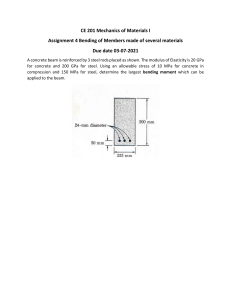
November 2023 – Eval Exam 2 Review Innovations INSTRUCTION: Select the correct answer for each of the following questions. Mark only one answer for each item by shading the box corresponding to the letter of your choice on the answer sheet provided. STRICTLY NO ERASURES ALLOWED.GOOD LUCK. INSTRUCTION: Select the correct answer for each of the following questions. GOOD LUCK. 1. Calculate the axial stiffness of a 3m long steel square hollow section (SHS) column, 200 mm on a side having a wall thickness of 6 mm. The modulus of elasticity for steel, E = 200 GPa. Hint: Corners of SHS are commonly rounded. To simplify the solution, assume that the corners are sharp. A. 157,600 kN/m C. 155,200 kN/m B. 310,400 kN/m D. 315,200 kN/m 2. A cantilever steel pipe pole, 3 meters high, has a diameter of 300mm and thickness of 6mm. A rigid beam, 1m long, is attached on the side of the pole on top, at the end of which, a horizontal load of 25 kN is applied. The shear modulus of the pipe material is 80 GPa. Determine the distance through which the end of the beam displaces due to torsion. A. 10.17 mm C. 1.17 mm B. 10.35 mm D. 1.35 mm Situation 1. Springs of a certain machine are fabricated using 2m long 12mm diameter high strength steel rods. The rods have an average shear modulus of 83 GPa. The deformation of springs is given by the following formula. δ 64PR n Gd 3. Calculate the maximum number of equal turns in a spring considering a mean diameter of 125mm. A. 6 C. 8 B. 7 D. 5 4. Find the value of the spring constant, k. A. 18.36 kN/m C. 15.74 kN/m B. 13.77 kN/m D. 22.03 kN/m 5. Determine the maximum shearing stress if during operation, the springs deflect by 50 mm. A. 212.64 MPa C. 132.91 MPa B. 177.22 MPa D. 151.93 MPa Situation 2. A cylindrical steel water tank is to be fabricated from 1.2 meter wide by 2.4m long steel sheets with a tensile strength of 414 MPa. The design diameter of the tank is 7.64 m and the design height including a freeboard of 0.6 m is 4.8 m. 6. Find the minimum number of steel sheets required for the wall of the tank. A. 35 C. 40 B. 45 D. 50 7. Determine the pressure at the bottom of the tank at the design capacity. A. 35.32 kPa C. 47.09 kPa B. 23.54 kPa D. 41.20 kPa 8. If after 15 years, the tank material is expected to corrode on the outside by 30% of the original thickness, determine the minimum thickness in order to maintain a safety factor for hoop stress of at least 4.5 at 15 years. A. 2.5 mm C. 2.25 mm B. 2.0 mm D. 2.80 mm Manila:https://www.facebook.com/ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao: https://www.facebook.com/reviewinnovations.davaobranch November 2023 – Eval Exam 2 Review Innovations Situation 3. A hoist beam, 1.5m long, is pin-connected to a column of an industrial building. To stabilize the system against the effect of the load W including the dynamic effects during lifting, the beam is provided with a 16mm diameter steel tension rod sloping by θ = 30 ° as shown in the figure below. Use E = 200 GPa. If the allowable axial strain in the rod is 0.0002 mm/mm, 30° 1.5m 9. Determine the allowable stress for the rod. A. 40.0 MPa C. 40.9 MPa B. 40.2 MPa D. 40.45 MPa W 10. Determine the allowable elongation for the rod. A. 0.354 mm C. 0.346 mm B. 0.348 mm D. 0.350 mm 11. If the dynamic effect of the load is taken into consideration by multiplying the lifted weight by 1.25, find the maximum weight that can be lifted. A. 512.3 kg C. 409.9 kg D. 329.5 kg B. 327.9 kg Situation 4. I-shaped steel beams 8m long pinned at the left end and supported by roller at 2m from the right end carry a one-way floor system with slabs spanning 3m on centers. The total load a slab panel carries is 10 kPa, including the weight of the slab. The properties of the I beams are as follows: A = 20,100 mm2 d = 328 mm Ix = 388 x 106 mm4 Unit weight of steel = 77 kN/m3 12. Determine the maximum positive moment in the beams. A. 112.2 kN m C. 121.2 kN m B. 106.7 kN m D. 107.6 