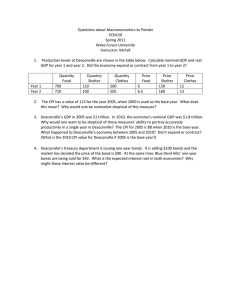
MGEB05 Week 1 1 Brief Summary of Week 1 Pre-recorded Lectures Gross Domestic Product • Gross domestic product (GDP) is the market value of all final goods and services produced within the economy during a given year. • According to the expenditure approach, GDP consists of 4 components: 1) Consumption (C): spending by households on goods and services. 2) Investment (I): spending on capital equipment, inventories; I = business fixed investment + residential investment + inventory investment. 3) Government spending (G): spending on goods and services by all levels of governments (excludes transfer payments such as EI). 4) Net exports (NX): exports – imports. GDP = C + I + G + X – IM = C + I + G + NX Nominal GDP vs. Real GDP • Nominal GDPt (NGDPt) = P1,tQ1,t + P2,tQ2,t …+ Pn,tQn,t = ∑𝑛𝑖=1 𝑃𝑖,𝑡 𝑄𝑖,𝑡 • Real GDPt (RGDPt) = P1,Base yearQ1,t + P2,Base yearQ2,t …+ Pn, Base yearQn,t = ∑𝑛𝑖=1 𝑃𝑖,𝐵𝑎𝑠𝑒 𝑦𝑒𝑎𝑟 𝑄𝑖,𝑡 • GDP deflatort = 𝑁𝑜𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝐺𝐷𝑃𝑡 𝑅𝑒𝑎𝑙 𝐺𝐷𝑃𝑡 × 100 MGEB05 Week 1 2 The consumer price index (CPI) • Cost of baskett: COBt = ∑𝑛𝑖=1 𝑃𝑖,𝑡 𝑄𝑖,𝐵𝑎𝑠𝑒 𝑦𝑒𝑎𝑟 • CPI in year t = Cost of (fixed) market basket in year t Cost of (fixed) market basket in base year × 100 • CPI is not a perfect measure of the cost of living because It ignores the substitution effect. It ignores the introduction of new products. It fails to capture changes in quality of goods. The GDP Deflator versus the Consumer Price Index • Although both the GDP deflator and the CPI measure the overall price levels, they are not necessarily be the same. CPIt = 𝐶𝑂𝐵𝑡 𝐶𝑂𝐵𝐵𝑎𝑠𝑒−𝑦𝑒𝑎𝑟 GDP deflatort = × 100 = = 𝑁𝑜𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝐺𝐷𝑃𝑡 𝑅𝑒𝑎𝑙 𝐺𝐷𝑃𝑡 ∑𝑛𝑖=1 𝑃𝑖,𝑡 𝑄𝑖,𝐵𝑎𝑠𝑒 𝑦𝑒𝑎𝑟 ∑𝑛𝑖=1 𝑃𝑖,𝐵𝑎𝑠𝑒 𝑦𝑒𝑎𝑟 𝑄𝑖,𝐵𝑎𝑠𝑒 𝑦𝑒𝑎𝑟 × 100 × 100 = × 100 ∑𝑛𝑖=1 𝑃𝑖,𝑡 𝑄𝑖,𝑡 ∑𝑛𝑖=1 𝑃𝑖,𝐵𝑎𝑠𝑒 𝑦𝑒𝑎𝑟 𝑄𝑖,𝑡 × 100