _________ phase of Acute Renal Failure, Oliguria develops and the kidneys cannot efficiently eliminate metabolic wastes, water, electrolytes, and acids. 1. maintenance 2. initiation 3. recovery 62) What tests and results prove the presence of dilute urine? 1. Fixed Specific Gravity (1.010), and/or Fixed osmolality (300 mOsm/l) 2. GFR (100 ml/min), and/or Specific Gravity (1.030) 3. Serum Creatinine (1.5 mg/dl) 63) Which of the following are abnormal to be found in the urine? 1. K 2. Amino acids 3. Glucose 4. all of the above 5. Amino acids and glucose 64) ESRD occurs when the GFR is less than ___ per minute. 1. 5 ml 2. 10 ml 3. 15 ml 4. 25 ml 65) “urine in the blood” 1. uremia 2. urticaria 3. urethritis 4. urethrorrhea Answers and Rationales 1. A. prerenal 2. E. All of the above 3. D. creatinine clearance 4. A. Hypovolemia 5. B. False . Creatinine, phosphate, sulfates, and uric acid should be found in urine. 6. D. Serum potassium 6 mEq/L . Although all of these findings are abnormal, the elevated potassium is a life threatening finding and must be reported immediately. 7. A. Hourly urine output . After nephrectomy, it is necessary to measure urine output hourly. This is done to assess the effectiveness of the remaining kidney also to detect renal failure early. 8. A. Provide oral care every 3-4 hours . Providing oral care is within the scope of practice for the nursing assistant. Monitoring and assessing clients, as well as administering IV fluids, require the additional education and skill of the RN. 9. B. Decrease 10. C. hyperkalemia 11. D. fluid overload 12. A. Acute glomerulonephritis ○ Acute glomerulonephritis is also associated with varicella zoster virus, hepatitis B, and Epstein-Barr virus. ○ Acute renal failure is associated with hypoperfusion to the kidney, parenchymal damage to the glomeruli or tubules, and obstruction at a point distal to the kidney. ○ Chronic renal failure may be caused by systemic disease, hereditary lesions, medications, toxic agents, infections, and medications. ○ Nephrotic syndrome is caused by disorders such as chronic glomerulonephritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple myeloma, and renal vein thrombosis. 13. D. diabetes Mellitus 14. A. acute tubular necrosis or tubular necrosis 15. A. antidiuretic hormone 16. A. H2O (Water) 17. C. 1-2 liters 18. C. 3 19. A. Renal Clearance/Creatinine Clearance 20. C. Limiting fluid intake . During the oliguric phase of ARF, urine output decreases markedly, possibly leading to fluid overload. Limiting oral and I.V. Fluid intake can prevent fluid overload and its complications, such as heart failure and pulmonary edema. Encouraging coughing and deep breathing is important for clients with various respiratory disorders. Promoting carbohydrate intake may be helpful in ARF but doesn’t take precedence over fluid limitation. Controlling pain isn’t important because ARF rarely causes pain. 21. D. 6-8 g 22. B. 5-20 mg/dL 23. B. limited 24. D. Ambulating the client in the room and hall for short distances 25. A. Hyponatremia . The normal serum sodium level is 135 – 145 mEq/L. The client’s serum sodium is below normal. Hyponatremia also manifests itself with abdominal cramps and nausea and vomiting 26. A. 30 27. B. fever and painful transplant site 28. A. chronic 29. B. adequate calorie intake, high carbohydrate, limited protein 30. C. Hypovolemia, wide fluctuations in serum sodium and potassium levels. The second phase of ARF is the diuretic phase or high output phase. The diuresis can result in an output of up to 10L/day of dilute urine. Loss of fluids and electrolytes occur. 31. 32. 33. 34. A. hypertension A. Hypovolemia A. hyperkalemia D. Serum potassium 6 mEq/L. Although all of these findings are abnormal, the elevated potassium is a life threatening finding and must be reported immediately. 35. A. End-stage renal disease (ESRD) 36. A. acute 37. A. The kidneys release renin, which controls angiotensin. The angiotensin controls aldosterone. Aldosterone controls the levels of Na+ and K+ 38. C. Both renal and cardiovascular protection 39. D. Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy 40. C. postrenal 41. B. nephrotoxins 42. B. maintenance phase 43. B. extensive vascular disease 44. A. Ibuprofen 45. A. confusion, headache, and seizures. Dialysis equilibrium syndrome causes confusion, a decreasing level of consciousness, headache, and seizures. These findings, which may last several days, probably result from a relative excess of interstitial or intracellular solutes caused by rapid solute removal from the blood. The resultant organ swelling interferes with normal physiologic functions. To prevent this syndrome, many dialysis centers keep first-time sessions short and use a reduced blood flow rate. Acute bone pain and confusion are associated with aluminum intoxication, another potential complication of dialysis. Weakness, tingling, and cardiac arrhythmias suggest hyperkalemia, which is associated with renal failure. Hypotension, tachycardia, and tachypnea signal hemorrhage, another dialysis complication. 46. D. gain of 5 pounds over a 2 day period 47. C. hyperkalemia. Hyperkalemia is a common complication of acute renal failure. It’s life-threatening if immediate action isn’t taken to reverse it. The administration of glucose and regular insulin, with sodium bicarbonate if necessary, can temporarily prevent cardiac arrest by moving potassium into the cells and temporarily reducing serum potassium levels. Hypernatremia, hypokalemia, and hypercalcemia don’t usually occur with acute renal failure and aren’t treated with glucose, insulin, or sodium bicarbonate. 48. C. ineffective management of therapeutic regimen related to lack of knowledge of treatment plan 49. C. 1000 times more acidic 50. C. uremia 51. B. Intrarenal 52. A. True 53. C. Infection . Infection is responsible for one third of the traumatic or surgically induced death of clients with renal failure as well as medical induced acute renal failure (ARF) 54. A. Notify the physician 55. A. 6-8 g 56. C. 4-6 57. C. NSAIDs 58. A. Polyuria 59. D. The patient is infected and experiencing peritonitis 60. C. 15 61. A. maintenance 62. A. Fixed Specific Gravity (1.010), and/or Fixed osmolality (300 mOsm/l) 63. E. Amino acids and glucose. Amino acids (proteins) found in the urine indicate trauma to the glomeruli. Glucose found in the urine indicates BS levels to be above the renal threshold. 64. C. 15 ml 65. A. uremia TEST 4 - BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA Q.1) After undergoing a transurethral resection of the prostate to treat benign prostatic hypertrophy, a patient is returned to the room with continuous bladder irrigation in place. One day later, the patient reports bladder pain. What should the nurse do first? 1. Increase the I.V. flow rate 2. Notify the doctor immediately 3. Assess the irrigation catheter for patency and drainage 4. Administer meperidine (Demerol) as prescribed Q.2) Alpha blockers in the treatment of BPH are associated with all of the following except: 1. Improvement in symptoms in 2-3 weeks 2. Side effects of dizziness and fatigue 3. Once daily dosing 4. 25% decrease in prostate size 5. Minimal changes in blood pressure Q.3) Of the options below, is NOT a symptom of BPH? 1. Urinary incontinence 2. Difficulty urinating 3. Intestinal pain 4. Sexual dysfunction Q.4) An eighty five year old man was admitted for surgery for benign prostatic hypertrophy. Preoperatively he was alert, oriented, cooperative, and knowledgeable about his surgery. Several hours after surgery, the evening nurse found him acutely confused, agitated, and trying to climb over the protective side rails on his bed. The most appropriate nursing intervention that will calm an agitated client is 1. limit visits by staff. 2. encourage family phone calls. 3. position in a bright, busy area. 4. speak soothingly and provide quiet music. Q.5) What is the relationship between prostate cancer and the condition of an enlarged prostate, also known as BPH? 1. BPH and prostate cancer are unrelated 2. BPH causes prostate cancer 3. BPH is a symptom of prostate cancer Q.6) How common is BPH? 1. 10% of men in their 60s 2. 30% of men in their 60s 3. 50% of men in their 60s 4. 90% of men in their 60s Q.7) Romeo Diaz, age 78, is admitted to the hospital with the diagnosis of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). He is scheduled for a transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). It would be inappropriate to include which of the following points in the preoperative teaching? 1. TURP is the most common operation for BPH. 2. Explain the purpose and function of a two-way irrigation system. 3. Expect bloody urine, which will clear as healing takes place. 4. He will be pain free. Q.8) The obstructive and irritative symptom complex caused by benign prostatic hypertrophy is termed 1. prostatism. 2. prostatitis. 3. prostaglandin. 4. prostatectomy. Q.9) Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is associated with all of the following except: 1. Outpatient procedure in most cases 2. Transfusion rate of 2-4% 3. Retrograde ejaculation in 50% of men 4. Most effective long term treatment 5. Erectile dysfunction in 2% Q.10) A client is admitted to the hospital with benign prostatic hyperplasia, the nurse most relevant assessment would be: 1. Flank pain radiating in the groin 2. Distention of the lower abdomen 3. Perineal edema 4. Urethral discharge Q.11) What question would be most important to ask a male client who is in for a digital rectal examination? 1. “Have you noticed a change in the force of the urinary system?” 2. “Have you noticed a change in tolerance of certain foods in your diet?” 3. “Do you notice polyuria in the AM?” 4. “Do you notice any burning with urination or any odor to the urine?” Q.12) The nurse is administering a psychotropic drug to an elderly client who has a history of benign prostatic hypertrophy. It is most important for the nurse to teach this client to: 1. Add fiber to his diet. 2. Exercise on a regular basis. 3. Report incomplete bladder emptying 4. Take the prescribed dose at bedtime. Q.13) Which of the following is true of laser therapy? 1. Laser light exhibits all photons in phase (coherence) 2. The photons travel at right angles (collimation) 3. The photons have varying wavelengths (polychronicity) 4. May be legally performed in 48 of the 50 US states 5. Cause eye damage in most surgeons after prolonged use Answers and Rationales 1. C. Assess the irrigation catheter for patency and drainage . Although postoperative pain is expected, the nurse should ensure that other factors, such as an obstructed irrigation catheter, aren’t the cause of the pain. After assessing catheter patency, the nurse should administer an analgesic such as meperidine as prescribed. Increasing the I.V. flow rate may worsen the pain. Notifying the doctor isn’t necessary unless the pain is severe or unrelieved by the prescribed medication. 2. D. 25% decrease in prostate size 3. C. Intestinal pain. Recent studies suggest that there is a correlation between lower urinary tract symptoms and sexual dysfunction in aging patients. In fact, the severity of urinary symptoms and the degree of sexual dysfunction are strongly correlated, indepently of age. In particular, community-based studies have found that a significant number of patients with symptomatic BPH have sexual dysfunction. 4. D. speak soothingly and provide quiet music. The client needs frequent visits by the staff to orient him and to assess his safety. Phone calls from his family will not help a client who is trying to climb over the side rails and may even add to his danger. Putting the client in a bright, busy area would probably add to his confusion. The environment is an important factor in the prevention of injuries. Talking softly and providing quiet music have a calming effect on the agitated client. 5. A. BPH and prostate cancer are unrelated 6. C. 50% of men in their 60s . Although the prostate continues to grow during most of a man’s life, the enlargement doesn’t usually cause problems until late in life. BPH rarely causes symptoms before the age of 40, but more than half of men in their 60s, and as many as 90% in their 70s and 80s, have some symptoms of BPH 7. D. He will be pain free. Surgical interventions involve an experience of pain for the client which can come in varying degrees. Telling the pain that he will be pain free is giving him false reassurance. 8. A. prostatism. Symptoms of prostatism include increased frequency of urination, nocturia, urgency, dribbling, and a sensation that the bladder has not completely emptied. Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland.Prostaglandins are physiologically active substances present in tissues with vasodilator properties. Prostatectomy refers to the surgical removal of the prostate gland. 