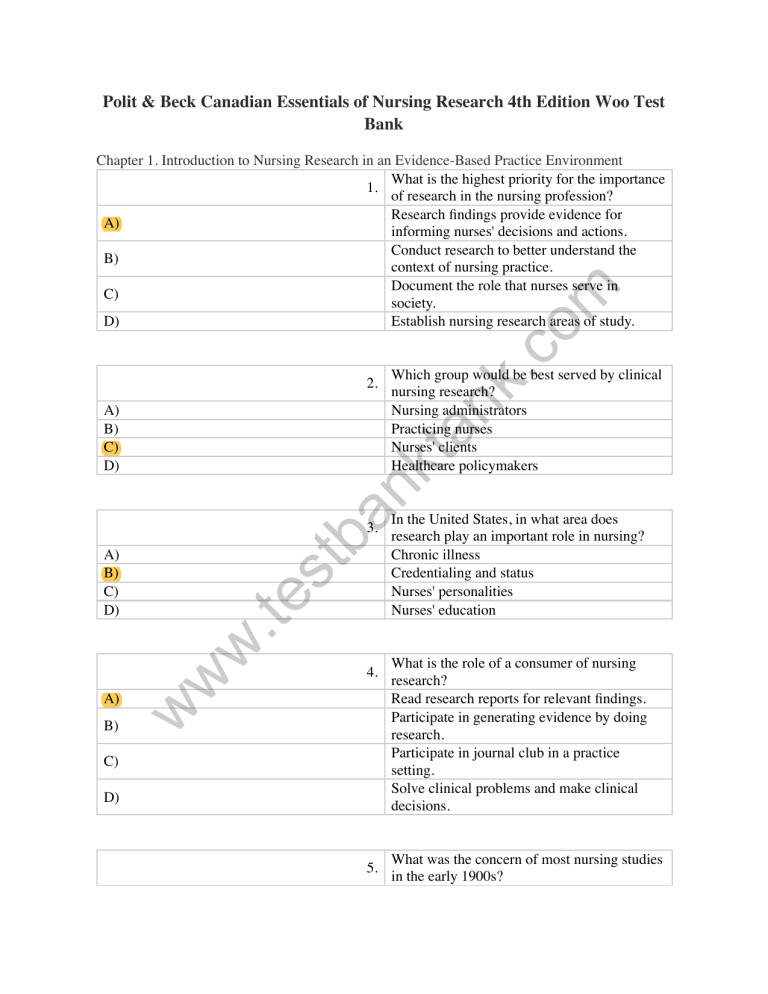
Polit & Beck Canadian Essentials of Nursing Research 4th Edition Woo Test Bank kt an k. c om Chapter 1. Introduction to Nursing Research in an Evidence-Based Practice Environment What is the highest priority for the importance 1. of research in the nursing profession? Research findings provide evidence for A) informing nurses' decisions and actions. Conduct research to better understand the B) context of nursing practice. Document the role that nurses serve in C) society. D) Establish nursing research areas of study. 2. ba n A) B) C) D) w .te w 4. w A) st 3. A) B) C) D) B) C) D) 5. A) B) C) D) Which group would be best served by clinical nursing research? Nursing administrators Practicing nurses Nurses' clients Healthcare policymakers In the United States, in what area does research play an important role in nursing? Chronic illness Credentialing and status Nurses' personalities Nurses' education What is the role of a consumer of nursing research? Read research reports for relevant findings. Participate in generating evidence by doing research. Participate in journal club in a practice setting. Solve clinical problems and make clinical decisions. What was the concern of most nursing studies in the early 1900s? Client satisfaction Clinical problems Health promotion Nursing education 5. A) B) C) D) Which topic most closely conforms to the 6. priorities that have been suggested for future nursing research? Attitudes of nursing students toward smoking. Promotion of excellence in nursing science. Nursing staff morale and turnover. Number of doctorate prepared nurses in various clinical specialties. om A) B) C) kt an k. c D) 7. What is the process of deductive reasoning? Verifying assumptions that are part of our heritage. Developing specific predictions from general principles. Empirically testing observations that are made known through our senses. Forming generalizations from specific observations. A) B) ba n C) w C) 8. w B) w .te st D) A) D) 9. A) B) C) D) What was the concern of most nursing studies in the early 1900s? Client satisfaction Clinical problems Health promotion Nursing education What is the ontological assumption of those espousing a naturalistic paradigm? Objective reality and those natural phenomena are regular and orderly. Phenomena are not haphazard and result from prior causes. Reality is multiply constructed and multiply interpreted by humans. Reality is not fixed, but is rather a construction of human minds. What is the epistemological assumption of those espousing a positivist paradigm? The researcher is objective and independent of those being studied. Phenomena are not haphazard, but rather have antecedent causes. The researcher instructs those being studied to be objective in providing information. Reality is not fixed, but is rather a construction of human minds. 9. A) B) C) D) 10. A) C) kt an k. c D) 11. What is empiricism? Making generalizations from specific observations. Deducing specific predictions from generalizations. Gathering evidence rooted in reality. Verifying the assumptions on which the study was based. A) B) ba n C) w w w .te st D) A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) Which is not a characteristic of traditional scientific method? Control over external factors. Systematic measurement and observation of natural phenomena. Deductive reasoning. Emphasis on a holistic view of a phenomenon, studied in a rich context. om B) those espousing a positivist paradigm? The researcher is objective and independent of those being studied. Phenomena are not haphazard, but rather have antecedent causes. The researcher instructs those being studied to be objective in providing information. Reality is not fixed, but is rather a construction of human minds. 12. What is a hallmark of the scientific method? Infallible Holistic Systematic Flexible Which of the following limits the power of 13. the scientific method to answer questions about human life? The necessity of departing from traditional beliefs. The difficulty of accurately measuring complex human traits. The inability to control potential biases. The shortage of theories about human behavior. 14. What is a criticism of the scientific method? Deductive Deterministic Empirical Reductionist A) B) C) D) 15. om A) B) What is involved in naturalistic qualitative research? Involves deductive processes Takes places in the field. Focuses on the idiosyncrasies of those being studied. Attempts to control the research context to better understand the phenomenon being studied. C) kt an k. c D) A researcher wants to investigate the effect of 16. patients' body position on blood pressure. This is an example of what type of study? Qualitative Constructivist inquiry Quantitative Researcher preference of either quantitative or qualitative ba n A) B) C) w w A) B) C) D) w .te st D) A) B) C) D) A researcher is studying the effect of massage 17. on the alleviation of pain in cancer patients. This is an example of what type of study? Descriptive Exploratory Applied Basic A researcher wants to study the process by which people make decisions about seeking 18. treatment for infertility. What is the researcher's paradigmatic orientation? Positivism Determinism Empiricism Naturalism 19. A) B) C) D) What is the continuum of participation on research? Academics to practitioners Consumers to producers Journalists to educators Mentors to novice nurses om 20. What is the goal of explanatory research? Understand the underpinnings of natural phenomena and to explain systematic relationships among them. Begins with the phenomenon of interest, but rather than simply observing and describing it, exploratory research investigates the full nature of the phenomenon, the manner in which it is manifested, and the other factors to which it is related. Study phenomena about which little is known. Make predictions and to control phenomena based on research findings. kt an k. c A) B) C) ba n D) w w w .te st Answer Key 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. A C B A D B B C A D C C B D B B C D B A 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. B D B B C D B A kt an k. c om Chapter 2. Fundamentals of Evidence-Based Nursing Practice Research utilization begins with empirical 1. findings for consideration in practice settings. Where does evidence-based practice begin? Integration of clinical judgments with A) research evidence A desire to abandon decisions based on B) custom and authority opinion A search for the best possible information for C) addressing a clinical problem D) A critique of existing practices 2. What is indirect research utilization? Involves changes in nurses' thinking Involves the direct use of findings in giving patient care Involves use of findings to persuade others Involves changes in patient thinking toward nurses A) B) ba n C) B) w C) w A) w .te st D) D) A) B) C) D) The student nurse is constructing a presentation on evidence-based practice. 