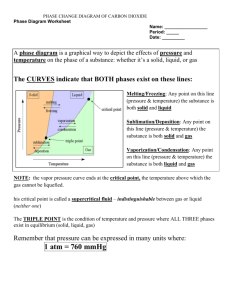
Name: ___________________________________________________ Date: _______________________________ Period: ________ PHASE DIAGRAMS WORKSHEET NOTE: “Normal” refers 1 atm = 101.3 kpa = 760 mmHg Part A – Generic Phase Diagram. Answer questions 1 – 10 in relation to the following generic phase diagram. 1. Which section represents the solid phase? ___________ 2. What section represents the liquid phase? __________ 3. What section represents the gas phase? ____________ 4. What letter represents the triple point? ____________ In your own words, what is the definition of a triple point? _______________________________________________ 5. What is this substance’s normal melting point, at 1 atmosphere of pressure? __________________________ 6. What is this substance’s normal boiling point, at 1 atmosphere of pressure? ___________________________ 7. Above what temperature is it impossible to liquefy this substance, no matter what the pressure? __________________ 8. At what temperature and pressure do all three phases coexist? ____________________________________________ 9. At a constant temperature, what would you do to cause this substance to change from the liquid phase to the solid phase? ________________________________________________________________________________________ 10. What does sublimation mean? _____________________________________________________________________ Part B – Phase Diagram for Water. 11. 12. 13. At a pressure of 1 atmosphere, what is the normal freezing point of water? _____________________ What is the normal boiling point of water, at one atmosphere of water? ______________________ People in Albuquerque live approximately 5,500 feet above sea level, which means the normal atmospheric pressure is less than 1 atm. In Albuquerque, will water freeze at a lower temperature or a higher temperature than at 1 atmosphere? __________________ Will water boil at a higher or lower temperature, than at 1 atmosphere? ___________________ Part C – Phase Diagram for Carbon Dioxide. 14. 15. At 1 atmosphere and room temperature (25C), would you expect solid carbon dioxide to melt to the liquid phase, or sublime to the gas phase? ______________ Some industrial processes require carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide is stored on-site in large tanks as liquid carbon dioxide. Assuming we lived at sea level (1 atm), how could carbon dioxide be liquefied? _________________________________ Part D - Refer to the phase diagram below when answering the questions: 15. What is the normal freezing point of this substance? ________ 16. What is the normal boiling point of this substance? ________ 17. What is the normal melting point of this substance? ________ 18. What is the phase (s, l, g) of a substance at 2.0 atm and 100 °C? _________ 19. What is the phase (s, l, g) of a substance at 0.75 atm and 100 °C? _________ 20. What is the phase (s, l, g) of a substance at 0.5 atm and 100 °C? _________ 21. What is the phase (s, l, g) of a substance at 1.5 atm and 50 °C? _________ 22. What is the phase (s, l, g) of a substance at 1.5 atm and 200 °C? _________ 23. What is the phase (s, l, g) of a substance at 1.5 atm and 800 °C? _________ 24. What is the condition of the triple point of this substance? T= ________, P= _______ 25. If a quantity of this substance was at an initial pressure of 1.25 atm and a temperature of 3000 C was lowered to a pressure of 0.25 atm, what phase transition(s) would occur? ____________ 26. If a quantity of this substance was at an initial pressure of 1.25 atm and a temperature of 00 C was lowered to a pressure of 0.25 atm, what phase transition(s) would occur? ____________ 27. If a quantity of this substance was at an initial pressure of 1.0 atm and a temperature of 2000 C was lowered to a temperature of -2000 C, what phase transition(s) would occur? ____________ 28. If a quantity of this substance was at an initial pressure of 0.5 atm and a temperature of 2000 C was lowered to a temperature of -2000 C, what phase transition(s) would occur? ____________ 29. Label the melting and freezing points on the graph. 30. Label the vaporization and condensation points on the graph. 31. Label the sublimation and deposition points on the graph. 32. Label the triple point on the graph. 33. Label the critical point on the graph.