9. A. Outpatient procedure in most cases 10. B. Distention of the lower abdomen . This indicates that the bladder is distended with urine, therefore palpable. 11. A. “Have you noticed a change in the force of the urinary system?” This change would be most indicative of a potential complication with (BPH) benign prostate hypertrophy. 12. C. Report incomplete bladder emptying . Urinary retention is a common anticholinergic side effect of psychotic medications, and the client with benign prostatic hypertrophy would have increased risk for this problem. Adding fiber to one’s diet and exercising regularly are measures to counteract another anticholinergic effect, constipation. Depending on the specific medication and how it is prescribed, taking the medication at night may or may not be important. However, it would have nothing to do with urinary retention in this client. 13. A. Laser light exhibits all photons i phase (coherence) TEST 5 - BLADDER CANCER 1) A client with bladder cancer is being treated with iridium seed implants. The nurse’s discharge teaching should include telling the client to: 1. Strain his urine 2. Increase his fluid intake 3. Report urinary frequency 4. Avoid prolonged sitting 2) Aniline dyes have been linked to cancer 1. true 2. false 3) Does not respond at all to radiation 1. grade 2 2. grade 3 3. grade 1 4. grade 4 4) Occupational exposure to pizza making has been linked to bladder cancer 1. true 2. false 5) Toxicity levels are unacceptable if the patient is worse off then before treatment 1. true 2. false 6) Superficial bladder cancer can be treated by direct installation of the antineoplastic antibiotic agent mitomycin (Mutamycin). This process is termed: 1. Intraventricular administration 2. Intravesical administration 3. Intravascular administration 4. Intrathecal administration 7) very low degree of malignancy 1. grade 2 2. grade 3 3. grade 1 4. grade 4 8) A client has been diagnosed as having bladder cancer, and a cystectomy and an ileal conduit are scheduled. Preoperatively, the nurse plans to: 1. Limit fluid intake for 24 hours 2. Teach the procedure for irrigation of the stoma 3. Teach muscle-tightening exercises 4. Provide cleansing enemas and laxatives as ordered 9) anticholinergics 1. drugs that decrease bladder outlet resistance 2. drugs that simulate detrusor contractility and promote bladder emptying 3. drugs that inhibit contractility and promote urine storage 4. drugs that increase bladder outlet resistance 10) What is the most common type of Bladder Cancer? 1. Squamous Cell Carcinoma 2. Transistional cell carcinoma 3. Epithelial hyperplasia 11) Can coffee cause bladder tumors? 1. yes 2. no 12) How does bladder cancer rate on the most commonly occurring GU cancer in adults list? 1. 1st 2. 2nd 3. 4th 4. 8th 13) Well differentiated but fully malignant 1. grade 1 2. grade 2 3. grade 3 4. grade 4 14) Recurring UTI, N/V and leukopenia are all adverse reactions to Chemotherapy and what else is one? 1. fistula’s 2. BPH 3. Penile Prosthetic 4. nephrotoxicity 15) Beta-adrenergics 1. drugs that increase bladder outlet resistance 2. drugs that inhibit contractility and promote urine storage 3. drugs that simulate detrusor contractility and promote bladder emptying 4. drugs that decrease bladder outlet resistance 16) Response is poor to radiation 1. grade 3 2. grade 1 3. grade 2 4. grade 4 17) The female client who has been receiving radiation therapy for bladder cancer tells the nurse that it feels as if she is voiding through the vagina. The nurse interprets that the client may be experiencing: 1. Rupture of the bladder 2. The development of a vesicovaginal fistula 3. Extreme stress caused by the diagnosis of cancer 4. Altered perineal sensation as a side effect of radiation therapy 18) What would be a indication to use Chemotherapy? 1. complete resolution of abnormal serum tumor markers 2. location of tumor 3. chronic reflux 4. N/V 5. Recurring CIS 19) High degree of malignancy, usually anaplastic CA 1. grade 2 2. grade 1 3. grade 4 4. grade 3 20) Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) is 1. a poorly differentiated carcinoma often without any papillary growth 2. a benign proliferation of urothelium in response to inflammation or irritation 3. a type of malignancy that arises from the urothelial lining of the urinary tract 4. a cancerous growth on the urothelium causing disintegration of the bladder wall and urothelium. 21) What is a random bladder biopsy done for? 1. stage and grade verification 2. invasive 3. noninvasive 4. smaller tumors 5. stages T1-T4 22) From below what are symptoms of bladder cancer? (Choose answer that apply) 1. painful hematuria 2. frequency and urgency 3. dysuria 4. flank pain 5. abdominal pain 23) estrogens 1. drugs that simulate detrusor contractility and promote bladder emptying 2. drugs that increase bladder outlet resistance 3. drugs that decrease bladder outlet resistance 4. drugs that inhibit contractility and promote urine storage 24) drugs that decrease bladder outlet resistance 1. alpha-adrenergics blockers 2. Estrogens 3. beta-adrenergics 4. alpa-adrenergics 25) The health of the patient is a factor in deciding to use or not to use Chemo 1. true 2. false 26) Does respond to radiation 1. grade 3 2. grade 4 3. grade 2 4. grade 1 27) Beta-adrenergic blockers 1. drugs that increase bladder outlet resistance 2. drugs that decrease bladder outlet resistance 3. drugs that simulate detrusor contractility and promote bladder emptying 4. drugs that inhibit contractility and promote urine storage 28) Alpha-adrenergics 1. drugs that inhibit contractility and promote urine storage 2. drugs that decrease bladder outlet resistance 3. drugs that simulate detrusor contractility and promote bladder emptying 4. drugs that increase bladder outlet resistance 29) A male client is being transferred to the nursing unit for admission after receiving a radium implant for bladder cancer. The nurse in-charge would take which priority action in the care of this client? 1. Place client on reverse isolation. 2. Admit the client into a private room. 3. Encourage the client to take frequent rest periods. 4. Encourage family and friends to visit. 30) lowest degree of malignancy 1. grade 1 2. grade 2 3. grade 3 4. grade 4 31) Resistant 1. grade 1 2. grade 2 3. grade 3 4. grade 4 32) Cigarette smoking can cause bladder cancer, but at what ratio to non-smokers? 1. 3 times greater 2. 4 times greater 3. 5 times greater 4. 2 times greater 33) most frequent presenting symptom is? 1. painless hematuria 2. flank pain due to ureteral obstruction or pelvic mass 3. frequency 4. constipation 34) Occupational exposure to aromatic amines cannot cause cancer 1. true 2. false 35) How many grades of cancer are there? 1. 5 2. 4 3. 3 4. 6 5. 8 36) What percentage of bladder cancers does squamous cell carcinoma account for? 1. 3% 2. 5% 3. 50% 4. 95% 5. 75% 37) Mr. Pablo, diagnosed with Bladder Cancer, is scheduled for a cystectomy with the creation of an ileal conduit in the morning. He is wringing his hands and pacing the floor when the nurse enters his room. What is the best approach? 1. “Good evening, Mr. Pablo. Wasn’t it a pleasant day, today?” 2. “Mr, Pablo, you must be so worried, I’ll leave you alone with your thoughts. 3. “Mr. Pablo, you’ll wear out the hospital floors and yourself at this rate.” 4. “Mr. Pablo, you appear anxious to me. How are you feeling about tomorrow’s surgery?” 38) Tricyclic antidepressants 1. drugs that inhibit contractility and promote urine storage 2. drugs that increase bladder outlet resistance 3. drugs that simulate detrusor contractility and promote bladder emptying 4. drugs that decrease bladder outlet resistance 39) A male client with bladder cancer has had the bladder removed and an ileal conduit created for urine diversion. While changing this client’s pouch, the nurse observes that the area around the stoma is red, weeping, and painful. What should nurse Katrina conclude? 1. The skin wasn’t lubricated before the pouch was applied. 2. The pouch faceplate doesn’t fit the stoma. 3. A skin barrier was applied properly. 4. Stoma dilation wasn’t performed. 40) cholinergics 1. drugs that increase bladder outlet resistance 2. drugs that inhibit contractility and promote urine storage 3. drugs that simulate detrusor contractility and promote bladder emptying 4. drugs that decrease bladder outlet resistance 41) Drugs that inhibit contractility and promote urine storage 1. antispasmodics 2. alpha-adrenergics 3. cholinergics 4. external sphincter/striated muscle relaxant 42) A male client is receiving the cell cycle–nonspecific alkylating agent thiotepa (Thioplex), 60 mg weekly for 4 weeks by bladder instillation as part of a chemotherapeutic regimen to treat bladder cancer. The client asks the nurse how the drug works. How does thiotepa exert its therapeutic effects? 1. It interferes with deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) replication only. 2. It interferes with ribonucleic acid (RNA) transcription only. 3. It interferes with DNA replication and RNA transcription. 4. It destroys the cell membrane, causing lysis. 43) artificial sweeteners, pelvic irradiation and chronic cystitis can’t cause cancer 1. true 2. false 44) higher levels of toxicity are acceptable if the cure can be achieved? 1. true 2. false Answers and Rationales 1. A. Strain his urine . Iridium seeds can be expelled during urination, so the client should be taught to strain his urine and report to the doctor if any of the seeds are expelled. Increasing fluids, reporting urinary frequency, and avoiding prolonged sitting are not necessary 2. A. true 3. D. grade 4 4. B. false 5. A. true 6. B. Intravesical administration. Medications administered intravesically are instilled into the bladder. Intraventricular administration involves the ventricles of the brain. Intravascular administration involves blood vessels. Intrathecal administration involves the fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord. 7. A. grade 2 8. D. Provide cleansing enemas and laxatives as ordered 9. C. drugs that inhibit contractility and promote urine storage 10. B. Transistional cell carcinoma 11. A. yes 12. B. 2nd 13. C. grade 3 14. D. nephrotoxicity 15. B. drugs that inhibit contractility and promote urine storage 16. C. grade 2 17. B. The development of a vesicovaginal fistula. A vesicovaginal fistula is a genital fistula that occurs between the bladder and vagina. The fistula is an abnormal opening between these two body parts and, if this occurs, the client may experience drainage of urine through the vagina. 18. A. complete resolution of abnormal serum tumor markers, B. location of tumor 19. C. grade 4 20. C. a type of malignancy that arises from the urothelial lining of the urinary tract 21. A. stage and grade verification 22. B. frequency and urgency, C. dysuria, D. flank pain 23. B. drugs that increase bladder outlet resistance 24. A. alpha-adrenergics blockers 25. A. true 26. A. grade 3 27. A. drugs that increase bladder outlet resistance 28. D. drugs that increase bladder outlet resistance 29. B. Admit the client into a private room. The client who has a radiation implant is placed in a private room and has a limited number of visitors. This reduces the exposure of others to the radiation. 30. A. grade 1 31. A. grade 1 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. B. 4 times greater A. painless hematuria B. false B. 4 A. 3% D. “Mr. Pablo, you appear anxious to me. How are you feeling about tomorrow’s surgery?” The client is showing signs of anxiety reaction to a stressful event. Recognizing the client’s anxiety conveys acceptance of his behavior and will allow for verbalization of feelings and concerns. 38. A. drugs that inhibit contractility and promote urine storage 39. B. The pouch faceplate doesn’t fit the stoma. If the pouch faceplate doesn’t fit the stoma properly, the skin around the stoma will be exposed to continuous urine flow from the stoma, causing excoriation and red, weeping, and painful skin. A lubricant shouldn’t be used because it would prevent the pouch from adhering to the skin. When properly applied, a skin barrier prevents skin excoriation. Stoma dilation isn’t performed with an ileal conduit, although it may be done with a colostomy if ordered. 40. C. drugs that simulate detrusor contractility and promote bladder emptying 41. A. antispasmodics 42. C. It interferes with DNA replication and RNA transcription.Thiotepa interferes with DNA replication and RNA transcription. It doesn’t destroy the cell membrane. 43. B. false 44. A. true TEST 6 - CYSTITIS 1) The physician has prescribed Cytoxan (cyclophosphamide) for a client with nephotic syndrome. The nurse should: 1. Encourage the client to drink extra fluids 2. Request a low-protein diet for the client 3. Bathe the client using only mild soap and water 4. Provide additional warmth for swollen, inflamed joints 2) Symptoms of interstitial cystitis are similar to what other condition? 