3. Which statement should be included in the introduction about evidence-based practice? Conscientious integration of current best evidence with clinical expertise Utilization of nursing preferences in making clinical decisions Theoretical problem-solving strategy Emphasis on decision making based on custom Evidence-based practice typically involves weighing various types of evidence in an 4. effort to determine best evidence. Most evidence hierarchies put which systematic review at the pinnacle? Randomized controlled trials Program evaluations Clinical practice guidelines Meta-analyses of multiple clinical trials weighing various types of evidence in an 4. effort to determine best evidence. Most evidence hierarchies put which systematic review at the pinnacle? Randomized controlled trials Program evaluations Clinical practice guidelines Meta-analyses of multiple clinical trials A) B) C) D) The terms research utilization and evidencebased practice are sometimes used 5. synonymously. The two concepts are distinct. Where does research utilization start? Uses findings of a study that are related to the previous research of the topic. Emphasis is on translating historical knowledge into real-world applications. Use of a set of studies in a practical application unrelated to the original research. Critique of existing practical applications unrelated to historical research. om A) B) kt an k. c C) A) B) w .te w w A) st C) D) B) C) D) Which activity will limit researchers to 6. improve the prospect for evidence-based practice and research utilization? Conducting high-quality, methodologically sound studies Disseminating results to a broad audience Providing periodical available supports during regular work hours Discussing the clinical implications of their study results in their research reports ba n D) 7. Which is not a major barrier to evidencebased practice in nursing? The fact that many clinical nurses are not academically prepared to critically evaluate nursing research studies The support of organizations that reward nurses who engage in research utilization efforts The low number of replication of nursing studies that show promise for utilization The absence of quality, clinically relevant nursing studies There are several resources to support 8. evidence-based practice. What are care bundles? Rigorous integrations of research evidence from multiple studies of a topic Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines that combine a synthesis and appraisal of research evidence Set of interventions to treat or prevent a cluster of symptoms Meta-analysis or quantitative methods that integrate findings statistically A) B) C) om D) kt an k. c There are several resources to support 9. evidence-based practice. What is metasynthesis? Qualitative, narrative approach to integration of a study Quantitative method that integrate findings statistically Synthesis and appraisal of research evidence with specific recommendations Set of interventions to treat or prevent a cluster of symptoms A) B) ba n C) w w A) B) C) D) w .te st D) A) B) C) D) Several models of evidence-based practice have been developed. Which model focuses 10. on the use of research from the perspective of individual clinicians? ARCC Model Clinical Nurse Scholar Model Iowa Model Stetler Model A RN is putting research into practice. What 11. step of the process is involved with the validity of study findings? Framing an answerable clinical question Searching for relevant research evidence Appraising the evidence Integrating evidence with other factors B) C) D) A student nurse is trying to find out what a 12. mixed methods synthesis is. What is a mixed methods synthesis? Integrate and synthesize both quantitative and qualitative evidence. Integrate quantitative evidence. Integrate and synthesize qualitative evidence. Integrate qualitative evidence. A) B) C) D) Systematic reviews are published in professional journals. Which database 13. contains thousands of systematic reviews related to healthcare interventions? Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Campbell Collaboration Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Joanna Briggs Institute kt an k. c om A) ba n A) st B) w w w .te C) D) A) B) C) D) A) B) C) Clinical practice guidelines distill a large 14. body of evidence into a manageable form. Which describes clinical practice guidelines? Give general recommendations for evidencebased decision making. Address all of the issues relevant to a clinical decision. Guide clinical practice when there are a number of published articles. Completed by researchers. Which reference is a comprehensive reference resource that provides an array of clinical 15. information for nurses, including evidencebased care sheets, best practice guidelines, and point-of-care drug information? Clinical Evidence Evidence-based Nursing Worldviews on Evidence Based Nursing Nursing Reference Center Evidence-based practice writers distinguish 16. between background and foreground questions. What is a background question? Based on current best research evidence. Specific, detailed questions about a clinical problem. General, foundational questions about a clinical issue. D) Evidence-based practice writers distinguish 16. between background and foreground questions. What is a background question? Based on current best research evidence. Specific, detailed questions about a clinical problem. General, foundational questions about a clinical issue. Questions located on websites. A) B) C) D) Fineout-Overholt and Johnston recommended a 5-component scheme for formulating evidence-based practice questions, using the 17. acronym PICOT as a guide. Which two components are not always needed in this model? P and C I and O C and T P and O A) B) C) D) A nurse is putting research into practice. What 18. is the first step that should be considered in the process? Framing an answerable clinical question Searching for relevant research evidence Appraising and synthesizing the evidence Integrating evidence with other factors A) B) kt an k. c ba n st w .te w B) C) w A) om C) D) A) B) C) D) 19. Which occurs with individual evidence-based practice efforts? Tend to be less formalized approach than organizational evidence-based practice. Must take organizational factors into account. Must take interpersonal factors into account. Triggers for an individual project include pressing clinical problems. Appraisal of Guidelines Research and 20. Evaluation (AGREE) Instrument consists of ratings of quality on what type of scale? 