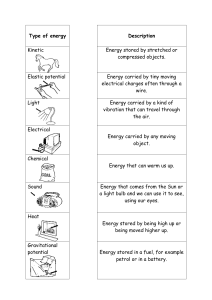
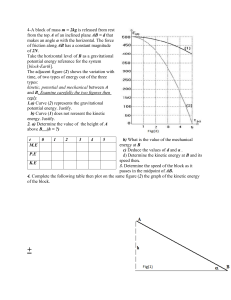
5. Work, Energy and Power 5. Work, Energy and Power 5. Work, energy and power–The objectives 1. Define Work, energy, Potential energy Power, Efficiency 2. Differentiate between Gravitational potential energy, Elastic PE and Electric PE. 3. Be competent in using following equations W=F.x 𝒌𝒙𝟐 𝟐 W= P.V 𝑬= 𝒎𝒗𝟐 𝟐 𝒌(𝑿𝟐𝟐 −𝑿𝟐𝟏 ) 𝟐 𝑬 = 𝒎𝒈𝒉 𝑾 𝒕 𝑷 = = 𝑭. 𝑽 4. Be able to analyze Force-distance graph 𝑬= 𝑾=𝑬= A warm-up Question for you Which block will move higher? Explain your answer. The video 1.Work (W) Work = Force x Distance travelled in the direction of force Units: J (kgm2s-2) Scalar 1. 2019 May P11 Q17 2. 10M.1.HL.TZ1.5 Which of the following is a correct definition of work? A. Product of force and distance B. Product of force and distance moved in the direction of the force. C. Product of power and time D. Product of force and displacement 3. Find the work done when the plate rotates twice 4. What is the work done by the centripetal force in one circle? The mass at the end of a pendulum is made to move in a horizontal circle of radius r at constant speed. The magnitude of the net force on the mass is F. What is the direction of F and the work done by F during half a revolution? 1.Work done on a gas • Work done = Force x Distance to force direction. • In gases, more useful concepts are pressure and volume. Not the force and distance. • Hence, we change W=F.x into a different form W= F. x = (F/A). (A. x) Hence, W= P.V 2018 Nov P12 Q16 Force- Distance graph ∆𝑠 ∆𝑡 𝑉= ∆𝑠 = 𝑉. ∆𝑡 Area under graph= The work done = The energy used. 15M.1.HL.TZ2.4 A girl is standing on a moving skateboard. She pushes backwards on the ground at intervals as shown on the graph. How much kinetic energy is gained by the girl during the period represented on the graph? Frictional forces are negligible. A. 200 J B. 400 J C. 600 J D. 1200 J 2 .Energy (E) The ability of doing work is called Energy. • When you do work, you lose energy. • When work is done on you, you gain energy The ball drop activity. Part 1: teacher demo Explain why the smaller ball ends up with higher energy?. Extension 1: Two balls are identical except that one ball has hard outer crust. When the two balls are thrown at a window at same speed, the hardball may break the glass while the softball does not. Explain this phenomena using newtons laws. Students: Get the collision moment. Use app jianying for video analysis Extension 2: Explain the concept of egg drop in terms of Newtons laws Kinetic Energy • Energy due to the motion of an object is called Kinetic energy. 1. 2020 May 13 Q18 2. 2021 May 13 Q18 Kinetic Energy- Deriving the equation • Kinetic energy=The work done on the object • W= F.x • But, F=ma • So, W= K.E.=mas • Using linear motion equation of 𝑣 2 = 𝑢2 + 2𝑎𝑠 16N.1.HL.TZ0.7 An object of mass 2kg is thrown vertically downwards with an initial kinetic energy of 100J. What is the distance fallen by the object at the instant when its kinetic energy has doubled? A. 2.5m B. 5.0m C. 10m D. 14m 3. 2019 March P11 Q10 4. 2020 May 13 Q16 An astronaut is moving at a constant velocity in the absence of a gravitational field when he throws a tool away from him. What is the effect of throwing the tool on the total kinetic energy of the astronaut and the tool and the total momentum of the astronaut and the tool? 19M.1.SL.TZ2.7 Potential energy The energy due to position or the compressed/ stretched state of an object is called potential energy. Gravitational Potential Energy: Deriving the equation • The energy a mass processes due to the position in a gravitational field is called the GPE. • But, F=ma • So, W= mg.h Q1. An object has a weight of 2 6.10 × 10 N. What is the change in gravitational potential energy of the object when it moves through 8.0 m vertically? A. 5 kJ B. 4.9 kJ C. 4.88 kJ D. 4.880 kJ Elastic Potential Energy 𝒌𝒙2 𝑬= 2 Work done from Extension X1 to Extension X2 𝒌(𝑿22 − 𝑿12 ) 𝑾=𝑬= 2 A compressed spring is used to launch an object along a horizontal frictionless surface. When the spring is compressed through a distance x and released, the object leaves the spring at speed v. What is the distance through which the spring must be compressed for the object to leave the spring at v/2? 18N.1.SL.TZ0.8 A. C. 𝒙 𝟒 𝒙 𝟐 B. 𝒙 𝟐 D. 𝒙 𝟐 An increasing force acts on a metal wire and the wire extends from an initial length l0 to a new length l. The graph shows the variation of force with length for the wire. The energy required to extend the wire from l0 to l is E. The wire then contracts to half its original extension. What is the work done by the wire as it contracts? A. B. C. D. 0.25E 0.50E 0.75E E Electric potential energy Electric potential Difference The energy conversion happens for 1C charge is called the potential difference between two points. 𝐖 = ∆𝑬 = ∆𝑽. 𝑸 An electron is accelerated through a potential difference of 2.5 MV. What is the change in kinetic energy of −𝟏𝟗 the electron? (𝒆 = 𝟏. 𝟔𝒙𝟏𝟎 𝑪 ) 17M.1.SL.TZ1.19 A. 0.4μJ B. 0.4 nJ C. 0.4 pJ D. 0.4 fJ Power (P) • The rate of doing work is called power. • Power= Work/ Time (P=W/t) • Scalar quantity. Unit Power Equations. Efficiency P=W/t P=Fx/t P= FV Efficiency= Useful work Total work Efficiency= Useful Power For electric Total Power circuits: P=VI=I2R=V2/R 5. Work, energy and power–The objectives 1. Define Work, energy, Potential energy Power, Efficiency 2. Differentiate between Gravitational potential energy, Elastic PE and Electric PE. 3. Be competent in using following equations W=F.x 𝒌𝒙𝟐 𝟐 W= P.V 𝑬= 𝒎𝒗𝟐 𝟐 𝒌(𝑿𝟐𝟐 −𝑿𝟐𝟏 ) 𝟐 𝑬 = 𝒎𝒈𝒉 𝑾 𝒕 𝑷 = = 𝑭. 𝑽 4. Be able to analyze Force-distance graph 𝑬= 𝑾=𝑬=