1. Bladder Cancer 2. Urinary Tract Infection 3. Tuberculosis of the bladder 4. Radition Cystisis 3) What test is used to diagnose interstitial cystitis? 1. Cystoscopy 2. Ultrasound of bladder 3. Biopsy 4. Urine culture 4) Which of the following may cause an increase in the cystitis symptoms? 1. Water 2. Orange juice 3. Coffee 4. Mango juice 5) Interstitial cystitis is a condition of which organ of the body? 1. Uterus 2. Bladder 3. Prostate 4. Colon 6) Which of the following terms is used to refer to inflammation of the renal pelvis? 1. Pyelonephritis 2. Cystitis 3. Urethritis 4. Interstitial nephritis 7) Over 700,000 Americans have interstitial cystitis. What causes the disease? 1. A defect 2. Autoimmune 3. The cause is unknown 4. Hereditary 8) Which of the following are the most commonly assessed findings in cystitis? 1. Frequency, urgency, dehydration, nausea, chills, and flank pain 2. Nocturia, frequency, urgency dysuria, hematuria, fever and suprapubic pain 3. Dehydration, hypertension, dysuria, suprapubic pain, chills, and fever 4. High fever, chills, flank pain nausea, vomiting, dysuria, and frequency 9) Interstitial cystitis affects whom? 1. Woman 2. Children 3. Men 4. All of these 10) Which of the following are the most commonly assessed findings in cystitis? 1. Frequency, urgency, dehydration, nausea, chills, and flank pain 2. Nocturia, frequency, urgency dysuria, hematuria, fever and suprapubic pain 3. Dehydration, hypertension, dysuria, suprapubic pain, chills, and fever 4. High fever, chills, flank pain nausea, vomiting, dysuria, and frequency Answers and Rationales 1. A. Encourage the client to drink extra fluids . The client taking Cytoxan should increase his fluid intake to prevent hemorrhagic cystitis. 2. B. Urinary Tract Infection. IC can have some similar symptoms of the incorrect answers but is most similar to a UTI. The biggest difference between them is that a UTI is caused by bacteria and treated with antibiotics. Since IC is not bacterial, antibiotics don’t help IC patients. The common symptoms are frequency of urination, urgency to urinate (accompanied by pain, pressure and/or spasms) Pain in the bladder, pelvic region, and/or urethral. IC patients have a wide variety of symptoms. Some have all the mentioned symptoms (plus other symptoms) while some have only a few. 3. A. Cystoscopy . A cystoscopy under general or regional anesthesia is to needed to check for glomerulations (pinpoint hemorrages) Before a cystoscopy there are other tests performed. Such as urine culture and potassium sensitivity test. It is not uncommon to suffer for years before receiving a diagnosis. 4. C. Coffee 5. B. Bladder. Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic inflammatory condition of the bladder wall. 6. A. Pyelonephritis . Pyelonephritis is an upper urinary tract inflammation, which may be acute or chronic. Cystitis is inflammation of the urinary bladder. Urethritis is inflammation of the urethra. Interstitial nephritis is inflammation of the kidney. 7. C. The cause is unknown. Researchers have yet to determine one specific cause. There are many theories that have been looked into. The one gaining the most attention in the medical community is a antiproliferative factor (APF) Which blocks the normal growth of cells in the bladder lining. APF is found almost exclusively in IC patients. Many other theories are out there such as; inflammatory response to injury, autoimmune disorder, undetected bacteria, and hereditary. 8. B. Nocturia, frequency, urgency dysuria, hematuria, fever and suprapubic pain. Manifestations of cystitis include, frequency, urgency, dysuria, hematuria nocturia, fever, and suprapubic pain. Dehydration, hypertension, and chills are not typically associated with cystitis. High fever chills, flank pain, nausea, vomiting, dysuria, and frequency are associated with pvelonephritis. 9. D. All of these . IC can affect people of any age, race or sex. Statics do show that 90% of cases are women. The average age of onset is 40. 10. B. Nocturia, frequency, urgency dysuria, hematuria, fever and suprapubic pain. Manifestations of cystitis include, frequency, urgency, dysuria, hematuria nocturia, fever, and suprapubic pain. Dehydration, hypertension, and chills are not typically associated with cystitis. High fever chills, flank pain, nausea, vomiting, dysuria, and frequency are associated with pvelonephritis. TEST 7 - KIDNEY STONES, BLADDER CANCER AND PROSTATE DISORDERS 1. A client is complaining of severe flank and abdominal pain. A flat plate of the abdomen shows urolithiasis. Which of the following interventions is important? 1. Strain all urine 2. Limit fluid intake 3. Enforce strict bed rest 4. Encourage a high calcium diet 2. A client is receiving a radiation implant for the treatment of bladder cancer. Which of the following interventions is appropriate? 1. Flush all urine down the toilet 2. Restrict the client’s fluid intake 3. Place the client in a semi-private room 4. Monitor the client for signs and symptoms of cystitis 3. A client has just received a renal transplant and has started cyclosporine therapy to prevent graft rejection. Which of the following conditions is a major complication of this drug therapy? 1. Depression 2. Hemorrhage 3. Infection 4. Peptic ulcer disease 4. A client received a kidney transplant 2 months ago. He’s admitted to the hospital with the diagnosis of acute rejection. Which of the following assessment findings would be expected? 1. Hypotension 2. Normal body temperature 3. Decreased WBC count 4. Elevated BUN and creatinine levels 5. The client is to undergo kidney transplantation with a living donor. Which of the following preoperative assessments is important? 1. Urine output 2. Signs of graft rejection 3. Signs and symptoms of rejection 4. Client’s support system and understanding of lifestyle changes. 6. A client had a transurethral prostatectomy for benign prostatic hypertrophy. He’s currently being treated with a continuous bladder irrigation and is complaining of an increase in severity of bladder spasms. Which of the interventions should be done first? 1. Administer an oral analgesic 2. Stop the irrigation and call the physician 3. Administer a belladonna and opium suppository as ordered by the physician. 4. Check for the presence of clots, and make sure the catheter is draining properly. 7. A client is admitted with a diagnosis of hydronephrosis secondary to calculi. The calculi have been removed and postobstructive diuresis is occurring. Which of the following interventions should be done? 1. Take vital signs every 8 hours 2. Weigh the client every other day 3. Assess for urine output every shift 4. Monitor the client’s electrolyte levels. 8. A client has passed a renal calculus. The nurse sends the specimen to the laboratory so it can be analyzed for which of the following factors? 1. Antibodies 2. Type of infection 3. Composition of calculus 4. Size and number of calculi 9. Which of the following symptoms indicate acute rejection of a transplanted kidney? 1. Edema, nausea 2. Fever, anorexia 3. Weight gain, pain at graft site 4. Increased WBC count, pain with voiding 10. Adverse reactions of prednisone therapy include which of the following conditions? 1. Acne and bleeding gums 2. Sodium retention and constipation 3. Mood swings and increased temperature 4. Increased blood glucose levels and decreased wound healing. 11. The nurse suspects that a client with polyuria is experiencing water diuresis. Which laboratory value suggests water diuresis? 1. High urine specific gravity 2. High urine osmolarity 3. Normal to low urine specific gravity 4. Elevated urine pH 12. A client is diagnosed with prostate cancer. Which test is used to monitor progression of this disease? 1. Serum creatinine 2. Complete blood cell count (CBC) 3. Prostate specific antigen (PSA) 4. Serum potassium 13. a 27-year old client, who became paraplegic after a swimming accident, is experiencing autonomic dysreflexia. Which condition is the most common cause of autonomic dysrelexia? 1. Upper respiratory infection 2. Incontinence 3. Bladder distention 4. Diarrhea 14. When providing discharge teaching for a client with uric acid calculi, the nurse should an instruction to avoid which type of diet? 1. Low-calcium 2. Low-oxalate 3. High-oxalate 4. High-purine 15. The client with urolithiasis has a history of chronic urinary tract infections. The nurse concludes that this client most likely has which of the following types of urinary stones? 1. Calcium oxalate 2. Uric acid 3. Struvite 4. Cystine 16. The nurse is receiving in transfer from the postanesthesia care unit a client who has had a percutaneous ultrasonic lithrotripsy for calculuses in the renal pelvis. The nurse anticipates that the client’s care will involve monitoring which of the following? 1. Suprapubic tube 2. Urethral stent 3. Nephrostomy tube 4. Jackson-Pratt drain 17. The client is admitted to the ER following a MVA. The client was wearing a lap seat belt when the accident occurred. The client has hematuria and lower abdominal pain. To determine further whether the pain is due to bladder trauma, the nurse asks the client if the pain is referred to which of the following areas? 1. Shoulder 2. Umbilicus 3. Costovertebral angle 4. Hip 18. The client complains of fever, perineal pain, and urinary urgency, frequency, and dysuria. To assess whether the client’s problem is related to bacterial prostatitis, the nurse would look at the results of the prostate examination, which should reveal that the prostate gland is: 1. Tender, indurated, and warm to the touch 2. Soft and swollen 3. Tender and edematous with ecchymosis 4. Reddened, swollen, and boggy. 19. The nurse is taking the history of a client who has had benign prostatic hyperplasia in the past. To determine whether the client currently is experiencing difficulty, the nurse asks the client about the presence of which of the following early symptoms? 1. Urge incontinence 2. Nocturia 3. Decreased force in the stream of urine 4. Urinary retention 20. The client who has a cold is seen in the emergency room with inability to void. Because the client has a history of BPH, the nurse determines that the client should be questioned about the use of which of the following medications? 1. Diuretics 2. Antibiotics 3. Antitussives 4. Decongestants 21. The nurse is preparing to care for the client following a renal scan. Which of the following would the nurse include in the plan of care? 1. Place the client on radiation precautions for 18 hours 2. Save all urine in a radiation safe container for 18 hours 3. Limit contact with the client to 20 minutes per hour. 4. No special precautions except to wear gloves if in contact with the client’s urine. 22. The client passes a urinary stone, and lab analysis of the stone indicates that it is composed of calcium oxalate. Based on this analysis, which of the following would the nurse specifically include in the dietary instructions? 1. Increase intake of meat, fish, plums, and cranberries 2. Avoid citrus fruits and citrus juices 3. Avoid green, leafy vegetables such as spinach. 4. Increase intake of dairy products. 23. The client returns to the nursing unit following a pyelolithotomy for removal of a kidney stone. A Penrose drain is in place. Which of the following would the nurse include on the client’s postoperative care? 1. Sterile irrigation of the Penrose drain 2. Frequent dressing changes around the Penrose drain 3. Weighing the dressings 4. Maintaining the client’s position on the affected side 24. The nurse is caring for a client following a kidney transplant. The client develops oliguria. Which of the following would the nurse anticipate to be prescribed as the treatment of oliguria? 1. Encourage fluid intake 2. Administration of diuretics 3. Irrigation of foley catheter 4. Restricting fluids 25. A week after kidney transplantation the client develops a temperature of 101, the blood pressure is elevated, and the kidney is tender. The x-ray results the transplanted kidney is enlarged. Based on these assessment findings, the nurse would suspect which of the following? 1. Acute rejection 2. Chronic rejection 3. Kidney infection 4. Kidney obstruction 26. The client with BPH undergoes a transurethral resection of the prostate. Postoperatively, the client is receiving continuous bladder irrigations. The nurse assesses the client for signs of transurethral resection syndrome. Which of the following assessment data would indicate the onset of this syndrome? 1. Bradycardia and confusion 2. Tachycardia and diarrhea 3. Decreased urinary output and bladder spasms 4. Increased urinary output and anemia 27. The client is admitted to the hospital with BPH, and a transurethral resection of the prostate is performed. Four hours after surgery the nurse takes the client’s VS and empties the urinary drainage bag. Which of the following assessment findings would indicate the need to notify the physician? 