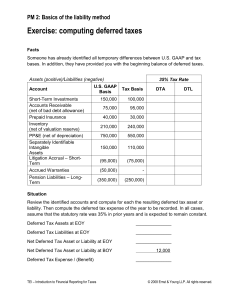
Income Tax November 3, 2022 8:22 PM Accounting Income - Income for the period before deducting income tax expense - Income that appears in the traditional income statements and computed in accordance with the accounting standard Taxable Income - Income for the period in accordance with the rules established by the taxation authorities upon which income taxes are payable or recoverable - Income that appears in income tax return and computed in accordance with the income tax law - BIR - the excess of taxable revenue over tax deductible expense and exemptions for the period Note: The difference between accounting income and taxable income may be classified into two: 1. Permanent Differences 2. Temporary Differences Permanent Differences - Items of revenue and expense which are included in EITHER accounting income or taxable income but will NEVER BE INCLUDED IN THE OTHER - Pertains to nontaxable revenue and nondeductible expenses - Permanent Differences do not give rise to deferred tax asset and liability because they have no future tax consequences EXAMPLES: a. Interest income on time deposit b. Dividends received c. Life Insurance Premium - when the entity is the beneficiary of a life insurance on an officer, the premium PAID is not tax deductible but said premium is an expense for accounting purposes d. Tax penalties, surcharges and fines are nondeductible Temporary Differences - The differences between the carrying amount of an asset or liability and the tax base - Temporary Differences includes timing differences - Timing differences are items of income and expenses which are included in both accounting income and taxable income but at different time periods NOTE: For every temporary differences, eventually that item's treatment will be the same in accounting and taxable income Temporary differences give rise either to: 1. Deferred Tax Liability 2. Deferred Tax Asset Kinds of Temporary Differences A. Taxable temporary Differences ○ Temporary differences that will result in future taxable amount ○ Give rise to DEFERRED TAX LIABILITY B. Deductible Temporary Difference ○ Temporary differences that will result in future deductible amount ○ Give rise to DEFERRED TAX ASSET Tax Base - The amount attributable to the asset or liability for tax purposes - Amount of the asset or liability that is recognized or allowed for tax purposes Tax Base of an Asset - Amount that will be deductible for tax purposes against future income - If the amount is a one-time deduction for tax purposes, the tax base is zero because New Section 6 Page 1 - If the amount is a one-time deduction for tax purposes, the tax base is zero because the entire amount is expensed in the current year Tax Base of a Liability - Normally the carrying amount less the amount that will be deductible for tax purposes in the future - Tax base is zero if the liability cost is a future deductible amount Deferred Tax Liability - The amount of income tax payable in future periods with respect to a taxable temporary differences - The deferred tax consequence attributable to a taxable temporary difference or future taxable amount A deferred tax liability arises from the following: a. When the accounting income is higher than taxable income because of timing differences b. When the carrying amount of an assets is higher than the tax base c. When the carrying amount of a liability is lower than the tax base Accounting for Income Higher than Taxable Income Temporary Differences that result in accounting income higher than taxable income include the following: 1. Revenues and Gains are included in accounting income of the current period but are taxable in the future periods ○ Example: Installment sale that is included in accounting income at the time of sale and included in taxable income when cash is collected in future periods - revenues and gains are taxable income for the period it is collected as cash 2. Expenses and losses are deductible for tax purposes in the current period but deductible for accounting purposes in future periods a. Accelerated depreciation for tax purposes and straight line depreciation for accounting purposes b. Development cost may be capitalized and amortized over future periods in determining accounting income but deducted in determining taxable income in the period in which it is paid c. Prepaid expense has already been deducted on a cash basis in determining taxable income of the current period - expenses and losses are deductible if it is already paid in cash Other Taxable Temporary Differences Taxable temporary differences that technically are not timing differences but give rise to deferred tax liability a. Asset is revalued upward and no equivalent adjustment is made for tax purposes b. The carrying amount of investment in subsidiary, associate or joint venture is higher than the tax base because the subsidiary, associate or joint venture has not distributed its entire income to the parent or investor c. The cost of a business combination accounted for as an acquisition is allocated to the identifiable assets and liabilities acquired at fair value Recognition of a Deferred Tax Liability PAS 12, 15 - deferred tax liability shall be recognized for all taxable temporary differences However, a deferred tax liability is not recognized when the taxable temporary differences arises from: a. Goodwill resulting from a business combination and which is nondeductible for tax purposes b. Initial Recognition of an asset or liability in a transaction that is not a business combination and affects neither accounting income nor taxable income c. Undistributed profit of subsidiary, associate or joint venture when the parent, investor or venturer is able to control the timing of the reversal of the temporary difference Deferred Tax Asset - The amount of income tax recoverable in future periods with respect to a deductible temporary difference and operating loss carryforward New Section 6 Page 2 temporary difference and operating loss carryforward - The deferred tax consequence attributable to a future deductible amount and operating loss carryforward A Deferred Tax Asset arises from the following a. When taxable income is higher than accounting income because of timing difference b. When tax base of asset is higher than the carrying amount c. When the tax base of a liability is lower than the carrying amount Taxable Income Higher than Accounting Income Temporary Differences that result in accounting income higher than taxable income because of timing differences include the following: 1. Revenues and gains are included in taxable income of current period but are included in accounting income of future periods ○ EXAMPLE: Rent received in advance is taxable at the time of receipt but deferred in future periods for accounting purposes - NOTE: Cash received in advance for revenue