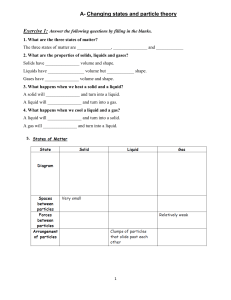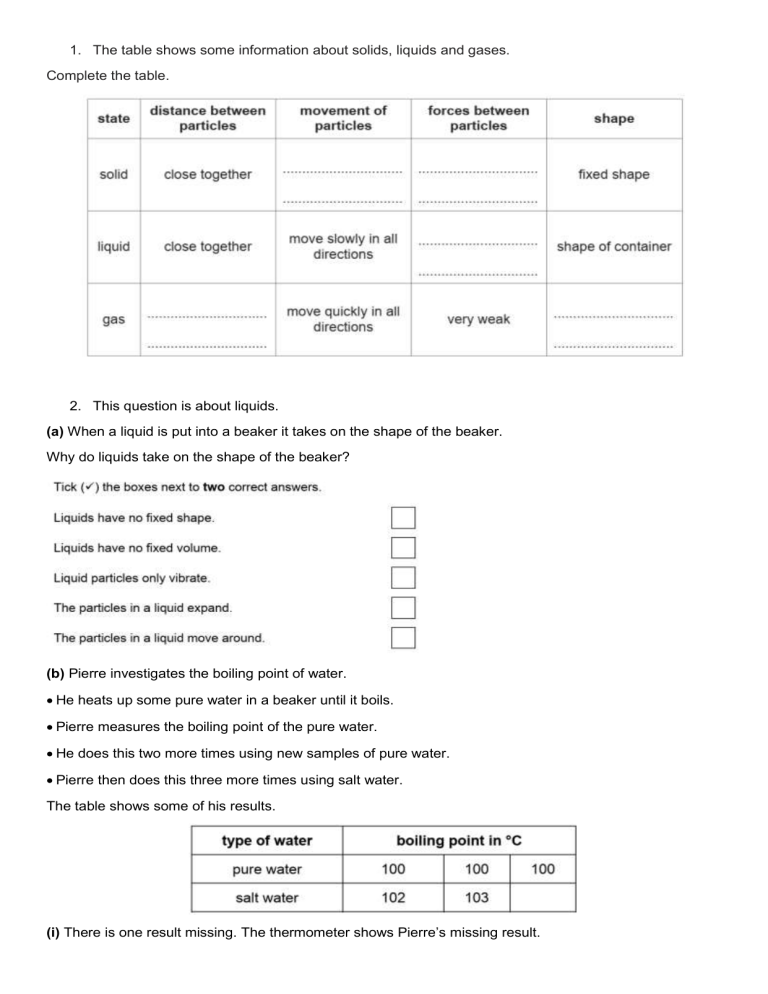
1. The table shows some information about solids, liquids and gases. Complete the table. 2. This question is about liquids. (a) When a liquid is put into a beaker it takes on the shape of the beaker. Why do liquids take on the shape of the beaker? (b) Pierre investigates the boiling point of water. He heats up some pure water in a beaker until it boils. Pierre measures the boiling point of the pure water. He does this two more times using new samples of pure water. Pierre then does this three more times using salt water. The table shows some of his results. (i) There is one result missing. The thermometer shows Pierre’s missing result. What is the temperature on the thermometer? ______________ (ii) What effect does adding salt have on the boiling point of water? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. This question is about the three states of matter. (a) Which state of matter has the strongest forces between its particles? ___________________________ (b) Draw straight lines to match the state of matter with the description of the spacing of the particles. 4. Aiko and Carlos are investigating states of matter. They do three tests on five different substances. Test 1 Fill a syringe with the substance and try to squash it. Test 2 Put the substance into a beaker. Test 3 Heat the substance in an evaporating dish. Here are their results. Use their results to answer these questions. (a) Which substance is a gas? Choose from A, B, C, D or E. ________ (b) Which two substances are solids? Choose from A, B, C, D and E. ________ and ________ 5. Look at the diagrams. They show the arrangement of particles in solids, liquids and gases. Look at the statements about solids, liquids and gases. A are usually hard B take the shape of the container they are put into C can be compressed (squashed) D completely fill any container they are put into E have a fixed shape F cannot flow easily (a) Complete the table by putting the letter for each statement into the correct column.