1. Red bloody urine 2. Urinary output of 200 ml greater than intake 3. Blood pressure of 100/50 and pulse 130. 4. Pain related to bladder spasms. 28. Which of the following symptoms is the most common clinical finding associated with bladder cancer? 1. Suprapubic pain 2. Dysuria 3. Painless hematuria 4. Urinary retention 29. A client who has been diagnosed with bladder cancer is scheduled for an ileal conduit. Preoperatively, the nurse reinforces the client’s understanding of the surgical procedure by explaining that an ileal conduit: 1. Is a temporary procedure that can be reversed later. 2. Diverts urine into the sigmoid colon, where it is expelled through the rectum. 3. Conveys urine from the ureters to a stoma opening in the abdomen. 4. Creates an opening in the bladder that allows urine to drain into an external pouch. 30. After surgery for an ileal conduit, the nurse should closely evaluate the client for the occurrence of which of the following complications related to pelvic surgery? 1. Peritonitis 2. Thrombophlebitis 3. Ascites 4. Inguinal hernia 31. The nurse is assessing the urine of a client who has had an ileal conduit and notes that the urine is yellow with a moderate amount of mucus. Based on the assessment data, which of the following nursing interventions would be most appropriate at this time? 1. Change the appliance bag 2. Notify the physician 3. Obtain a urine specimen for culture 4. Encourage a high fluid intake 32. When teaching the client to care for an ileal conduit, the nurse instructs the client to empty the appliance frequently, primarily to prevent which of the following problems? 1. Rupture of the ileal conduit 2. Interruption of urine production 3. Development of odor 4. Separation of the appliance from the skin 33. The client with an ileal conduit will be using a reusable appliance at home. The nurse should teach the client to clean the appliance routinely with what product? 1. Baking soda 2. Soap 3. Hydrogen peroxide 4. Alcohol 34. The nurse is evaluating the discharge teaching for a client who has an ileal conduit. Which of the following statements indicates that the client has correctly understood the teaching? Select all that apply. 1. “If I limit my fluid intake I will not have to empty my ostomy pouch as often.” 2. “I can place an aspirin tablet in my pouch to decrease odor.” 3. “I can usually keep my ostomy pouch on for 3 to 7 days before changing it.” 4. “I must use a skin barrier to protect my skin from urine.” 5. “I should empty my ostomy pouch of urine when it is full.” 35. A female client with a urinary diversion tells the nurse, “This urinary pouch is embarrassing. Everyone will know that I’m not normal. I don’t see how I can go out in public anymore.” The most appropriate nursing diagnosis for this patient is: 1. Anxiety related to the presence of urinary diversion. 2. Deficient Knowledge about how to care for the urinary diversion. 3. Low Self-Esteem related to feelings of worthlessness 4. Disturbed Body Image related to creation of a urinary diversion. 36. The nurse teaches the client with a urinary diversion to attach the appliance to a standard urine collection bag at night. The most important reason for doing this is to prevent: 1. Urine reflux into the stoma 2. Appliance separation 3. Urine leakage 4. The need to restrict fluids 37. The nurse teaches the client with an ileal conduit measures to prevent a UTI. Which of the following measures would be most effective? 1. Avoid people with respiratory tract infections 2. Maintain a daily fluid intake of 2,000 to 3,000 ml 3. Use sterile technique to change the appliance 4. Irrigate the stoma daily. 38. A client who has been diagnosed with calculi reports that the pain is intermittent and less colicky. Which of the following nursing actions is most important at this time? 1. Report hematuria to the physician 2. Strain the urine carefully 3. Administer meperidine (Demerol) every 3 hours 4. Apply warm compresses to the flank area 39. A client has a ureteral catheter in place after renal surgery. A priority nursing action for care of the ureteral catheter would be to: 1. Irrigate the catheter with 30 ml of normal saline every 8 hours 2. Ensure that the catheter is draining freely 3. Clamp the catheter every 2 hours for 30 minutes. 4. Ensure that the catheter drains at least 30 ml an hour 40. Which of the following interventions would be most appropriate for preventing the development of a paralytic ileus in a client who has undergone renal surgery? 1. Encourage the client to ambulate every 2 to 4 hours 2. Offer 3 to 4 ounces of a carbonated beverage periodically. 3. Encourage use of a stool softener 4. Continue intravenous fluid therapy 41. The nurse is conducting a postoperative assessment of a client on the first day after renal surgery. Which of the following findings would be most important for the nurse to report to the physician? 1. Temperature, 99.8 2. Urine output, 20 ml/hour 3. Absence of bowel sounds 4. A 2×2 inch area of serous sanguineous drainage on the flank dressing. 42. Because a client’s renal stone was found to be composed to uric acid, a low-purine, alkaline-ash diet was ordered. Incorporation of which of the following food items into the home diet would indicate that the client understands the necessary diet modifications? 1. Milk, apples, tomatoes, and corn 2. Eggs, spinach, dried peas, and gravy. 3. Salmon, chicken, caviar, and asparagus 4. Grapes, corn, cereals, and liver. 43. Allopurinol (Zyloprim), 200 mg/day, is prescribed for the client with renal calculi to take home. The nurse should teach the client about which of the following side effects of this medication? 1. Retinopathy 2. Maculopapular rash 3. Nasal congestion 4. Dizziness 44. The client has a clinic appointment scheduled 10 days after discharge. Which laboratory finding at that time would indicate that allopurinol (Zyloprim) has had a therapeutic effect? 1. Decreased urinary alkaline phosphatase level 2. Increased urinary calcium excretion 3. Increased serum calcium level 4. Decreased serum uric acid level 45. When developing a plan of care for the client with stress incontinence, the nurse should take into consideration that stress incontinence is best defined as the involuntary loss of urine associated with: 1. A strong urge to urinate 2. Overdistention of the bladder 3. Activities that increase abdominal pressure 4. Obstruction of the urethra 46. Which of the following assessment data would most likely be related to a client’s current complaint of stress incontinence? 1. The client’s intake of 2 to 3 L of fluid per day. 2. The client’s history of three full-term pregnancies 3. The client’s age of 45 years 4. The client’s history of competitive swimming 47. The nurse is developing a teaching plan for a client with stress incontinence. Which of the following instructions should be included? 1. Avoid activities that are stressful and upsetting 2. Avoid caffeine and alcohol 3. Do not wear a girdle 4. Limit physical exertion 48. A client has urge incontinence. Which of the following signs and symptoms would the nurse expect to find in this client? 1. Inability to empty the bladder 2. Loss of urine when coughing 3. Involuntary urination with minimal warning 4. Frequent dribbling of urine 49. A 72-year old male client is brought to the emergency room by his son. The client is extremely uncomfortable and has been unable to void for the past 12 hours. He has known for some time that he has an enlarged prostate but has wanted to avoid surgery. The best method for the nurse to use when assessing for bladder distention in a male client is to check for: 1. A rounded swelling above the pubis. 2. Dullness in the lower left quadrant 3. Rebound tenderness below the symphysis 4. Urine discharge from the urethral meatus 50. During a client’s urinary bladder catherization, the bladder is emptied gradually. The best rationale for the nurse’s action is that completely emptying an overdistended bladder at one time tends to cause: 1. Renal failure 2. Abdominal cramping 3. Possible shock 4. Atrophy of bladder musculature 51. The primary reason for taping an indwelling catheter laterally to the thigh of a male client is to: 1. Eliminate pressure at the penoscrotal angle 2. Prevent the catheter from kinking in the urethra 3. Prevent accidental catheter removal 4. Allow the client to turn without kinking the catheter 52. The primary function of the prostate gland is: 1. To store underdeveloped sperm before ejaculation 2. To regulate the acidity and alkalinity of the environment for proper sperm development. 3. To produce a secretion that aids in the nourishment and passage of sperm 4. To secrete a hormone that stimulates the production and maturation of sperm 53. The nurse is reviewing a medication history of a client with BPH. Which medication should be recognized as likely to aggravate BPH? 1. Metformin (Glucophage) 2. Buspirone (BuSpar) 3. Inhaled ipratropium (Atrovent) 4. Ophthalmic timolol (Timoptic) 54. A client is scheduled to undergo a transurethral resection of the prostate gland (TURP). The procedure is to be done under spinal anesthesia. Postoperatively, the nurse should be particularly alert for early signs of: 1. Convulsions 2. Cardiac arrest 3. Renal shutdown 4. Respiratory paralysis 55. A client with BPH is being treated with terazosin (Hytrin) 2mg at bedtime. The nurse should monitor the client’s: 1. Urinary nitrites 2. White blood cell count 3. Blood pressure 4. Pulse 56. A client underwent a TURP, and a large three way catheter was inserted in the bladder with continuous bladder irrigation. In which of the following circumstances would the nurse increase the flow rate of the continuous bladder irrigation? 1. When the drainage is continuous but slow 2. When the drainage appears cloudy and dark yellow 3. When the drainage becomes bright red 4. When there is no drainage of urine and irrigating solution 57. A priority nursing diagnosis for the client who is being discharged t home 3 days after a TURP would be: 1. Deficient fluid volume 2. Imbalanced Nutrition: Less than Body Requirements 3. Impaired Tissue Integrity 4. Ineffective Airway Clearance 58. If a client’s prostate enlargement is caused by a malignancy, which of the following blood examinations should the nurse anticipate to assess whether metastasis has occurred? 1. Serum creatinine level 2. Serum acid phosphatase level 3. Total nonprotein nitrogen level 4. Endogenous creatinine clearance time 59. Steroids, if used following kidney transplantation would cause which of the following side effects? 1. Alopecia 2. Increase Cholesterol Level 3. Orthostatic Hypotension 4. Increase Blood Glucose Level 60. Mr. Roberto was readmitted to the hospital with acute graft rejection. Which of the following assessment finding would be expected? 1. Hypotension 2. Normal Body Temperature 3. Decreased WBC 4. Elevated BUN and Creatinine Answers and Rationales 1. A. Urine should be strained for calculi and sent to the lab for analysis. Fluid intake of 3 to 4 L is encouraged to flush the urinary tract and prevent further calculi formation. A low-calcium diet is 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. recommended to help prevent the formation of calcium calculi. Ambulation is encouraged to help pass the calculi through gravity. D. Cystitis is the most common adverse reaction of clients undergoing radiation therapy; symptoms include dysuria, frequency, urgency, and nocturia. Clients with radiation implants require a private room. Urine of clients with radiation implants for bladder cancer should be sent to the radioisotopes lab for monitoring. It is recommended that fluid intake be increased. C. Infections is the major complication to watch for in clients on cyclosporine therapy because it’s an immunosuppressive drug. Depression may occur posttransplantation but not because of cyclosporine. Hemorrhage is a complication associated with anticoagulant therapy. Peptic ulcer disease is a complication of steroid therapy. D. In a client with acute renal graft rejection, evidence of deteriorating renal function is expected. The nurse would see elevated WBC counts and fever because the body is recognizing the graft as foreign and is attempting to fight it. The client would most likely have acute hypertension. D. The client undergoing a renal transplantation will need vigilant follow-up care and must adhere to the medical regimen. The client is most likely anuric or oliguric preoperatively, but postoperatively will require close monitoring of urine output to make sure the transplanted kidney is functioning optimally. While the client will always need to be monitored for signs and symptoms of infection, it’s most important post-op will require close monitoring of urine output