4-point scale 5-point scale 6-point scale 7-point scale 20. Evaluation (AGREE) Instrument consists of ratings of quality on what type of scale? 4-point scale 5-point scale 6-point scale 7-point scale A) B) C) D) C A A A C C B C A D C A A B D C C A A A st ba n kt an k. c 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. om Answer Key w w w .te Chapter 3. Key Concepts and Steps in Quantitative and Qualitative Research A pediatric RN undertakes a study of the effect of low birth weight on infants' cognitive development. A developmental psychologist collaborates on the study. A second RN helps 1. by recruiting families into the study. A graduate student is asked to give statistical advice in analyzing the data. This is an example of what type of study? A) Multisite research B) Qualitative research C) Funded research D) Collaborative research A) B) C) D) Which term is not used by qualitative 2. researchers to refer to people who participate in a study? Informants Key informants Study participants Subjects A) B) C) D) Which term is used by both qualitative and 3. quantitative researchers to refer to the abstractions under study? Concept Construct Phenomenon Variable A) B) C) D) The RN is reading a research article. The 4. article talks about constructs. Which would most likely be called a construct? Gender Body temperature Uncertainty in illness Blood type w w A) B) C) D) w .te st ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) Which term is not used by qualitative 2. researchers to refer to people who participate in a study? Informants Key informants Study participants Subjects A) B) C) D) What is the dependent variable(s) in the research question “Is the quality of life of 5. nursing home residents affected by their functional ability or hearing acuity”? Quality of life Functional ability Hearing acuity Nursing home residents What is the independent variable in the hypothesis “Baccalaureate degree prepared 6. nurses will practice more rehabilitative nursing measures on a client in an ICU than will associate degree prepared nurses”? Associate degree prepared nurses Baccalaureate degree prepared nurses Rehabilitative nursing measures Type of educational background of nurses 7. A) B) C) D) om Which is a datum from a quantitative study of 8. the labor and delivery experiences of women over age 40? Length of time in labor 107 ounces Infant's Apgar score Vaginal versus cesarean delivery kt an k. c A) B) C) D) Which is a datum from a qualitative research 9. study on the labor and delivery experiences of women over age 40? 14.6 hours in labor 60-minute interviews 1 day after delivery “It was a lot more painful than I ever imagined.” 15 women with a vaginal delivery ba n A) B) st C) w w w .te D) A) B) C) D) Which pair of variables is there most likely to 10. be a relationship that could be described as causal? Degree of physical activity and heart rate Stress and coping style Age and health beliefs Parity and postpartum depression 11. A) B) C) D) What is the purpose of an operational definition in a quantitative study? State the theoretical meaning of the concept. Specify how a variable will be defined and measured. State the expected relationship between the variables under investigation. Designate the conceptual underpinnings of the variable. What is the basic distinction in quantitative studies? Quantitative and qualitative research Empirical and nonempirical research Experimental and nonexperimental research Population-based and sample-based research 12. A) B) C) D) Which is widely used by quantitative nurse researchers? Ask research questions Phenomenological Ethnographic Grounded theory A) B) C) D) What is the research tradition that is an 14. approach to understanding people's life experiences? Experimental Phenomenological Ethnographic Grounded theory w w A) B) C) D) w .te st ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) What is the research tradition that focuses on 13. understanding phenomena within a cultural context? Experimental Phenomenological Ethnographic Grounded theory What is the statement of the researcher's 15. expectations or predictions about relationships among study variables? Hypothesis Framework Research question Conceptual definition 16. A) B) C) D) What is the overall plan for answering the research question? Sampling plan Proposal Problem statement Research design What is the aggregate of those to whom a 17. researcher wishes to generalize study results called? Gate keepers Population Sample Consumers A) B) C) D) 18. kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) What is the research design in qualitative studies called? Experimental Narrative Interpretive Emergent 19. st ba n A) B) C) D) Where are registered nurses most likely to find research results? Conference presentations Journal articles Books Dissertations w .te A) 20. B) C) w w D) What is included in the methods section of a study? Review of the literature. Names of the statistical tests that are going to be used. Strategies used to address the problem. Discussion including recommendations for the research. Answer Key 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. D D A C A D B B C A C A om A C A D B B C A C A C B A D B D B C kt an k. c 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. w w A) B) C) D) w .te st ba n Chapter 4. Reading and Critiquing Research Articles Which electronic database is