kN m 13. Determine the maximum negative moment in the beams. A. 60.0 kN m C. 63.1 kN m B. 67.7 kN m D. 64.5 kN m 14. Determine the maximum flexural stress in the beams. A. 47.4 MPa C. 45.1 MPa B. 45.5 MPa D. 51.2 MPa 15. If the roller supports were moved to the right end of the beams, what would be the maximum flexural stress? A. 101.4 MPa C. 104.1 MPa B. 106.7 MPa D. 103.3 MPa 16. The reduction on the nominal strength of a tension-controlled section to achieve the design strength according to NSCP is ____. A. 65% C. 90% B. 35% D. 10% 17. Sections are tension-controlled if the net tensile strain in the extreme tension steel, εt, is equal to or greater than _____ when the concrete in compression reaches its assumed strain limit of 0.003. A. 0.002 C. 0.004 B. 0.003 D. 0.005 18. The type of beam section that has a ductile failure and will provide ample warning of failure with its noticeable deflection and cracking. A. Balance section C. Compression-controlled B. Over-reinforced section D. Under-reinforced Manila:https://www.facebook.com/ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao: https://www.facebook.com/reviewinnovations.davaobranch November 2023 – Eval Exam 2 Review Innovations Situation 5. Data of a beam section is given below. Beam width = 300 mm Effective depth = 420 mm Concrete fc’ = 35 MPa Steel fyl = 420 MPa Bar diameter = 20 mm 19. Based on the given dimensions and properties of materials, the code requires to provide a tension steel area (mm2) of at least? A. 425 C. 590 B. 385 D. 444 20. For the beam to be singly-reinforced, tension-controlled, the tension area (mm2) must not exceed? A. 3,169 C. 2,773 B. 2,677 D. 2,946 21. If the factored bending moment is 180 kN-m, determine the required number of tension bars. A. 2 C. 4 B. 3 D. 5 Situation 6. Data of a beam section is given below. B×H = 250 mm × 600 mm Bar diameter = 16 mm Clear concrete cover to 10 mm diameter ties = 40 mm Concrete fc’ = 35 MPa Steel fyl = 415 MPa ϕ=0.90 The beam is simply supported with a span of 6m. It will carry an 8.6 kN/m total factored dead load and 11.4 kN/m factored live load. 22. Which of the following most nearly gives the critical factored moment (kN-m). A. 90.0 C. 231.0 B. 128.5 D. 186.5 23. Determine the required number of tension bars. A. 2 C. 4 B. 3 D. 5 24. If a 20 kN service live load is added at midspan, determine the required number of tension bars. A. 3 C. 5 B. 4 D. 6 Situation 7. A 6m reinforced concrete simply supported beam is 300 mm wide with an effective depth of 400 mm. Use f’c= 21.5 MPa and fy = 415 MPa. The section is reinforced with 6– ϕ20mm tension bars. Use 2010/2015 NSCP. 25. At failure, determine the stress in the tension steel. A. 527 MPa C. 378 MPa B. 830 MPa D. 415 MPa 26. Calculate the design flexural strength (kN-m) of the section. A. 257.1 C. 179.4 B. 212.6 D. 231.4 27. Determine the factored live load (kN/m) the beam can support if total factored dead load is 20 kN/m. A. 17.0 C. 19.8 B. 27.2 D. 31.4 Manila:https://www.facebook.com/ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao: https://www.facebook.com/reviewinnovations.davaobranch November 2023 – Eval Exam 2 Review Innovations Situation 8. A T-beam section has a flange width of 600 mm, flange thickness of 100 mm, width of web of 350 mm, effective depth of 480 mm and a total depth of 550 mm. Use f’c = 21 MPa and fy = 415 MPa. Tensile reinforcement is 4 - 28mm. Use 0.90 as a strength reduction factor. Use 2010/2015 NSCP. 28. Calculate the depth (mm) of the concrete rectangular stress block. A. 110.87 C. 122.21 B. 67.56 D. 95.44 29. Determine the design flexural strength (kN-m) of the concrete beam section. A. 441.85 C. 577.34 B. 397.66 D. 267.55 30. Determine the total factored uniform load that the beam can support, if the beam is 8m, simply supported. A. 55.23 C. 72.16 B. 49.70 D. 33.44 Manila:https://www.facebook.com/ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao: https://www.facebook.com/reviewinnovations.davaobranch