to make sure the transplanted kidney is functioning optimally. While the client will always need to be monitored for signs and symptoms of infection, it’s most important postoperatively due to the immunosuppressant therapy. Rejection can occur postoperatively. D. Blood clots and blocked outflow if the urine can increase spasms. The irrigation shouldn’t be stopped as long as the catheter is draining because clots will form. A belladonna and opium suppository should be given to relieve spasms but only afterassessment of the drainage. Oral analgesics should be given if the spasms are unrelieved by the belladonna and opium suppository. D. Postobstructive diuresis seen in hydronephrosis can cause electrolyte imbalances; lab values must be checked so electrolytes can be replaced as needed. VS should initially be taken every 30 minutes for the first 4 hours and then every 2 hours. Urine output needs to be assessed hourly. The client’s weight should be taken daily to assess fluid status more closely. C. The calculus should be analyzed for composition to determine appropriate interventions such as dietary restrictions. Calculi don’t result in infections. The size and number of calculi aren’t relevant, and they don’t contain antibodies. C. Pain at the graft site and weight gain indicates the transplanted kidney isn’t functioning and possibly is being rejected. Transplant clients usually have edema, anorexia, fever, and nausea before transplantation, so those symptoms may not indicate rejection. D. Steroid use tends to increase blood glucose levels, particularly in clients with diabetes and borderline diabetes. Steroids also contribute to poor wound healing and may cause acne, mood swings, and sodium and water retention. Steroids don’t affect thermoregulation, bleeding tendencies, or constipation. C. Water diuresis causes low urine specific gravity, low urine osmolarity, and a normal to elevated serum sodium level. High specific gravity indicates dehydration. Hypernatremia signals acidosis and shock. Elevated urine pH can result from potassium deficiency, a high-protein diet, or uncontrolled diabetes. C. The PSA test is used to monitor prostate cancer progression; higher PSA levels indicate a greater tumor burden. Serum creatinine levels may suggest blockage from an enlarged prostate. CBC is used to diagnose anemia and polycythemia. Serum potassium levels identify hypokalemia and hyperkalemia. C. Autonomic dysreflexia is a potentially life-threatening complication of spinal cord injury, occurring from obstruction of the urinary system or bowel. Incontinence and diarrhea don’t result in obstruction of the urinary system or bowel, respectively. An URI could obstruct the respiratory system, but not the urinary or bowel system. 14. D. To control uric acid calculi, the client should follow a low-purine diet, which excludes high-purine foods such as organ meats. A low-calcium diet decreases the risk for oxalate renal calculi. Oxalate is an essential amino acid and must be included in the diet. A low-oxalate diet is used to control calcium or oxalate calculi. 15. C. Struvite stones commonly are referred to as infection stones because they form in urine that is alkaline and rich in ammonia, such as with a urinary tract infection. Calcium oxalate stones result from increased calcium intake or conditions that raise serum calcium concentrations. Uric acid stones occur in clients with gout. Cystine stones are rare and occur in clients with a genetic defect that results in decreased renal absorption of the amino acid cystine. 16. C. A nephrostomy tube is put in place after a percutaneous ultrasonic lithotripsy to treat calculuses in the renal pelvis. The client may also have a foley catheter to drain urine produced by the other kidney. The nurse monitors the drainage from each of these tubes and strains the urine to detect elimination of the calculus fragments. 17. A. Bladder trauma or injury is characterized by lower abdominal pain that may radiate to one of the shoulders. Bladder injury pain does not radiate to the umbilicus, CV angle, or hip. 18. A. The client with prostatitis has a prostate gland that is swollen and tender but that is also warm to the touch, firm, and indurated. Systemic symptoms include fever with chills, perineal and low back pain, and signs of urinary tract infection (which often accompany the disorder). 19. C. Decreased force in the stream of urine is an early sign of BPH. The stream later becomes weak and dribbling. The client then may develop hematuria, frequency, urgency, urge incontinence, and nocturia. If untreated, complete obstruction and urinary retention can occur. 20. D. In the client with BPH, episodes of urinary retention can be triggered by certain medications, such as decongestants, anticholinergics, and antidepressants. The client should be questioned about the use of these medications if the client has urinary retention. Retention can also be precipitated by other factors, such as alcoholic beverages, infection, bedrest, and becoming chilled. 21. D. No specific precautions are necessary following a renal scan. Urination into a commode is acceptable without risk from the small amount of radioactive material to be excreted. The nurse wears gloves to maintain body secretion precautions. 22. C. Oxalate is found in dark green foods such as spinach. Other foods that raise urinary oxalate are rhubarb, strawberries, chocolate, wheat bran, nuts, beets, and tea. 23. B. Frequent dressing changes around the Penrose drain is required to protect the skin against breakdown from urinary drainage. If urinary drainage is excessive, an ostomy pouch may be placed over the drain to protect the skin. A Penrose drain is not irrigated. Weighing the dressings is not necessary. Placing the client on the affected side will prevent a free flow of urine through the drain. 24. B. To increase urinary output, diuretics and osmotic agents are considered. The client should be monitored closely because fluid overload can cause hypertension, congestive heart failure, and pulmonary edema. Fluid intake would not be encouraged or restricted. Irrigation of the foley catheter will not assist in allievating this oliguria. 25. A. Acute rejection most often occurs in the first 2 weeks after transplant. Clinical manifestations include fever, malaise, elevated WBC count, acute hypertension, graft tenderness, and manifestations of deteriorating renal function. Chronic rejection occurs gradually during a period of months to years. Although kidney infection or obstruction can occur, the symptoms presented in the question do not relate specifically to these disorders. 26. A. Transurethral resection syndrome is caused by increased absorption of nonelectrolyte irrigating fluid used during surgery. The client may show signs of cerebral edema and increased intracranial pressure such as increased blood pressure, bradycardia, confusion, disorientation, muscle twitching, visual disturbances, and nausea and vomiting. 27. C. Frank bleeding (arterial or venous) may occur during the first few days after surgery. Some hematuria is usual for several days 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. after surgery. A urinary output of 200 ml of greater than intake is adequate. Bladder spasms are expected to occur after surgery. A rapid pulse with a low blood pressure is a potential sign of excessive blood loss. The physician should be notified. C. Painless hematuria is the most common clinical finding in bladder cancer. Other symptoms include frequency, dysuria, and urgency, but these are not as common as the hematuria. Suprapubic pain and urinary retention do not occur in bladder cancer. C. An ileal conduit is a permanent urinary diversion in which a portion of the ileum is surgically resected and one end of the segment is closed. The ureters are surgically attached to this segment of the ileum, and the open end of the ileum is brought to the skin surface on the abdomen to form the stoma. The client must wear a pouch to collect the urine that continually flows through the conduit. The bladder is removed during the surgical procedure and the ileal conduit is not reversible. Diversion of the urine to the sigmoid colon is called a ureteroileosigmoidostomy. An opening in the bladder that allows urine to drain externally is called a cystostomy. B. After pelvic surgery, there is an increased chance of thrombophlebitis owing to the pelvic manipulation that can interfere with circulation and promote venous stasis. Peritonitis is a potential complication of any abdominal surgery, not just pelvic surgery. Ascites is most frequently an indication of liver disease. Inguinal hernia may be caused by an increase in abdominal pressure or a congenital weakness of the abdominal wall; ventral hernia occurs at the site of a previous abdominal surgery. D. Mucus is secreted by the intestinal segment used to create the conduit and is a normal occurrence. The client should be encouraged to maintain a large fluid intake to help flush the mucus out of the conduit. Because mucus in the urine is expected, it is not necessary to change the appliance bag or notify the physician. The mucus is not an indication of an infection, so a urine culture is not necessary. D. If the appliance becomes too full, it is likely to pull away from the skin completely or to leak urine onto the skin. A full appliance will not rupture the ileal conduit or interrupt urine production. Odor formation has numerous causes. B. A reusable appliance should be routinely cleaned with soap and water. C, D. The client with an ileal conduit must learn self-care activities related to care of the stoma and ostomy appliances. The client should be taught to increase fluid intake to about 3,000 ml per day and should not limit intake. Adequate fluid intake helps to flush mucus from the ileal conduit. The ostomy appliance should be changed approximately every 3 to 7 days and whenever a leak develops. A skin barrier is essential to protecting the skin from the irritation of the urine. An aspirin should not be used as a method of odor control because it can be an irritant to the stoma and lead to ulceration. The ostomy pouch should be emptied when it is one-third to one-half full to prevent the weight from pulling the appliance away from the skin. D. It is normal for clients to express fears and concerns about the body changes associated with a urinary diversion. Allowing the client time to verbalize concerns in a supportive environment and suggest that she discuss these concerns with people who have successfully adjusted to ostomy surgery can help her begin coping with these changes in a positive manner. Although the client may be anxious about this situation and self-esteem may be diminished, the underlying problem is disturbance in body image. There are no data to support a diagnosis of Deficient Knowledge. A. The most important reason for attaching the appliance to a standard urine collection bag at night is to prevent reflux into the stoma and ureters, which can result in infection. Use of a standard collection bag also keeps the appliance from separating from the skin and helps prevent urine leakage from an overly full bag, but the primary purpose is to prevent reflux of urine. A client with a urinary diversion should drink 2000-3000 ml of fluid each day; it would be inappropriate to suggest decreasing fluid intake. B. Maintaining a fluid intake of 2,000 to 3,000 ml/day is likely to be effective in preventing UTI. A high fluid intake results in high urine output, which prevents urinary stasis and bacterial growth. Avoiding people with respiratory tract infections will not prevent 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. urinary tract infections. Clean, not sterile, technique is used to change the appliance. An ileal conduit stoma is not irrigated. B. Intermittent pain that is less colicky indicates that the calculi may be moving along the urinary tract. Fluids should be encouraged to promote movement, and the urine should be strained to detect passage of the stone. Hematuria is to be expected from the irritation of the stone. Analgesics should be administered when the client needs them, not routinely. Moist heat to the flank area is helpful when renal colic occurs, but it is less necessary as pain is lessened. B. The ureteral catheter should drain freely without bleeding at the site. The catheter is rarely irrigated, and any irrigation would be done by the physician. The catheter is never clamped. The client’s total urine output (ureteral catheter plus voiding or foley catheter output) should be 30 ml/hour. A. Ambulation stimulates peristalsis. A client with paralytic ileus is kept NPO until peristalsis returns. Intravenous fluid infusion is a routine postoperative order that does not have any effect on preventing paralytic ileus. A stool softener will not stimulate peristalsis. B. The