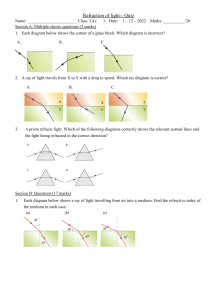
S3 Physics - Ch.17 Refraction of light 17.1 Refraction of light Light travels at different speeds in different media. At the boundary between two media, the light ray is bent away and the phenomenon is called refraction. Laws of Refraction Incident ray, refracted ray and normal are lie in same plan. The ration of sin I to sin r is a constant, i.e. (sin i/sin r) =constant. General form of Snell’s law Light ray travelling from medium 1 to medium 2. The general form of Snell’s law is Calculate method of the slope of graph: When comparing two media, the one with a larger refractive index is called the optically denser medium and the other is called the optically less dense medium. 1 17.2 Phenomena due to refraction of light Real depth = it is the actual depth which the body or container has Apparent depth = it is the depth which is visible or which is seen by us after the refraction, etc When an observer under water views some objects above the water surface, the image of the object appears farther to the observer than it actually is. Refraction in prism and dispersion 17.3 Total internal reflection When a light ray enters an optically less dense medium, it bends away from normal. As the angle of incidence increases, the angle of refraction also increase until it reaches 90°. In this case, the refracted ray travels along the boundary between two media. Critical angle and refractive index 2 17.4 Examples of total internal reflection Fish-eye view : Mirage Total internal reflection in prism Application of prisms 3 Total internal reflection in a diamond Prisms are used to reflect light because it can avoid the formation of multiple images, and the image formed is clearer. 4