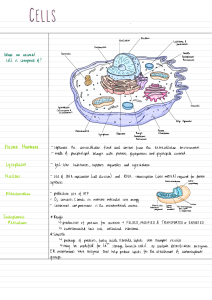
Ch4 A Tour of the Cell 靖永皓 Yung-Hao Ching, Ph.D. Department of Molecular Biology and Human Genetics yching@gms.tcu.edu.tw Extension 2693 Office: D615-1 Concepts 4.1 Biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry to study cells 4.2: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions 4.3: The eukaryotic cell’s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried out by the ribosomes 4.4: The endomembrane system regulates protein traffic and performs metabolic functions in the cell Concepts • Concept 4.5: Mitochondria and chloroplasts change energy from one form to another • Concept 4.6: The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell • Concept 4.7: Extracellular components and connections between cells help coordinate cellular activities 4.1 Biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry to study cells 4.1 Biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry to study cells 光學顯微鏡 • Light microscope (LM): visualize cells 電子顯微鏡 • Electron microscopes (EMS): study subcellular structures 掃描式 – Scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) : , providing images that look 3-D 穿透式 – Transmission electron microscopes (TEMs) :study the internal structure of cells Three important parameters of microscopy 放大率 解析度 Magnification Resolution The ratio of an object’s image size to its real size The measure of the clarity of the image, or the minimum distance of two distinguishable points 對比 Contrast Visible differences in parts of the sample 真核細胞 Concept 4.2: Eukaryotic cells have internal 膜 membranes that compartmentalize their functions Concept 4.2: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions • Cells : The basic structural and functional unit of every organism 原核 • Prokaryotic 細菌 • Bacteria 古細菌 • Archaea 真核 • Eukaryotic 原生生物 • Protists 真菌 • Fungi • Animals • Plants Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells • Basic features of all cells 細胞膜 –Plasma membrane 胞質溶膠 –Cytosol (Semifluid substance) 染色體 –Chromosomes (carry genes) 核糖體 –Ribosomes (make proteins) Prokaryotic cells 擬核 Fimbriae • No nucleus (Nucleoid) Nucleoid • No membrane-bound Ribosomes 胞器 organelles 細胞質 • Cytoplasm – bound by the plasma membrane – Cytoplasm = cytosol + organelles Plasma membrane Bacterial chromosome Cell wall Capsule Flagella (a) A typical rod-shaped bacterium 細胞膜 Plasma membrane • Biological membrane –double layer of 磷脂 phospholipids –selective barrier –passage of oxygen, nutrients, & waste Carbohydrate side chains Hydrophilic region Hydrophobic region Hydrophilic region Phospholipid Proteins (b) Structure of the plasma membrane ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER) Flagellum Figure 6.8a Rough ER Smooth ER Nuclear envelope Nucleolus NUCLEUS Chromatin Centrosome Plasma membrane CYTOSKELETON: Microfilaments Intermediate filaments Microtubules Ribosomes Microvilli Golgi apparatus Peroxisome Mitochondrion Lysosome NUCLEUS Nuclear envelope Nucleolus Chromatin Rough endoplasmic reticulum Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes Central vacuole Golgi apparatus Microfilaments Intermediate CYTOSKELETON filaments Microtubules Mitochondrion Peroxisome Plasma membrane Chloroplast Cell wall Wall of adjacent cell Plasmodesmata Concept 4.3: The eukaryotic cell’s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried out by the ribosomes Concept 4.3: The eukaryotic cell’s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried out by the ribosomes Cell Component Nucleus Structure • Surrounded by nuclear envelope 核膜 (double membrane) • perforated by nuclear pores 细胞核 核膜孔 (ER) Ribosome 核糖體 • nuclear envelope continuous with endoplasmic reticulum (ER) • Two subunits • ribosomal RNA + proteins • free in cytosol or bound to ER Function • Houses chromosomes: chromatin (DNA + proteins) • Nucleoli 核仁: where ribosomal subunits are made • nuclear pores : regulate entry and exit of materials • Protein synthesis Concept 4.4: The endomembrane system regulates protein traffic and performs metabolic functions in the cell Concept 4.4: The endomembrane system regulates protein traffic and performs metabolic functions in the cell Cell Component Endoplasmic reticulum 內質網 • (Nuclear envelope) • • Golgi apparatus 高基氏體 • • Lysosome 溶小體 Vacuole 液胞 Function Structure Network of membranebounded tubules and sacs Membrane separates lumen from cytosol continuous with nuclear envelope Stacks of flattened membranous sacs has polarity (cis and trans faces) Membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes (in animal cells) • • Large membranebounded vesicle • Smooth ER: synthesis of lipids, metabolism of carbohydrates, Ca2+ storage, detoxification of drugs and poisons • Rough ER: aids in synthesis of secretory and other proteins from bound ribosomes; adds carbohydrates to proteins to make glycoproteins; produces new membrane • Modification of proteins, carbohydrates on proteins, and phospholipids synthesis of polysaccharides Sorting of Golgi products, which are then released in vesicles • • • Breakdown of ingested substances, cell macromolecules, and damaged organelles for recycling • Digestion, storage, waste disposal, water balance, plant cell growth and protection Concept 4.5: Mitochondria and chloroplasts change energy from one form to another Concept 4.5: Mitochondria and chloroplasts change energy from one form to another Cell Component