decrease in urinary output may indicate inadequate renal perfusion and should be reported immediately. Urine output of 30 ml/hour or greater is considered acceptable. A slight elevation in temperature is expected after surgery. Peristalsis returns gradually, usually the second or third day after surgery. Bowel sounds will be absent until then. A small amount of serous sanguineous drainage is to be expected. A. Because a high-purine diet contributes to the formation of uric acid, a low-purine diet is advocated. An alkaline-ash diet is also advocated, because uric acid crystals are more likely to develop in acid urine. Foods that may be eaten as desired in a low-purine diet include milk, all fruits, tomatoes, cereals, and corn. Food allowed on an alkaline-ash diet include milk, fruits (except cranberries, plums, and prunes), and vegetables (especially legumes and green vegetables). Gravy, chicken, and liver are high in purine. B. Allopurinol is used to treat renal calculi composed of uric acid. Side effects of allopurinol include drowsiness, maculopapular rash, anemia, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and bone marrow depression. Clients should be instructed to report skin rashes and any unusual bleeding or bruising. Retinopathy, nasal congestion, and dizziness are not side effects of allopurinol. D. By inhibiting uric acid synthesis, allopurinol decreases its excretion. The drug’s effectiveness is assessed by evaluating for a decreased serum uric acid concentration. Allopurinol does not alter the level of alkaline phosphatase, not does it affect urinary calcium excretion or the serum calcium level. C. Stress incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine during such activities as coughing, sneezing, laughing, or physical exertion. These activities increase abdominal and detrusor pressure. A strong urge to urinate is associated with urge incontinence. Overdistention of the bladder can lead to overflow incontinence. Obstruction of the urethra can lead to urinary retention. B. The history of three pregnancies is most likely the cause of the client’s current episodes of stress incontinence. The client’s fluid intake, age, or history of swimming would not create an increase in intra-abdominal pressure. B. Client’s with stress incontinence are encouraged to avoid substances such as caffeine and alcohol which are bladder irritants. Emotional stressors do not cause stress incontinence. It is caused most commonly be relaxed pelvic musculature. Wearing girdles is not contraindicated. Although clients may be inclined to limit physical exertion to avoid incontinence episodes, they should be encouraged to seek treatment instead of limiting their activities. C. A characteristic of urge incontinence is involuntary urination with little or no warning. The inability to empty the bladder is urinary retention. Loss of urine when coughing occurs with stress incontinence. Frequent dribbling of urine is common in male clients after some types of prostate surgery or may occur in women after the development of vesicovaginal or urethrovaginal fistula. A. The best way to assess for a distended bladder in either a male or female client is to check for a rounded swelling above the pubis. The swelling represents the distended bladder rising above the pubis into the abdominal cavity. Dullness does not indicate a distended bladder. The client might experience tenderness or pressure above the symphysis. No urine discharge is expected; the urine flow is blocked by the enlarged prostate. 50. C. Rapid emptying of an overdistended bladder may cause hypotension and shock due to the sudden change of pressure within the abdominal viscera. Previously, removing no more than 1,000 ml at one time was the standard of practice, but this is no longer thought to be necessary as long as the overdistended bladder is emptied slowly. 51. A. The primary reason for taping an indwelling catheter to a male client soothe penis is held in a lateral position to prevent pressure at the penoscrotal angle. Prolonged pressure at the penoscrotal angle can cause a urethrocutaneous fistula. 52. C. The prostate gland is located below the bladder and surrounds the urethra. It serves one primary purpose: to produce a secretion that aids in the nourishment and passage of sperm. 53. C. Atrovent is a bronchodilator, and its anticholinergic effects can aggravate urinary retention. Glucophage and BuSpar do not affect the urinary system; timolol does not have a systemic effect. 54. D. If paralysis of vasomotor nerves in the upper spinal cord occurs when spinal anesthesia is used, the client is likely to develop respiratory paralysis. Artificial ventilation is required until the effects of the anesthesia subside. Convulsions, cardiac arrest, and renal shutdown are not likely results of spinal anesthesia. 55. C. Terazosin (Hytrin) is an antihypertensive drug that is also used in the treatment of BPH. Blood pressure must be monitored to ensure that the client does not develop hypotension, syncope, or postural hypotension. The client should be instructed to change positions slowly. Urinary nitrites, white blood cell count, and pulse rate are not affected by terazosin. 56. C. The decision made by the surgeon to insert a catheter after a TURP or prostatectomy depends on the amount of bleeding that is expected after the procedure. During continuous bladder irrigation after a TURP or prostatectomy, the rate at which the solution enters the bladder should be increased when the drainage becomes brighter red. The color indicates the presence of blood. Increasing the flow of irrigating solution helps flush the catheter well so clots do not plug it. There would be no reason to increase the flow rate when the return is continuous or when the return appears cloudy and dark yellow. Increasing the flow would be contraindicated when there is no return of urine and irrigating solution. 57. A. Deficient Fluid Volume is a priority diagnosis, because the client needs to drink a large amount of fluid to keep the urine clear. The urine should be almost without color. About 2 weeks after a TURP, when desiccated tissue is sloughed out, a secondary hemorrhage could occur. The client should be instructed to call the surgeon or go to the ED if at any time the urine turns bright red. The client is not specifically at risk for nutritional problems after a TURP. The client is not specifically at risk for impaired tissue integrity because there is no external incision, and the client is not specifically at risk for airway problems because the procedure is done after spinal anesthesia. 58. B. The most specific examination to determine whether a malignancy extends outside of the prostatic capsule is a study of the serum acid phosphatase level. The level increases when a malignancy has metastasized. The prostate specific antigen (PSA) determination and a digital rectal examination are done when screening for prostate cancer. Serum creatinine level, total nonprotein nitrogen level, and endogenous creatinine clearance time give information about kidney function, not prostate malignancy. 59. D. 60. D. TEST 8 - RENAL FAILURE AND DIALYSIS 1. Dialysis allows for the exchange of particles across a semipermeable membrane by which of the following actions? 1. Osmosis and diffusion 2. Passage of fluid toward a solution with a lower solute concentration 3. Allowing the passage of blood cells and protein molecules through it. 4. Passage of solute particles toward a solution with a higher concentration. 2. A client is diagnosed with chronic renal failure and told she must start hemodialysis. Client teaching would include which of the following instructions? 1. Follow a high potassium diet 2. Strictly follow the hemodialysis schedule 3. There will be a few changes in your lifestyle. 4. Use alcohol on the skin and clean it due to integumentary changes. 3. A client is undergoing peritoneal dialysis. The dialysate dwell time is completed, and the dwell clamp is opened to allow the dialysate to drain. The nurse notes that the drainage has stopped and only 500 ml has drained; the amount the dialysate instilled was 1,500 ml. Which of the following interventions would be done first? 1. Change the client’s position. 2. Call the physician. 3. Check the catheter for kinks or obstruction. 4. Clamp the catheter and instill more dialysate at the next exchange time. 4. A client receiving hemodialysis treatment arrives at the hospital with a blood pressure of 200/100, a heart rate of 110, and a respiratory rate of 36. Oxygen saturation on room air is 89%. He complains of shortness of breath, and +2 pedal edema is noted. His last hemodialysis treatment was yesterday. Which of the following interventions should be done first? 1. Administer oxygen 2. Elevate the foot of the bed 3. Restrict the client’s fluids 4. Prepare the client for hemodialysis. 5. A client has a history of chronic renal failure and received hemodialysis treatments three times per week through an arteriovenous (AV) fistula in the left arm. Which of the following interventions is included in this client’s plan of care? 1. Keep the AV fistula site dry. 2. Keep the AV fistula wrapped in gauze. 3. Take the blood pressure in the left arm 4. Assess the AV fistula for a bruit and thrill 6. Which of the following factors causes the nausea associated with renal failure? 1. Oliguria 2. Gastric ulcers 3. Electrolyte imbalances 4. Accumulation of waste products 7. Which of the following clients is at greatest risk for developing acute renal failure? 1. A dialysis client who gets influenza 2. A teenager who has an appendectomy 3. A pregnant woman who has a fractured femur 4. A client with diabetes who has a heart catherization 8. In a client in renal failure, which assessment finding may indicate hypocalcemia? 1. Headache 2. Serum calcium level of 5 mEq/L 3. Increased blood coagulation 4. Diarrhea 9. A nurse is assessing the patency of an arteriovenous fistula in the left arm of a client who is receiving hemodialysis for the treatment of chronic renal failure. Which finding indicates that the fistula is patent? 1. Absence of bruit on auscultation of the fistula. 2. Palpation of a thrill over the fistula 3. Presence of a radial pulse in the left wrist 4. Capillary refill time less than 3 seconds in the nail beds of the fingers on the left hand. 10. The client with chronic renal failure is at risk of developing dementia related to excessive absorption of aluminum. The nurse teaches that this is the reason that the client is being prescribed which of the following phosphate binding agents? 1. Alu-cap (aluminum hydroxide) 2. Tums (calcium carbonate) 3. Amphojel (aluminum hydroxide) 4. Basaljel (aluminum hydroxide) 11. The client newly diagnosed with chronic renal failure recently has begun hemodialysis. Knowing that the client is at risk for disequilibrium syndrome, the nurse assesses the client during dialysis for: 1. Hypertension, tachycardia, and fever 2. Hypotension, bradycardia, and hypothermia 3. 4. restlessness, irritability, and generalized weakness Headache, deteriorating level of consciousness, and twitching. 12. A client with chronic renal failure has completed a hemodialysis treatment. The nurse would use which of the following standard indicators to evaluate the client’s status after dialysis? 1. Potassium level and weight 2. BUN and creatinine levels 3. VS and BUN 4. VS and weight. 13. The hemodialysis client with a left arm fistula is at risk for steal syndrome. The nurse assesses this client for which of the following clinical manifestations? 1. Warmth, redness, and pain in the left hand. 2. Pallor, diminished pulse, and pain in the left hand. 3. Edema and reddish discoloration of the left arm 4. Aching pain, pallor, and edema in the left arm. 14. A client is admitted to the hospital and has a diagnosis of early stage chronic renal failure. Which of the following would the nurse expect to note on assessment of the client? 1. Polyuria 2. Polydipsia 3. Oliguria 4. Anuria 15. The client with chronic renal failure returns to the nursing unit following a hemodialysis treatment. On assessment the nurse notes that the client’s temperature is 100.2. Which of the following is the most appropriate nursing action? 1. Encourage fluids 2. Notify the physician 3. Monitor the site of the shunt for infection 4. Continue to monitor vital signs 16. The nurse is performing an assessment on a client who has returned from the dialysis unit following hemodialysis. The client is complaining of a headache and nausea and is extremely restless. Which of the following is the most appropriate nursing action? 1. Notify the physician 2. Monitor the client 3. Elevate the head of the bed 4. Medicate the client for nausea 17. The nurse is assisting a client on a low-potassium diet to select food items from the menu. Which of the following food items, if selected by the client, would indicate an understanding of this dietary restriction? 