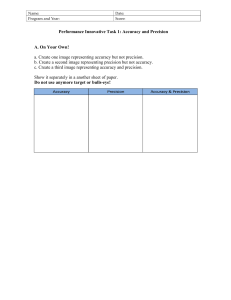
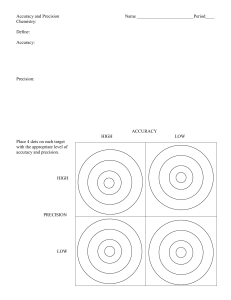
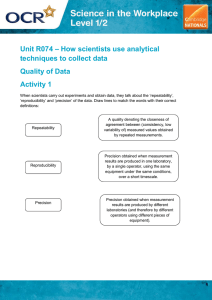
Subject: Science Grade Level: Grade 7 Objective: Differentiate accuracy and precision by citing examples. Learning across the curriculum: 1. Mathematics - Measurement and estimation 2. English - Writing a scientific explanation 3. Technology and Livelihood Education - Using measuring tools accurately Elicit: - Ask students if they have ever encountered situations where they needed to measure something precisely. Translate to English. Engage: 1. Show a video clip demonstrating the importance of accuracy and precision in scientific measurements. Translate to English. 2. Conduct a class discussion on the potential consequences of inaccurate measurements in various fields, such as medicine, engineering, and cooking. Translate to English. 3. Present real-life examples where accuracy and precision are crucial, such as measuring ingredients for a baking recipe or calculating the dosage of medication. Translate to English. Explore: Activity 1: Measuring Accuracy Materials: Various measuring tools (ruler, measuring tape, weighing scale, graduated cylinder, etc.), objects to measure (pencils, books, water, etc.) Instructions: In pairs, students will measure the objects using different tools and record their measurements. They will then compare their measurements with the actual values and determine the accuracy of each measurement. Rubric: Accuracy of measurements (5 points), recording of data (3 points) Assessment Questions: 1. How does accuracy differ from precision in measurements? 2. What factors can affect the accuracy of a measurement? Activity 2: Precision Experiment Materials: Small objects (paperclips, marbles, etc.), ruler, stopwatch Instructions Students will work individually or in small groups to measure the length of the objects using a ruler. They will repeat the measurements multiple times and calculate the average length. They will then discuss the precision of their measurements and identify any sources of error. Rubric: Precision of measurements (5 points), calculation of average (3 points) Assessment Questions: 1. How does precision contribute to the reliability of measurements? 2. What are some sources of error that can affect the precision of measurements? Activity 3: Accuracy vs. Precision Quiz Materials: Quiz questions, answer sheets Instructions: Students will answer a quiz that includes questions related to accuracy and precision in measurements. Rubric: Correctness of answers (5 points), explanation of concepts (3 points) Assessment Questions: 1. Define accuracy and provide an example. 2. Explain the difference between accuracy and precision using a real-life scenario. Explain: 1. Teacher-led explanation of accuracy and precision using visuals and examples. Translate to English. 2. Small group discussions where students explain the concept to their peers. Translate to English. Elaborate: 1. Conduct a hands-on experiment where students measure the volume of different liquids using graduated cylinders and compare their results. Translate to English. 2. Assign students to create a poster or infographic that explains the importance of accuracy and precision in scientific measurements. Translate to English. Evaluate: 1. Observe students during the exploration activities and assess their understanding of accuracy and precision through questioning. Translate to English. 2. Review and provide feedback on the accuracy vs. precision quiz. Translate to English. Extend: - Conduct a class debate on the importance of accuracy vs. precision in scientific research. Translate to English. Assignment: Write a short reflection paper discussing a real-life situation where accuracy and precision are crucial. Translate to English.