widely recognized as the premier source for 1. bibliographic coverage of the biomedical literature? A) CINAHL B) Health Source: Nursing/Academic Edition C) ProQuest D) MEDLINE A) B) C) D) The RN is doing a basic search of articles on nurses' stress in the ICU. In conducting a 2. subject search in an electronic database, what should the nurse type to initiate the search? An author's name Restrictions to the search A topic or keyword A mapping procedure In an electronic literature search, what is the researcher doing when she does not know the 3. precise keywords for retrieving information on a topic? Mapping Searching Restricting focus Copying A) B) C) D) 5. There are several strategies for finding studies on a topic. What is the ancestry approach? Search for articles that summarize prior research. Read the accompanying abstract to determine whether the article is pertinent to the topic. Tracking down earlier studies cited in a reference list of a report. Using a pivotal study to search forward to subsequent studies that cited it. kt an k. c A) What is a primary source for a research literature review? A description of a study written by researchers who did the study A summary of relevant research on the topic of interest A thesaurus that directs readers to subject headings germane to the topic Any journal article on a topic of interest om 4. B) C) st ba n D) C) w D) w B) w .te A) There are several strategies for finding studies 6. on a topic. What is the descendancy approach? Search for articles that summarize prior research. Read the accompanying abstract to determine whether the article is pertinent to the topic. Track down earlier studies cited in a reference list of a report. Use a pivotal study to search forward to subsequent studies that cited it. 7. A) B) C) D) What is a secondary source for a research literature review? A description of a study written by researchers who did the study A summary of relevant research on the topic of interest A thesaurus that directs readers to subject headings germane to the topic A description of the study by an individual unconnected with it A) researchers who did the study A summary of relevant research on the topic of interest A thesaurus that directs readers to subject headings germane to the topic A description of the study by an individual unconnected with it B) C) D) The nurse is conducting a literature review. 8. Which will not assist the nurse when conducting a literature review? One major purpose of a literature review is to learn what research has already been done in the area. A text word search allows searchers to look for specific words in all test fields of records in the electronic database. The literature review section should conclude with a critical evaluation of knowledge on the problem of interest. Information from anecdotal and opinion articles is usually included in research literature. om A) B) kt an k. c C) D) w .te w w B) st A) B) C) D) A) C) D) There are several major steps in preparing a written research review. What is the first step? Formulating a question Devising a search strategy Conducting a search Retrieving relevant sources ba n 9. When doing a literature review, what type of 10. information will a researcher undertaking a new study find as an undesirable attribute? Available research findings Descriptions of an expert's opinions about the phenomenon How the variables of interest have been operationally defined in prior studies What research approaches have been used to study similar problems Qualitative researchers have varying opinions about reviewing the literature before doing a 11. new study. What group of researchers is represented when collection of data occurs before reviewing the literature? Grounded theory researchers Phenomenologists Ethnographogists Grounded theory researchers and phenomenologist A) B) C) om D) kt an k. c Qualitative researchers have varying opinions about reviewing the literature before doing a 12. new study. What group of researchers often undertakes a search for relevant materials at the onset of a study? Grounded theory researchers Phenomenologists Ethnographogists Grounded theory researchers and phenomenologist A) B) C) w D) w A) B) C) w .te st ba n D) A) B) C) D) Qualitative researchers have varying opinions about reviewing the literature before doing a new study. What group of researchers does a 13. more thorough literature review during data analysis and interpretation so that findings can be compared with previous findings? Grounded theory researchers Phenomenologists Ethnographogists Grounded theory researchers and phenomenologist Matrices are a convenient means of abstracting and organizing information for a 14. literature review. How many dimension arrays are present? Two Three Four Five Matrices are a convenient means of abstracting and organizing information for a 15. literature review. When would a reviewer use an evaluation matrix? Record methodological features of a set of studies. Record research findings. Record quality assessment information. Facilitate thematic analysis of the retrieved information. A) B) C) om D) kt an k. c Matrices are a convenient means of abstracting and organizing information for a 16. literature review. When would a reviewer use a results matrix? Record methodological features of a set of studies. Record research findings. Record quality assessment information. Facilitate thematic analysis of the retrieved information. A) ba n B) C) w w A) B) C) D) w .te st D) A) B) C) D) Written literature reviews are undertaken for many different purposes. In a quantitative 17. research report, what section of the report would a review of prior research on the problem under study be located? Introduction Methods Results Discussion Written literature reviews are undertaken for many different purposes. In a research report, 18. what section of the report would limitations of the study be located? Introduction Methods Results Discussion A) B) C) D) Some features of an electronic search are 20. similar across databases. Which is an example of a wildcard symbol? And Not Or Question mark ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) Written literature reviews are undertaken for many different purposes. In a qualitative 19. research report, what section of the report would the thematic analysis of the data be presented? Introduction Methods Results Discussion w w w .te st Answer Key 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. D C A A C D D D A B A B C A C B A D C D Chapter 5. Ethics in Research 1. A) B) C) om D) What serves as the basis for regulations affecting research by the U.S. government? The Nuremberg Code The Declaration of Helsinki The Belmont Report The Code of Ethics of the American Psychological Association kt an k. c In response to human rights violations, various codes of ethics have been developed. 