1. Cantaloupe 2. Spinach 3. Lima beans 4. Strawberries 18. The nurse is reviewing a list of components contained in the peritoneal dialysis solution with the client. The client asks the nurse about the purpose of the glucose contained in the solution. The nurse bases the response knowing that the glucose: 1. Prevents excess glucose from being removed from the client. 2. Decreases risk of peritonitis. 3. Prevents disequilibrium syndrome 4. Increases osmotic pressure to produce ultrafiltration. 19. The nurse is preparing to care for a client receiving peritoneal dialysis. Which of the following would be included in the nursing plan of care to prevent the major complication associated with peritoneal dialysis? 1. Monitor the clients level of consciousness 2. Maintain strict aseptic technique 3. Add heparin to the dialysate solution 4. Change the catheter site dressing daily 20. A client newly diagnosed with renal failure is receiving peritoneal dialysis. During the infusion of the dialysate the client complains of abdominal pain. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate? 1. Slow the infusion 2. Decrease the amount to be infused 3. Explain that the pain will subside after the first few exchanges 4. Stop the dialysis 21. The nurse is instructing a client with diabetes mellitus about peritoneal dialysis. The nurse tells the client that it is important to maintain the dwell time for the dialysis at the prescribed time because of the risk of: 1. Infection 2. Hyperglycemia 3. Fluid overload 4. Disequilibrium syndrome 22. The client with acute renal failure has a serum potassium level of 5.8 mEq/L. The nurse would plan which of the following as a priority action? 1. Allow an extra 500 ml of fluid intake to dilute the electrolyte concentration. 2. Encourage increased vegetables in the diet 3. Place the client on a cardiac monitor 4. Check the sodium level 23. The client with chronic renal failure who is scheduled for hemodialysis this morning is due to receive a daily dose of enalapril (Vasotec). The nurse should plan to administer this medication: 1. Just before dialysis 2. During dialysis 3. On return from dialysis 4. The day after dialysis 24. The client with chronic renal failure has an indwelling catheter for peritoneal dialysis in the abdomen. The client spills water on the catheter dressing while bathing. The nurse should immediately: 1. Reinforce the dressing 2. Change the dressing 3. Flush the peritoneal dialysis catheter 4. Scrub the catheter with providone-iodine 25. The client being hemodialyzed suddenly becomes short of breath and complains of chest pain. The client is tachycardic, pale, and anxious. The nurse suspects air embolism. The nurse should: 1. Continue the dialysis at a slower rate after checking the lines for air 2. Discontinue dialysis and notify the physician 3. Monitor vital signs every 15 minutes for the next hour 4. Bolus the client with 500 ml of normal saline to break up the air embolism. 26. The nurse has completed client teaching with the hemodialysis client about self-monitoring between hemodialysis treatments. The nurse determines that the client best understands the information given if the client states to record the daily: 1. Pulse and respiratory rate 2. Intake, output, and weight 3. BUN and creatinine levels 4. Activity log 27. The client with an arteriovenous shunt in place for hemodialysis is at risk for bleeding. The nurse would do which of the following as a priority action to prevent this complication from occurring? 1. Check the results of the PT time as they are ordered. 2. Observe the site once per shift 3. Check the shunt for the presence of a bruit and thrill 4. Ensure that small clamps are attached to the AV shunt dressing. 28. The nurse is monitoring a client receiving peritoneal dialysis and nurse notes that a client’s outflow is less than the inflow. Select actions that the nurse should take. 1. Place the client in good body alignment 2. Check the level of the drainage bag 3. Contact the physician 4. Check the peritoneal dialysis system for kinks 5. Reposition the client to his or her side. 29. The nurse assesses the client who has chronic renal failure and notes the following: crackles in the lung bases, elevated blood pressure, and weight gain of 2 pounds in one day. Based on these data, which of the following nursing diagnoses is appropriate? 1. Excess fluid volume related to the kidney’s inability to maintain fluid balance. 2. Increased cardiac output related to fluid overload. 3. Ineffective tissue perfusion related to interrupted arterial blood flow. 4. Ineffective therapeutic Regimen Management related to lack of knowledge about therapy. 30. The nurse is caring for a hospitalized client who has chronic renal failure. Which of the following nursing diagnoses are most appropriate for this client? Select all that apply. 1. Excess Fluid Volume 2. Imbalanced Nutrition; Less than Body Requirements 3. Activity Intolerance 4. Impaired Gas Exchange 5. Pain. 31. What is the primary disadvantage of using peritoneal dialysis for long term management of chronic renal failure? 1. The danger of hemorrhage is high. 2. It cannot correct severe imbalances. 3. It is a time consuming method of treatment. 4. The risk of contacting hepatitis is high. 32. The dialysis solution is warmed before use in peritoneal dialysis primarily to: 1. Encourage the removal of serum urea. 2. Force potassium back into the cells. 3. Add extra warmth into the body. 4. Promote abdominal muscle relaxation. 33. During the client’s dialysis, the nurse observes that the solution draining from the abdomen is consistently blood tinged. The client has a permanent peritoneal catheter in place. Which interpretation of this observation would be correct? 1. Bleeding is expected with a permanent peritoneal catheter 2. Bleeding indicates abdominal blood vessel damage 3. Bleeding can indicate kidney damage. 4. Bleeding is caused by too-rapid infusion of the dialysate. 34. Which of the following nursing interventions should be included in the client’s care plan during dialysis therapy? 1. Limit the client’s visitors 2. Monitor the client’s blood pressure 3. Pad the side rails of the bed 4. Keep the client NPO. 35. Aluminum hydroxide gel (Amphojel) is prescribed for the client with chronic renal failure to take at home. What is the purpose of giving this drug to a client with chronic renal failure? 1. To relieve the pain of gastric hyperacidity 2. To prevent Curling’s stress ulcers 3. To bind phosphorus in the intestine 4. To reverse metabolic acidosis. 36. The nurse teaches the client with chronic renal failure when to take the aluminum hydroxide gel. Which of the following statements would indicate that the client understands the teaching? 1. “I’ll take it every 4 hours around the clock.” 2. “I’ll take it between meals and at bedtime.” 3. “I’ll take it when I have a sour stomach.” 4. “I’ll take it with meals and bedtime snacks.” 37. The client with chronic renal failure tells the nurse he takes magnesium hydroxide (milk of magnesium) at home for constipation. The nurse suggests that the client switch to psyllium hydrophilic mucilloid (Metamucil) because: 1. MOM can cause magnesium toxicity 2. MOM is too harsh on the bowel 3. Metamucil is more palatable 4. MOM is high in sodium 38. In planning teaching strategies for the client with chronic renal failure, the nurse must keep in mind the neurologic impact of uremia. Which teaching strategy would be most appropriate? 1. Providing all needed teaching in one extended session. 2. Validating frequently the client’s understanding of the material. 3. Conducting a one-on-one session with the client. 4. Using videotapes to reinforce the material as needed. 39. The nurse helps the client with chronic renal failure develop a home diet plan with the goal of helping the client maintain adequate nutritional intake. Which of the following diets would be most appropriate for a client with chronic renal failure? 1. High carbohydrate, high protein 2. High calcium, high potassium, high protein 3. Low protein, low sodium, low potassium 4. Low protein, high potassium 40. A client with chronic renal failure has asked to be evaluated for a home continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) program. The nurse should explain that the major advantage of this approach is that it: 1. Is relatively low in cost 2. 3. Allows the client to be more independent Is faster and more efficient than standard peritoneal dialysis 4. Has fewer potential complications than standard peritoneal dialysis 41. The client asks whether her diet would change on CAPD. Which of the following would be the nurse’s best response? 1. “Diet restrictions are more rigid with CAPD because standard peritoneal dialysis is a more effective technique.” 2. “Diet restrictions are the same for both CAPD and standard peritoneal dialysis.” 3. “Diet restrictions with CAPD are fewer than with standard peritoneal dialysis because dialysis is constant.” 4. “Diet restrictions with CAPD are fewer than with standard peritoneal dialysis because CAPD works more quickly.” 42. Which of the following is the most significant sign of peritoneal infection? 1. Cloudy dialysate fluid 2. Swelling in the legs 3. Poor drainage of the dialysate fluid 4. Redness at the catheter insertion site 43. The main indicator of the need for hemodialysis is: 1. Ascites 2. Acidosis 3. Hypertension 4. Hyperkalemia 44. To gain access to the vein and artery, an AV shunt was used for Mr. Roberto. The most serious problem with regards to the AV shunt is: 1. Septicemia 2. Clot formation 3. Exsanguination 4. Vessel sclerosis 45. When caring for Mr. Roberto’s AV shunt on his right arm, you should: 1. Cover the entire cannula with an elastic bandage 2. Notify the physician if a bruit and thrill are present 3. User surgical aseptic technique when giving shunt care 4. Take the blood pressure on the right arm instead Answers and Rationales 1. A. Osmosis allows for the removal of fluid from the blood by allowing it to pass through the semipermeable membrane to an area of high concentrate (dialysate), and diffusion allows for passage of particles (electrolytes, urea, and creatinine) from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Fluid passes to an area with a higher solute concentration. The pores of a semipermeable membrane are small, thus preventing the flow of blood cells and protein molecules through it. 2. B. To prevent life-threatening complications, the client must follow the dialysis schedule. Alcohol would further dry the client’s skin more than it already is. The client should follow a low-potassium diet because potassium levels increase in chronic renal failure. The client should know hemodialysis is time-consuming and will definitely cause a change in current lifestyle. 3. C. The first intervention should be to check for kinks and obstructions because that could be preventing drainage. After checking for kinks, have the client change position to promote drainage. Don’t give the next scheduled exchange until the dialysate is drained because abdominal distention will occur, unless the output is within parameters set by the physician. If unable to get more output despite checking for kinks and changing the client’s position, the nurse should then call the physician to determine the proper intervention. 4. A. Airway and oxygenation are always the first priority. Because the client is complaining of shortness of breath and his oxygen saturation is only 89%, the nurse needs to try to increase his levels by administering oxygen. The client is in pulmonary edema from fluid overload and will need to be dialyzed and have his fluids restricted, but the first interventions should be aimed at the immediate treatment of hypoxia. The foot of the bed may be elevated to reduce edema, but this isn’t the priority. 