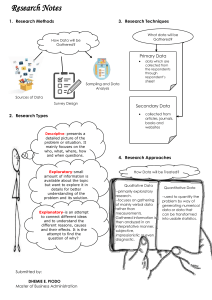
INTRODUCTION OF STATISTICS MEANING OF STATISTICS Statistics is a branch of applied mathematics that involves the collection, description, analysis, and inference of conclusions from quantitative data. The mathematical theories behind statistics rely heavily on differential and integral calculus, linear algebra, and probability theory. MEANING OF STATISTICS IN EDUCATION It refers to techniques or methods relating to the collection, classification, presentation, analysis, and interpretation of quantitative data. Statistics may be defined as the collection, presentation, analysis, and interpretation of numerical data. Statistics simply means numerical data and is the field of math that generally deals with the collection of data, tabulation, and interpretation of numerical data. It is actually a form of mathematical analysis that uses different quantitative models to produce a set of experimental data or studies of real life. DEFINITION OF STATISTICS IN RESEARCH Statistics is a branch of science that deals with the collection, organization, and analysis of data and drawing inferences from the samples to the whole population. This requires a proper design of the study, an appropriate selection of the study sample, and the choice of a suitable statistical test. IMPORTANCE OF STATISTICS It provides the exact description and a better understanding. It helps in designing the effective and proper planning of the statistical inquiry in any field. It gives valid inferences with reliability measures about the population parameters from the sample data. IMPORTANCE OF STATISTICS IN OUR DAILY LIFE It keeps us informed about, what is happening in the world around us. Statistics are important because today we live in the information world and much of this information's determined mathematically by Statistics. It means to be informed correct data and statistics concepts are necessary. IMPORTANCE OF STATISTICS IN BUSINESS Statistical research in business enables managers to analyze past performance, predict future business practices, and lead organizations effectively. Statistics can describe markets, inform advertising, set prices, and respond to changes in consumer demand. TRANSCRIBED BY: COSAIN, JUHAIMA P. IMPORTANCE OF STATISTICS IN MEDICINE Health statistics are used to understand risk factors for communities, track and monitor diseases, see the impact of policy changes, and assess the quality and safety of health care. Health statistics are a form of evidence or facts that can support a conclusion. IMPORTANCE OF STATISTICS IN BUSINESS AND FINANCE Statistics important in Business statistics offers data to managers who help them to make successful decisions based on fundamental values rather than intuitions. Statistics is used to analyze the data and make interpretations, whether for sales estimation, introducing a new product line, making new production strategies, etc. IMPORTANT TERMS IN STATISTICS Population Sampling Sample Variables Data THE TWO BASIC DIVISIONS OF STATISTICS Descriptive and Inferential Statistics The two major areas of statistics are known as: 1) Descriptive statistics, which describes the properties of sample and population data Descriptive statistics include mean (average), variance, skewness, and kurtosis. 2) Inferential statistics, which uses those properties to test hypotheses and draw conclusions. MEANING OF DATA Data are individual pieces of factual information recorded and used for the purpose of analysis. It is the raw information from which statistics are created. Statistics are the results of data analysis - its interpretation and presentation. DATA TYPES IN STATISTICS Quantitative data and qualitative data. This highest level of classification comes from the fact that data can either be measured or can be an observed feature of interest. Qualitative data are also referred to as categorical data. Quantitative data is provided in numerical form, like the weight, volume, or cost of an item. Qualitative data is descriptive, but non-numerical, like the name, sex, or eye color of a person. TRANSCRIBED BY: COSAIN, JUHAIMA P. MEANING OF DATA AND VARIABLES IN STATISTICS Data refers to a set of values, which are usually organized by variables (what is being measured) and observational units (members of the sample/population). MEANING OF INFORMATION Information is defined as knowledge gained through study, communication, research, or instruction. Essentially, information is the result of analyzing and interpreting pieces of data. Whereas data is individual figures, numbers, or graphs, information is the perception of those pieces of knowledge. For example, a set of data could include temperature readings in a location over several years. Without any additional context, those temperatures have no meaning. However, when you analyze and organize that information, you could determine seasonal temperature patterns or even broader climate trends. Only when the data is organized and compiled in a useful way can it provide information that is beneficial to others. THE KEY DIFFERENCES BETWEEN DATA vs. INFORMATION Data is a collection of facts, while information puts those facts into context. While data is raw and unorganized, information is organized. Data is defined as a collection of individual facts or statistics. (While “datum” is technically the singular form of “data,” it’s not commonly used in everyday language.) Data can come in the form of text, observations, figures, images, numbers, graphs, or symbols. For example, data might include individual prices, weights, addresses, ages, names, temperatures, dates, or distances. Data is