2. What was developed after Nazi atrocities were made public as an international effort to establish ethical standards? The Nuremberg Code The Declaration of Helsinki The Belmont Report The Code of Ethics of the American Psychological Association A) B) C) st ba n D) C) w D) w B) w .te A) A) B) C) D) What document covers primarily ethical 3. issues for practicing nurses and includes principles that apply to nurse researchers? Code of Ethics for Nurses with Interpretative Statements Ethical Research Guidelines for Registered Nurses Ethical Guidelines in the Conduct, Dissemination, and Implementation of Nursing Research ICN Code of Ethics for Nurses The Belmont Report articulated broad principles on which standards of ethical 4. conduct in research are based. Which is not considered an ethical principle for protecting study participants in the report? Beneficence Respect for human dignity Informed consent Justice 5. What is beneficence? Performance of some good Protection from physical and psychological harm and exploitation Participants right to self-determination Freedom to control their own actions A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) Which ethical principle may be violated if a 7. researcher unobtrusively studies interactions among patients in a psychiatric hospital? Confidentiality Freedom from harm Right to self-determination Right to privacy om C) D) 6. What is justice? Right to fair treatment Protection from physical and psychological harm and exploitation Participants right to self-determination Freedom to control their own actions A) w What is the safeguard mechanisms by which 8. even the researcher cannot link the participant with the information provided? Confidentiality Anonymity Informed consent Right to privacy w A) B) C) D) w .te st ba n kt an k. c B) A) B) C) D) What provides prospective participants with 9. information needed to make a reasoned decision about participation? Confidentiality Anonymity Informed consent Right to privacy 10. A) B) C) om D) 11. What is an example of a vulnerable group? Women hospitalized for a mastectomy Members of a senior citizen group People who do not speak English Pediatric clients kt an k. c A) B) C) D) 12. B) C) w w w .te st D) B) C) D) What is a major potential risk of research to participants? Monetary gains Access to a new and potentially beneficial treatment Opportunity to discuss personal feelings and experiences with an objective listener. Physical boredom ba n A) A) How can confidentiality of study participants be increased? Avoiding the collection of any identifying information Avoiding introducing the participants to any of the research personnel Placing all identifying information on computer files rather than in manual files Placing all identifying information on manual files rather than in computer files Researchers can often show their respect for participants—and proactively minimize 13. emotional risks—by carefully attending to the nature of the interactions they have with them. What are debriefing sessions? Discussions with prospective participants to obtain informed consent Discussions with participants after a study to explain various aspects of the study Discussions with a human subjects committee before a study to obtain permission Discussions before a study that findings will be shared after data have been analyzed In a qualitative study that involves multiple contacts between the researcher and study 14. participants, what can the researcher negotiate? Implied consent Stipend Process consent Risk/benefit ratio A) B) C) D) om 15. When is informed consent not obtained? Researcher pays a stipend to study participants. Researcher collects information covertly. Risk/benefit ratio is low. Study is determined exempt by Institutional Review Board. A) kt an k. c B) C) w .te w w B) st A) B) C) D) A) C) D) A) B) C) D) Most institutions where research is conducted have formal committees for reviewing 16. proposed research plans. In the United States, what will the committee likely be called? Research Ethics Board Institutional Review Board Ethical Advisory Board Human Subject Committee ba n D) 17. What is an expedited review? The committee must consist of five members to carry out the review. Research involving no more than minimal risk can use this procedure. The researcher must have an affiliation with an institution. The research is exempt from the review board process. What is an important consideration when 18. nurses choose to use animals as research subjects? Must obtain informed consent from the animal's owner. Recognize that it is more convenient to use an animal. Recognize that it is less costly to use animals than humans. Recognize that animals need humane care and What is an important consideration when 18. nurses choose to use animals as research subjects? Must obtain informed consent from the animal's owner. Recognize that it is more convenient to use an animal. Recognize that it is less costly to use animals than humans. Recognize that animals need humane care and treatment. A) B) C) D) om When can the researcher omit informed 19. consent, when existing data from records and/ or specimens are used? The study does not involve an intervention. The researcher is gathering data anonymously. Health professional students are used as subjects. The study is gathering data from records over 10 years old. A) kt an k. c B) C) Under HIPAA regulations, a covered entity such as a hospital can disclose individually 20. identifiable health information from its records if the patient signs an authorization granting access. What does this include? Who will receive the information Why they need the information The Social Security number of the patient If the data is not specifically obtained