Structure Function Mitochondrion 線粒體 • • Bounded by double membrane inner membrane has infoldings (cristae 脊突) • • Cellular respiration uses oxygen to generate ATP Chloroplast 葉綠體 • two membranes around fluid stroma 基質 Thylakoids 類囊體 stacked into grana 葉綠餅 • • found in plants and algae Photosynthesis 光合作用 Specialized metabolic compartment single membrane • enzymes that transfer H+ from certain molecules to oxygen producing (H2O2) H2O2 is converted to water by another enzyme • Peroxisome 過氧化物酶體 • • • The Endosymbiont theory Endoplasmic reticulum Nucleus Engulfing of oxygenNuclear using nonphotosynthetic envelope prokaryote, which becomes a mitochondrion Ancestor of eukaryotic cells (host cell) Mitochondrion Nonphotosynthetic eukaryote At least one cell Engulfing of photosynthetic prokaryote Chloroplast Mitochondrion Photosynthetic eukaryote 內共生理論 細胞骨架 Concept 4.6: The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell Concept 4.6: The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell 細胞骨架 • Cytoskeleton • Functions: – Support & Motility • Types: 微管 – Microtubules 微絲 – Microfilaments 中間絲 – Intermediate filaments Centrosome containing a pair of centrioles 中心體 中心粒 鞭毛 纖毛 Structure of a flagellum or motile cilium Cilia and flagella share a common structure 纖毛 鞭毛 Cilia v.s. Flagella Flagella Cilia Definition short, hair like appendages long, threadlike appendages Length Short Longer than cilia, can vary Motion Rotational, like a motor, very fast moving Wave-like slow movement compared to cilia Density Many (hundreds) per cell Few (less than 10) per cell Found in Eukaryotic cells Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Etymology Latin :eyelash Latin :whip. Concept 4.7: Extracellular components and connections between cells help coordinate cellular activities Concept 4.7: Extracellular components and connections between cells help coordinate cellular activities Plant cells Extracellular components Cell junctions Animal cells Cell wall • Cellulose 纖維素 fibers embedded in polysaccharides 多醣 & proteins Extracellular matrix (ECM) 細胞外基質 • glycoproteins 醣蛋白 & proteoglycans 蛋白聚醣 • Functions: support, adhesion, movement, and regulation • Plasmodesmata • Tight junctions • Desmosomes • Gap junction 細胞壁 Cell wall Cell wall Forms • Primary cell wall: relatively thin and flexible • Middle lamella 中薄層: thin layer between primary walls of adjacent cells • Secondary cell wall (in some cells): added between the plasma membrane and the primary cell wall Functions • Protects • Maintains shape • Prevents excessive uptake of water 原生質絲 Plasmodesmata in Plant Cells • Channels that perforate plant cell walls • Water and small solutes (proteins & RNA) can pass from cell to Cell walls cell Interior of cell Interior of cell 0.5 µ m Plasmodesmata Plasma membranes 細胞外基質 The Extracellular Matrix (ECM) of Animal Cells • Animal cells are covered by extracellular matrix (ECM) Collagen EXTRACELLULAR FLUID Proteoglycan complex 醣蛋白 – Glycoproteins 膠原蛋白 – Collagen Fibronectin Integrins 蛋白聚糖 – Proteoglycans 纖連蛋白 – Fibronectin • ECM proteins bind to receptor proteins integrins in the plasma membrane 整合素 Plasma membrane Micro- CYTOPLASM filaments Tight Junctions, Desmosomes, and Gap Junctions in Animal Cells 緊密連接 Intermediate filaments Tight junction : • membranes of neighboring cells are pressed together • preventing leakage of extracellular fluid 胞橋小體 Desmosome • anchoring junctions • fasten cells together into strong sheets Plasma membranes of adjacent cells Ions or small molecules Space between cells Extracellular matrix 間隙連接 Gap junction • communicating junctions • provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent cells DISCUSSION 抽籤 What is Biology? • • • • Scientific study of life an ongoing inquiry about the nature of life Life defies a simple, one-sentence definition Life is recognized by what living things do • Biologists ask questions, – How does a single cell develop into an organism? 37 性質 Some properties of life Order Regulation Evolutionary adaptation Energy processing Response to the environment Growth and development © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd. Reproduction 組織 Levels of Biological Organization 7 Tissues 1 The Biosphere 2 Ecosystems 6 Organs 3 Communities 10 Molecules 5 Organisms 4 Populations 9 Organelles 8 Cells 突現性質 Emergent properties • Result from the arrangement and interaction of parts within a system • Characterize non-biological entities as well – a functioning bicycle emerges only when all of the necessary parts connect in the correct 浮現性質 Emergent Properties • Considering some of the characteristics that define life, discuss the following statement: Life is an emergent property that appears at the level of the cell. • 考慮定義⽣命的特徵,討 論以下陳述;『⽣命是出 現在細胞層次上的浮現性 質』 Scientific Inquiry 科學探究 • Suppose you wish to separate two cellular proteins, A and B. Protein A binds with DNA and is found in the chromatin complex. Protein B binds with RNA and is found in nucleoli. How would you separate cell fractions containing protein A and protein B? Explain the rationale behind your method • 假設您希望分離兩種細胞 蛋⽩質 A 和 B。蛋⽩質 A 與 DNA 結合,存在於染⾊ 質複合物中。蛋⽩ B 與 RNA 結合,存在於核仁中。 如何分離含有蛋⽩質 A 和 蛋⽩質 B 的細胞分提?解 釋你的⽅法背後的基本科 學原理 Scientific Inquiry 科學探究 • What cell structure best reveal • 哪種細胞結構最能表現 evolutionary unity? 出演化的統⼀性? • Provide an example of • 舉⼀個以細胞因為功能 diversity related to specialized ⽽特化顯現多樣性的例 cellular modifications ⼦