5. D. Assessment of the AV fistula for bruit and thrill is important because, if not present, it indicates a non-functioning fistula. No blood pressures or venipunctures should be taken in the arm with the AV fistula. When not being dialyzed, the AV fistula site may get 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. wet. Immediately after a dialysis treatment, the access site is covered with adhesive bandages. D. Although clients with renal failure can develop stress ulcers, the nausea is usually related to the poisons of metabolic wastes that accumulate when the kidneys are unable to eliminate them. The client has electrolyte imbalances and oliguria, but these don’t directly cause nausea. D. Clients with diabetes are prone to renal insufficiency and renal failure. The contrast used for heart catherization must be eliminated by the kidneys, which further stresses them and may produce acute renal failure. A teenager who has an appendectomy and a pregnant woman with a fractured femur isn’t at increased risk for renal failure. A dialysis client already has end-stage renal disease and wouldn’t develop acute renal failure. D. In renal failure, calcium absorption from the intestine declines, leading to increased smooth muscle contractions, causing diarrhea. CNS changes in renal failure rarely include headache. A serum calcium level of 5 mEq/L indicates hypercalcemia. As renal failure progresses, bleeding tendencies increase. B. The nurse assesses the patency of the fistula by palpating for the presence of a thrill or auscultating for a bruit. The presence of a thrill and bruit indicate patency of the fistula. Although the presence of a radial pulse in the left wrist and capillary refill time less than 3 seconds in the nail beds of the fingers on the left hand are normal findings, they do not assess fistula patency. B. Phosphate binding agents that contain aluminum include Alu-caps, Basaljel, and Amphojel. These products are made from aluminum hydroxide. Tums are made from calcium carbonate and also bind phosphorus. Tums are prescribed to avoid the occurrence of dementia related to high intake of aluminum. Phosphate binding agents are needed by the client in renal failure because the kidneys cannot eliminate phosphorus. D. Disequilibrium syndrome is characterized by headache, mental confusion, decreasing level of consciousness, nausea, and vomiting, twitching, and possible seizure activity. Disequilibrium syndrome is caused by rapid removal of solutes from the body during hemodialysis. At the same time, the blood-brain barrier interferes with the efficient removal of wastes from brain tissue. As a result, water goes into cerebral cells because of the osmotic gradient, causing brain swelling and onset of symptoms. The syndrome most often occurs in clients who are new to dialysis and is prevented by dialyzing for shorter times or at reduced blood flow rates. D. Following dialysis, the client’s vital signs are monitored to determine whether the client is remaining hemodynamically stable. Weight is measured and compared with the client’s predialysis weight to determine effectiveness of fluid extraction. Laboratory studies are done as per protocol but are not necessarily done after the hemodialysis treatment has ended. B. Steal syndrome results from vascular insufficiency after creation of a fistula. The client exhibits pallor and a diminished pulse distal to the fistula. The client also complains of pain distal to the fistula, which is due to tissue ischemia. Warmth, redness, and pain more likely would characterize a problem with infection. A. Polyuria occurs early in chronic renal failure and if untreated can cause severe dehydration. Polyuria progresses to anuria, and the client loses all normal functions of the kidney. Oliguria and anuria are not early signs, and polydipsia is unrelated to chronic renal failure. D. The client may have an elevated temperature following dialysis because the dialysis machine warms the blood slightly. If the temperature is elevated excessively and remains elevated, sepsis would be suspected and a blood sample would be obtained as prescribed for culture and sensitivity purposes. A. Disequilibrium syndrome may be due to the rapid decrease in BUN levels during dialysis. These changes can cause cerebral edema that leads to increased intracranial pressure. The client is exhibiting early signs of disequilibrium syndrome and appropriate treatments with anticonvulsant medications and barbituates may be necessary to prevent a life-threatening situation. The physician must be notified. C. Cantaloupe (1/4 small), spinach (1/2 cooked) and strawberries (1 ¼ cups) are high potassium foods and average 7 mEq per serving. Lima beans (1/3 c) averages 3 mEq per serving. 18. D. Increasing the glucose concentration makes the solution increasingly more hypertonic. The more hypertonic the solution, the greater the osmotic pressure for ultrafiltration and thus the greater amount of fluid removed from the client during an exchange. 19. B. The major complication of peritoneal dialysis is peritonitis. Strict aseptic technique is required in caring for the client receiving this treatment. Although changing the catheter site dressing daily may assist in preventing infection, this option relates to an external site. 20. C. Pain during the inflow of dialysate is common during the first few exchanges because of peritoneal irritation; however, the pain usually disappears after 1 to 2 weeks of treatment. The infusion amount should not be decreased, and the infusion should not be slowed or stopped. 21. B. An extended dwell time increases the risk of hyperglycemia in the client with diabetes mellitus as a result of absorption of glucose from the dialysate and electrolyte changes. Diabetic clients may require extra insulin when receiving peritoneal dialysis. 22. C. The client with hyperkalemia is at risk for developing cardiac dysrhythmias and cardiac arrest. Because of this the client should be placed on a cardiac monitor. Fluid intake is not increased because it contributes to fluid overload and would not affect the serum potassium level significantly. Vegetables are a natural source of potassium in the diet, and their use would not be increased. The nurse may also assess the sodium level because sodium is another electrolyte commonly measured with the potassium level. However, this is not a priority action at this time. 23. C. Antihypertensive medications such as enalapril are given to the client following hemodialysis. This prevents the client from becoming hypotensive during dialysis and also from having the medication removed from the bloodstream by dialysis. No rationale exists for waiting a full day to resume the medication. This would lead to ineffective control of the blood pressure. 24. B. Clients with peritoneal dialysis catheters are at high risk for infection. A dressing that is wet is a conduit for bacteria for bacteria to reach the catheter insertion site. The nurse assures that the dressing is kept dry at all times. Reinforcing the dressing is not a safe practice to prevent infection in this circumstance. Flushing the catheter is not indicated. Scrubbing the catheter with povidone-iodine is done at the time of connection or disconnecting of peritoneal dialysis. 25. B. If the client experiences air embolus during hemodialysis, the nurse should terminate dialysis immediately, notify the physician, and administer oxygen as needed. 26. B. The client on hemodialysis should monitor fluid status between hemodialysis treatments by recording intake and output and measuring weight daily. Ideally, the hemodialysis client should not gain more than 0.5 kg of weight per day. 27. D. An AV shunt is a less common form of access site but carries a risk for bleeding when it is used because two ends of an external cannula are tunneled subcutaneously into an artery and a vein, and the ends of the cannula are joined. If accidental connection occurs, the client could lose blood rapidly. For this reason, small clamps are attached to the dressing that covers the insertion site to use if needed. The shunt site should be assessed at least every four hours. 28. A, B, D, E. If outflow drainage is inadequate, the nurse attempts to stimulate outflow by changing the client’s position. Turning the client to the other side or making sure that the client is in good body alignment may assist with outflow drainage. The drainage bag needs to be lower than the client’s abdomen to enhance gravity drainage. The connecting tubing and the peritoneal dialysis system is also checked for kinks or twisting and the clamps on the system are checked to ensure that they are open. There is no reason to contact the physician. 29. A. Crackles in the lungs, weight gain, and elevated blood pressure are indicators of excess fluid volume, a common complication in chronic renal failure. The client’s fluid status should be monitored carefully for imbalances on an ongoing basis. 30. A, B, C. Appropriate nursing diagnoses for clients with chronic renal failure include excess fluid volume related to fluid and sodium retention; imbalanced nutrition, less than body requirements related to anorexia, nausea, and vomiting; and activity intolerance related to fatigue. The nursing diagnoses of impaired gas exchange and pain are not commonly related to chronic renal failure. 31. C. The disadvantages of peritoneal dialysis in long-term management of chronic renal failure is that is requires large blocks of time. The risk of hemorrhage or hepatitis is not high with PD. PD is effective in maintaining a client’s fluid and electrolyte balance. 32. A. The main reason for warming the peritoneal dialysis solution is that the warm solution helps dilate peritoneal vessels, which increases urea clearance. Warmed dialyzing solution also contributes to client comfort by preventing chilly sensations, but this is a secondary reason for warming the solution. The warmed solution does not force potassium into the cells or promote abdominal muscle relaxation. 33. B. Because the client has a permanent catheter in place, blood tinged drainage should not occur. Persistent blood tinged drainage could indicate damage to the abdominal vessels, and the physician should be notified. The bleeding is originating in the peritoneal cavity, not the kidneys. Too rapid infusion of the dialysate can cause pain. 34. B. Because hypotension is a complication of peritoneal dialysis, the nurse records intake and output, monitors VS, and observes the client’s behavior. The nurse also encourages visiting and other diversional activities. A client on PD does not need to be placed in bed with padded side rails or kept NPO. 35. C. A client in renal failure develops hyperphosphatemia that causes a corresponding excretion of the body’s calcium stores, leading to renal osteodystrophy. To decrease this loss, aluminum hydroxide gel is prescribed to bind phosphates in the intestine and facilitate their excretion. Gastric hyperacidity is not necessarily a problem associated with chronic renal failure. Antacids will not prevent Curling’s stress ulcers and do not affect metabolic acidosis. 36. D. Aluminum hydroxide gel is administered to bind the phosphates in ingested foods and must be given with or immediately after meals and snacks. There is no need for the client to take it on a 24-hour schedule. It is not administered to treat hyperacidity in clients with CRF and therefore is not prescribed between meals. 37. A. Magnesium is normally excreted by the kidneys. When the kidneys fail, magnesium can accumulate and cause severe neurologic problems. MOM is harsher than Metamucil, but magnesium toxicity is a more serious problem. A client may find both MOM and Metamucil unpalatable. MOM is not high in sodium. 38. B. Uremia can cause decreased alertness, so the nurse needs to validate the client’s comprehension frequently. Because the client’s ability to concentrate is limited, short lesions are most effective. If family members are present at the sessions, they can reinforce the material. Written materials that the client can review are superior to videotapes, because the clients may not be able to maintain alertness during the viewing of the videotape. 39. C. Dietary management for clients with chronic renal failure is usually designed to restrict protein, sodium, and potassium intake. Protein intake is reduced because the kidney can no longer excrete the byproducts of protein metabolism. The degree of dietary restriction depends on the degree of renal impairment. The client should also receive a high carbohydrate diet along with appropriate vitamin and mineral supplements. Calcium requirements remain 1,000 to 2,000 mg/day. 40. B. The major benefit of CAPD is that it frees the client from daily dependence on dialysis centers, home health care personnel, and machines for life-sustaining treatment. The independence is a valuable outcome for some people. CAPD is costly and must be done daily. Side effects and complications are similar to those of standard peritoneal dialysis. 41. C. Dietary restrictions with CAPD are fewer than those with standard peritoneal dialysis because dialysis is constant, not intermittent. The constant slow diffusion of CAPD helps prevent accumulation of toxins and allows for a more liberal diet. CAPD does not work more quickly, but more consistently. Both types of peritoneal dialysis are effective. 42. A. Cloudy drainage indicates bacterial activity in the peritoneum. Other signs and symptoms of infection are fever, hyperactive bowel sounds, and abdominal pain. Swollen legs may be indicative of congestive heart failure. Poor drainage of dialysate fluid is probably the result of a kinked catheter. Redness at the insertion site indicates local infection, not peritonitis. However, a local infection that is left untreated can progress to the peritoneum. 43. D. 44. C. 45. C.