for the research ba n D) w .te st A) B) C) w D) w Answer Key 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. C A A C A A C B C A D D B C B A C B C A D D B C B B B D B A om 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. C) w D) w .te B) w A) st ba n kt an k. c Chapter 6. Research Problems, Research Questions, and Hypotheses 1. What is a research problem? Situation involving an enigmatic or disturbing A) situation amenable to disciplined inquiry Articulation of the problem and description of B) the need for a study through the development of an argument Specific queries researchers want to answer in C) addressing the problem Specific accomplishments that will be D) achieved by conducting the study A) B) C) D) The nature of the research question is closely 2. allied to paradigms. What is the focus of research questions for a quantitative study? Undertaken because some aspect of a phenomenon is poorly understood Developed within a rich and context bound understanding of the problem Initiated to heighten awareness and create a dialogue about a phenomenon Identified major variables in the study and populations under investigation are present. Which is correct about the research question “What is the decision making process 3. among intensive care unit nurses who decide to assist terminally ill patients to die?” Most likely to be addressed using a quantitative approach Most likely to be addressed using a qualitative approach Not researchable Not appropriately worded to assist terminally ill patients to die?” Most likely to be addressed using a quantitative approach Most likely to be addressed using a qualitative approach Not researchable Not appropriately worded B) C) D) 4. A) B) C) D) 5. w w w .te B) D) A) B) C) D) A) B) Researchers communicate their aims as problem statements, statements of purpose, 6. research questions, or hypotheses. What are hypotheses? Essential to the conduct of respectable scientific enquiry Needed only when there is an explicit theoretical framework Useful in giving direction to quantitative studies Not appropriate for many nursing research studies ba n st A) C) Which is not considered in determining the feasibility of a research question? Cooperation of participants Ethical concerns Relevant theories Researcher experience kt an k. c A) B) C) D) Where is the nurse likely to have difficulty getting an idea for research problems? Theories of conceptual frameworks Clinical experience Nursing code of ethics Nursing literature om A) “Women who jog regularly are more likely to have amenorrhea than those who do not jog 7. regularly” is an example of what type of hypothesis? Null Not corrected stated Directional Nondirectional 8. What is a moderator variable? Affect the strength or direction of a relationship between independent variables Affect the strength or direction of a relationship between the independent and dependent variables 8. What is a moderator variable? Affect the strength or direction of a relationship between independent variables Affect the strength or direction of a relationship between the independent and dependent variables Intervene between the independent and dependent variable Help to explain why the relationship exists A) B) C) D) om 9. What is a complex hypothesis? Predicted relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable Predicted direction of the relationship Anticipated existence of relationships, not their direction Anticipated relationship between two independent variables and two dependent variables A) kt an k. c B) C) st w .te w w A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) What is the type of hypothesis for “a person's 10. emotional status is not affected by relocation to a nursing home”? Directional Nondirectional Research Null ba n D) Researchers communicate their aims as problem statements, statements of purpose, 11. research questions, or hypotheses. What is the statement of purpose? Summarizes the overall study goal. Specific query researchers want to answer in addressing the research problem. Articulate the nature, context, and significance of the problem. Statement of predicted relationships between two or more variables. 12. A) B) C) om D) The registered nurse knows that which is correct about hypotheses in research reports? Hypotheses derived from theory are generally nondirectional in wording. Hypotheses are more abstract than purpose statements. Qualitative research proceeds with hypotheses. Hypotheses must express the expected relationship among at least three variables. kt an k. c Researchers communicate their aims as problem statements, statements of purpose, research questions, or hypotheses. What does 13. “subjects receiving antiemetic therapy by a patient controlled pump will be less nauseous” represent? Hypothesis Problem statement Statement of purpose Research question w .te w w A) B) C) D) st ba n A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) What type of hypothesis is represented by the statement “the fewer social supports an 14. elderly person has, the more likely the individual will be institutionalized.”? Directional Nondirectional Research Null What type of hypothesis is represented by the statement “women who smoke are as likely to 15. have low-birth-weight babies as women who do not”? Directional Nondirectional Research Null A) B) C) D) What intervenes between the independent and dependent variable? Moderator variable Mediating variable Hypothesis Simple hypothesis A) B) C) D) Researchers communicate their aims as problem statements, statements of purpose, research questions, or hypotheses. What does the following statement represent, “Nausea and vomiting are common side effects among 17. patients on chemotherapy, and interventions to date have been only moderately successful in reducing these effects? New interventions that can reduce or prevent these side effects need to be identified.” Hypothesis Problem statement Statement of purpose Research question C) w D) w .te B) w A) st ba n kt an k. c om 16. A) B) C) D) Not all problems are amendable to research 18. inquiry. Which question cannot be researched? Should voluntary tubal ligations be performed on women without children? What are nurses' attitudes toward voluntary tubal ligations? What moral dilemmas are perceived by nurses who might