Atomic Number & Element Synthesis: Periodic Table Concepts
advertisement

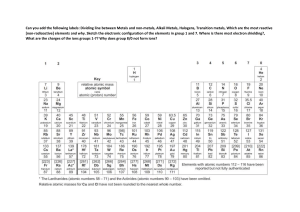
Concept of Atomic Number that Led to the Synthesis of New Elements in the Laboratory INTRODUCTION QUARTER 1- MODULE 2 PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS is a rows and columns arrangement of the chemical elements. It is widely used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences, and is generally seen as an icon of chemistry. KEY POINTS: Henry Gwyn-Jeffreys Moseley was an English physicist who demonstrated that the atomic number, the number of protons in an atom, determines most of the properties of an element. KEY POINTS: In 1919, Ernest Rutherford successfully carried out a nuclear transmutation reaction a process of transforming one element or isotope into another element KEY POINTS: Dmitri Mendeleev created a classification of elements based on their atomic weight. He found that organizing the elements at the time by their calculated weight demonstrated a periodic pattern of both physical and chemical properties, such as luster, physical state, reactivity to water, and others. HOW TO READ PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS Group in Periodic Table Groups are the columns of the periodic table, and periods are the rows. There are 18 groups. The Alkali Metals (Group 1) The alkali metals consist of all of the elements in group one with the exception of hydrogen. These elements are extremely reactive and for this reason, are usually found in compounds. In addition, they are water-sensitive (they react violently with water), so they must be stored in oil. The most reactive alkali metal is francium and it decreases as you go up the group. This means lithium is the least reactive. Physically, the alkali metal family is silvery, white, and light. They also have low melting and low boiling points. The Alkaline Earth Metals (Group 2) The alkaline earth metals are the second most reactive family on the periodic table (following behind the alkali metals). Moreover, they are strong reducing agents which means they donate electrons in chemical reactions. They are also good thermal and electrical conductors. Physically, they have low density, low melting point, and a low The Transition Metals (Groups 3-11) The transition metals typically form two or more oxidation states. They have low ionization energies and high conductivity. In addition, they have high melting points, high boiling points, and high conductivity. Physically they are both metallic and Post Transition Metal The post transition metals are located in between the transition metals and the metalloids. At standard temperature, they are in a solid state of matter. They tend to have a high density as well as high conductivity. Physically they are malleable and ductile. The Metalloids The metalloids display properties of both metals and non-metals. For example, metals are good conductors and non-metals are poor conductors. This means metalloids are semiconductors (only conducts electricity at high temperatures.). Also, they are more brittle than metals but less brittle than non-metals. Physically they can be either shiny or dull and are typically ductile and malleable. The Halogens (Group 17) The name halogen means “salt formers” in greek. This is evident in nature as halogens interact with metals to form various salts. On another note, the halogens are a unique group of elements. They are the only periodic family that contains elements in the three states of matter at standard temperature. There are 6 halogens and they are located in group 17. These elements include fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At). They are highly reactive, highly electronegative, and highly toxic non-metals. Noble Metals The noble metals consist of ruthenium (Ru), osmium (Os), rhodium (Rh), iridium (Ir), Pd, platinum (Pt), gold (Au), silver (Ag). Like the noble gases, they are inert due to having a complete valence shell. In addition, noble metals have catalytic tendencies. Also, they are very resistant to corrosion, tarnishing, and oxidation. Finally, like many of the other metals, they are soft and ductile. Noble Gases (Group 18) The noble gases, also called aerogens, are inert gases. Some examples include argon, krypton, and neon. They can be found in group eighteen on the periodic table. Likewise, this means they have a complete valence shell. For this reason, they are stable and relatively unreactive. Furthermore, the noble gases have low boiling points and low melting points. Physically they are colorless and have no smell. WHAT IS PERIOD? The elements are arranged in seven horizontal rows, in order of increasing atomic number from left to right and top to bottom. The rows are called periods, and they are numbered from 1 to 7 HOW TO READ ELEMENTS WHAT IS ATOMIC NUMBER? The atomic number is the number of protons (positively charged particles) in an atom. WHAT The IS ATOMIC MASS? atomic mass is a weighted average of all of the isotopes of that element, in which the mass of each isotope is multiplied by the abundance of that particular isotope.