purposes is taxable in the period it is received but deferred in future period for accounting purposes 2. Expenses and Losses are deducted from accounting income of current period but are deductible for tax purposes in future periods - Future Deductible temporary Differences a. A probable and measurable litigation loss is recognized for accounting purposes but deducted in determining taxable income when actually incurred or paid b. Estimated product warranty cost is recognized for accounting purposes in the current period but deducted in determining taxable income when actually incurred or paid c. Research cost is recognized as expense in determining accounting income but not permitted as a deduction in determining taxable income until a later period d. An impairment loss is recognized for accounting purposes but ignored for tax purposes until the asset is sold e. Doubtful accounts are recognized as expense for accounting purpose but deductible for tax purposes only when written off as worthless Other Deductible Temporary Differences - Taxable temporary differences that technically are not timing differences but give rise to deferred tax asset a. Asset is revalued downward and no equivalent adjustment is made for tax purposes b. The tax base of investment in subsidiary, associate or joint venture is higher than the carrying amount because the subsidiary, associate or joint venture has suffered continuing losses in current and prior years Recognition of Deferred Tax Asset PAS 12, p4 - deferred tax asset shall be recognized for all deductible temporary differences and operating loss carryforward when it is probable that taxable income will be available against which the deferred tax asset can be used Operating Loss Carryforward - An excess of tax deductions over gross income in a year that may be carried forward to reduce taxable income in a future year Note: Certain entities registered with the Board of Investments are permitted to carry over net operating loss for tax purposes subject to limitations of the relevant law and implementing regulations of the Board of Investment Methods of Accounting A. Income Statement Approach ○ Focuses on timing differences only in the computation of deferred tax asset or deferred tax liability ○ Timing differences affect the income statement of one period and will reverse in the income statement of one or more subsequent periods B. Statement of Financial Position Approach ○ Considers all temporary differences including timing differences ○ There are temporary differences that affect the statement of financial position only and therefore technically are not timing differences but nonetheless are recognized in computing deferred tax asset or deferred tax liability New Section 6 Page 3 recognized in computing deferred tax asset or deferred tax liability Current Tax Liability and Current Tax Asset • Current Tax Liability - The current tax expense or the amount of income tax actually payable and appropriately classified as current liability • Under our income tax law, income tax for corporations is payable every quarter • If the amount of tax already paid for the current period exceeds the amount actually payable for the current period, the excess is recognized as a current tax asset • Current Tax Asset - a prepaid income tax and shall be classified as current asset • A current tax liability or current tax asset shall be measured using the tax rate that has been enacted and effective at the end of the reporting period Presentation of Deferred Tax Assets or Liability - PAS 12, par.70- An entity makes a distinction between current and noncurrent assets and liabilities, it shall not classify deferred tax assets as current assets and tax liabilities as current liabilities - Accordingly, a deferred tax asset shall be classified as noncurrent asset and a deferred tax liability shall be classified as noncurrent liability regardless of reversal period - Moreover, a deferred tax asset or deferred tax liability shall not be discounted Offset of Deferred Tax Asset and Liability Under PAS 1, assets and liabilities shall not be offset unless required or permitted by another standard PAS 12, par74 - provides that an entity shall offset a deferred tax asset against a deferred tax liability when: a. The deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability relate to income taxes levied by the same tax authorities b. The entity has a legal enforceable right to set off a current tax asset against a current tax liability Measurement of Deferred Tax Asset and Liability - Shall be measured using the tax rate that has been enacted by the end of the reporting period and expected to apply to the period when the asset is realized or the liability is settled Intraperiod and Interperiod Tax Allocation Intraperiod Tax Allocation - The allocation of income tax expense to the various revenues that brought about the tax - The total income tax expense is allocated to income from continuing operations, income from discontinued operations and prior periods errors or items directly charge or credited to retained earnings Interperiod tax allocation - the recognition of a deferred tax asset or deferred tax liability Statement Of Financial Position Approach To account for a deferred tax asset or liability, a statement of financial position that shows all the assets and liabilities at their carrying amount is first prepared. The Following Procedures are then followed: 1. Determine the tax base of the assets and liabilities in the statement of financial position 2. Compare the carrying amounts with the tax base 3. The difference between the carrying amount and tax base normally will result to a deferred tax asset or liability 4. Permanent differences do not give rise to deferred tax asset or liability 5. Apply the tax rate to the future temporary differences 6. Determine the beginning and ending balance of deferred tax asset or liability 7. Recognize the net change between the beginning and ending balance of deferred tax asset or liability Disclosures 1. Components of the total income tax expense, for example, current tax expense, deferred tax expense, and deferred tax benefit 2. An explanation of the relationship between total income tax expense and accounting income New Section 6 Page 4 income - NOTE: This essentially disclose the accounting income subject to tax which is the accounting income after considering permanent differences 3. The applicable tax rate, the basis on whichthe tax rate has been applied, and the explanation any change in the applicable tax rate. 4. The aggregate amount of temporary differences associated with investments in subsidiary, associate and joint venture for which no deferred tax liability has been recognized 5. Analysis of the beginning and ending balance of deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability+ New Section 6 Page 5