a raw form of knowledge and, on its own, doesn’t carry any significance or purpose. In other words, you have to interpret data for it to have meaning. Data can be simple—and may even seem useless until it is analyzed, organized, and interpreted. TRANSCRIBED BY: COSAIN, JUHAIMA P. Data is a collection of facts, while information puts those facts into context. While data is raw and unorganized, information is organized. Data points are individual and sometimes unrelated. Information maps out that data to provide a big-picture view of how it all fits together. Data, on its own, is meaningless. When it’s analyzed and interpreted, it becomes meaningful information. Data does not depend on information; however, information depends on data. Data typically comes in the form of graphs, numbers, figures, or statistics. Information is typically presented through words, language, thoughts, and ideas. Data isn’t sufficient for decision-making, but you can make decisions based on information. MAIN SOURCES OF DATA Data can be gathered from two places: internal and external sources. The information collected from internal sources is called “primary data,” while the information gathered from outside references is called “secondary data”. In data analysis, it must be collected through primary or secondary research. THE SIX (6) SOURCES OF DATA The most commonly used methods are: 1)published literature sources, surveys (email and mail), interviews (telephone, face-to-face, or focus group), observations, documents and records, and experiments. WHAT IS DATA COLLECTION? Data collection is a systematic method of collecting and measuring data gathered from different sources of information in order to provide answers to relevant questions. An TRANSCRIBED BY: COSAIN, JUHAIMA P. accurate evaluation of collected data can help researchers predict future phenomenon and trends. Data collection can be classified into two, namely: primary and secondary data. Primary data are raw data i.e. fresh and are collected for the first time. Secondary data, on the other hand, are data that were previously collected and tested. METHODS OF DATA COLLECTION The system of data collection is based on the type of study being conducted. Depending on the researcher’s research plan and design, there are several ways data can be collected. The most commonly used methods are: published literature sources, surveys (email and mail), interviews (telephone, face-to-face or focus group), observations, documents and records, and experiments. 1. Literature sources This involves the collection of data from the already published text available in the public domain. Literature sources can include textbooks, government or private companies’ reports, newspapers, magazines, online published papers, and articles. This method of data collection is referred to as secondary data collection. In comparison to primary data collection, it is inexpensive and not time-consuming. 2. Surveys The survey is another method of gathering information for research purposes. Information is gathered through a questionnaire, mostly based on individual or group experiences regarding a particular phenomenon. There are several ways by which this information can be collected. The most notable ways are web-based questionnaires and paper-based questionnaires (printed form). The results of this method of data collection are generally easy to analyze. 3. Interviews Interview is a qualitative method of data collection whose results are based on intensive engagement with respondents about a particular study. Usually, interviews are used in order to collect in-depth responses from the professionals being interviewed. Interviews can be structured (formal), semi-structured, or unstructured (informal). In essence, an interview method of data collection can be conducted through face-to-face meetings with the interviewee(s) or through telephone. 4. Observations Observation method of information gathering is used by monitoring participants in a specific situation or environment at a given time and day. Basically, researchers observe the behavior of the surrounding environments or people that are being studied. This type of study can be controlled, natural or participant. Controlled observation is when the researcher uses a standardized procedure of observing participants or the environment. Natural observation is when participants are being TRANSCRIBED BY: COSAIN, JUHAIMA P. observed in their natural conditions. Participant observation is where the researcher becomes part of the group being studied. 5. Documents and records This is the process of examining existing documents and records of an organization for tracking changes over a period of time. Records can be tracked by examining call logs, email logs, databases, minutes of meetings, staff reports, information logs, etc. For instance, an organization may want to understand why there are lots of negative reviews and complaints from customers about its products or services. In this case, the organization will look into records of their products or services and recorded interactions of employees with customers. 6. Experiments Experimental research is a research method where the causal relationship between two variables are being examined. One of the variables can be manipulated, and the other is measured. These two variables are classified as dependent and independent variables. In experimental research, data are mostly collected based on the cause and effect of the two variables being studied. This type of research is common among medical researchers, and it uses a quantitative research approach. TRANSCRIBED BY: COSAIN, JUHAIMA P.