be involved in assisted suicide? Do terminally ill patients living with high levels of pain hold more favorable attitudes toward assisted suicide than those with less pain? 19. What is a nondirectional hypothesis? Predicted relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable Predicted direction of the relationship Anticipated existence of relationships, not their direction Anticipated relationship between two independent variables and two dependent variables 19. What is a nondirectional hypothesis? Predicted relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable Predicted direction of the relationship Anticipated existence of relationships, not their direction Anticipated relationship between two independent variables and two dependent variables A) B) C) D) 20. What is a simple hypothesis? Predicted relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable Predicted direction of the relationship Anticipated existence of relationships, not their direction Anticipated relationship between two independent variables and two dependent variables om A) B) kt an k. c C) D) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. A D B C C C C B D D A B A A D B B A C A w w w .te st ba n Answer Key Chapter 7. Finding and Reviewing Research Evidence in the Literature 1. A) B) C) D) om What criteria do quantitative researchers use 2. to assess the accuracy and consistency of information obtained in a study? Reliability Trustworthiness Dependability Confirmability kt an k. c A) B) C) D) 3. st w .te w w A) B) C) D) What refers to evidence of the researcher's objectivity? Reliability Trustworthiness Dependability Confirmability ba n A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) What criteria do qualitative researchers use to assess the quality of a study? Validity Reliability Accuracy Dependability A thermometer measured a child's temperature as 98.1°F one minute and as 4. 98.1°F the next minute. What can we assume about the thermometer? Valid instrument Reliable instrument Trustworthy instrument Dependable instrument What is achieved when the research methods 5. engender confidence in the truth of the data and the researchers' interpretations? Trustworthiness Dependability Confirmability Credibility 6. A) B) C) D) Qualitative researchers discuss methods of enhancing the study's data by what method? Trustworthiness Dependability Confirmability Credibility A) B) C) D) A researcher finds that a small number of subjects did not provide accurate information 8. because they had just completed a rigorous session with the physical therapist. What is this an example of? Sample bias Systematic bias Random bias Absolute bias w A spring scale consistently measures people's weights 4 pounds lighter than their true 9. weight. What type of bias would this data be on the weight? Sample bias Systematic bias Random bias Absolute bias w A) B) C) D) w .te st ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) 7. Which can cause bias in a study? Participants' truthful responses Researcher subjectivity Consistent methods of data collection Adequate study design A) B) C) D) The researcher wants to explore the extent to 10. which qualitative findings can be transferred to other settings. What is this called? Reflexivity Generalizability Transferability Thick description A) B) C) D) The researcher wants to explore the extent to 12. which quantitative findings can be applied to other groups and settings. What is this called? Reflexivity Generalizability Transferability Thick description A) B) C) D) What is concealing information from participants, research agents such as data 13. collectors, care providers, or data analysts to enhance objectivity called? Comparing Relative timing Masking Transferring w w A) B) C) D) w .te st ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) What is the process of reflecting critically on 11. the self and of scrutinizing personal values that could affect interpretation? Reflexivity Generalizability Transferability Thick description A) B) C) D) A researcher uses multiple sources or 14. referents to draw conclusions about what constitutes the truth. What is this called? Triangulation Dependability Confirmability Credibility A researcher designs a study to determine if a new teaching modality will benefit a particular group of special education students 15. that the researcher has been working. Which design would the researcher be most likely to use? Comparison between two or more groups. Comparison of one group's status at two or more points in time. Comparison of one group's status under different circumstances. Comparison based on relative rankings. 15. A) B) C) D) particular group of special education students that the researcher has been working. Which design would the researcher be most likely to use? Comparison between two or more groups. Comparison of one group's status at two or more points in time. Comparison of one group's status under different circumstances. Comparison based on relative rankings. A) B) C) D) Researchers often incorporate comparisons into their designs to enhance interpretability. 17. What occurs when different groups of people are compared? Between-subjects design Within-subjects design Mixed design Cross-sectional design w w A) B) C) D) w .te st ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) What technique is the researcher using to 16. control extraneous variables to the study purpose that can obscure understanding? Confounding Reflexivity Generalizability Transferability A) B) C) D) 18. What type of research design involves collecting data at one point in time? Between-subjects design Within-subjects design Longitudinal design Cross-sectional design A study addressing quality of life of a group of patients who had undergone various 19. treatments for coronary artery disease was gathered 1 year and 8 years after their treatment. What type of study is this called? Panel Follow-up Trend Cohort A) B) C) D) Answer Key D A D B D A B C B C A B C A C A A D B B w w w .te st ba n kt an k. c 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. om A researcher is conducting a small-scale trial run designed to test methods to be used in a 20. larger, more rigorous study. What type of study is this called? Panel Feasibility Trend Cohort Chapter 8. Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks What is a broad abstract characterization of 1. phenomena? A) Theory B) Descriptive theory C) Grand theory D) Middle-range theories 2. A) B) om C) kt an k. c D) 3. What thoroughly describes a phenomenon? Theory Descriptive theory Grand theory Middle-range theories 4. w w w .te st A) B) C) D) 5. What are the building blocks of theory? Propositions Relationships Hypotheses Concepts 6. A) B) C) D) What attempt to describe large segments of the human experience? Theory Descriptive theory Grand theory Middle-range theories ba n A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) The power of theories lies in the ability to do what? Capture the complexity of human nature by the richness of the operational definitions associated with the variables. Minimize the number of words required to explain phenomena and, thereby, eliminate semantic problems. Prove conclusively that relationships exist among the phenomena studied. Specify the nature of the relationships that exist among phenomena and offer explanations. What is the major similarity between theories and conceptual models? Use concepts as their building blocks. Use the deductive reasoning process almost exclusively. Contain a set of logically interrelated propositions. Provide a mechanism for developing new propositions from the original propositions. A) Use concepts as their building blocks. Use the deductive reasoning process almost exclusively. Contain a set of logically interrelated propositions. Provide a mechanism for developing new propositions from the original propositions. B) C) D) 7. What are conceptual maps? Stimulate new research with the use of a schematic model. Explain phenomena and relationships among them with a map. Map the integration of knowledge into coherent systems to explain the key relationships that exist. Graphic, theory-driven representations of phenomena and their relationships using symbols or diagrams and a minimal use of words. A) B) om C) kt an k. c D) 8. w w A) B) C) D) w .te st ba n A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) Which model explains and predicts the health promotion component of lifestyle? Adaptation Model Conservation Model Health Promotion Model Self-Care Model Several conceptual models and grand theories 9. of nursing have been developed. Which concept is not central to models for nursing? Human beings Environment Health Social support Which model finds humans as adaptive 10. systems that cope with change through adaptation? Adaptation Model Conservation Model Health Promotion Model Self-Care Model 11. A) B) C) D) Whose major conceptual model of nursing is used by researchers? Rogers' Science of Unitary Human Beings Bandura's Social Cognitive Theory Watson's Theory of Caring Rizzo's Theory of Human Becoming A) B) C) D) 13. What did the nurse theorist Roy develop? Adaptation Model Theory of Caring Science of Unitary Human Beings Health Care Systems Model ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) 12. Which is an example of a borrowed theory? Rogers' Science of Unitary Human Beings Bandura's Social Cognitive Theory Watson's Theory of Caring Rizzo's Theory of Human Becoming 15. w w .te 14. What did the nurse theorist Neuman develop? Adaptation Model Theory of Caring Science of Unitary Human Beings Health Care Systems Model w A) B) C) D) st A) B) C) D) 16. A) B) C) D) Which type of theory is often a precursor to predictive theories? Explanatory theory Grand theory Middle-range theory Situation-specific theory What is an example of a nursing theory that has been described as a grand theory? Adaptation Model Theory of Caring Science of Unitary Human Beings Theory of Human Becoming A) B) C) D) Theories differ in their level of generality and abstraction. What type of theory attempts to 18. explain such phenomena as decision making, stress, comfort, health promotion, and unpleasant symptoms? Explanatory theory Grand theory Middle-range theory Situation-specific theory A) B) C) D) All research studies have a framework. What 19. type of framework is used in a research study based on a theory? Schematic framework Practice framework Theoretical framework Conceptual framework w w w .te st ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) Theories differ in their level of generality and abstraction. What type of theory purports to 17. describe and explain large segments of the human experience? Explanatory theory Grand theory Middle-range theory Situation-specific theory A) B) C) D) The key to Rogers' conceptual framework are her principles of homeodynamics, which represent a way of viewing unitary human 20. beings and provide guidance to nursing practice. The principles include integrality, helicy, and resonancy. What is resonancy? Nonlinear domain without temporal or spatial attributes Concerns the continuous and mutual processes between human and environmental fields Continuous and innovative diversity of human and environmental field patterns Continuous change from lower- to higherfrequency wave patterns in human and environmental energy fields. Concerns the continuous and mutual processes between human and environmental fields Continuous and innovative diversity of human and environmental field patterns Continuous change from lower- to higherfrequency wave patterns in human and environmental energy fields. B) C) D) A D B C D A D C D A A B A D A D B C C D w .te st ba n kt an k. c 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. om Answer Key Chapter 9. Quantitative Research Design A) B) C) D) What type of design occurs when the 2. researcher simultaneously manipulates two independent variables? Crossover Factorial Single-blind Cluster randomization w w A) B) C) D) What type of research design occurs when researchers start with a presumed cause and 1. then go forward in time to the presumed effect? Cohort Counterfactual Randomized controlled Factorial What type of design occurs when the 2. researcher simultaneously manipulates two independent variables? Crossover Factorial Single-blind Cluster randomization 3. A) B) C) D) 4. A) B) C) D) What would happen to the same people simultaneously exposed and not exposed to 5. the casual factor in an idealized research model? Confounding Counterfactual Causality Manipulation ba n st w .te w w A) B) C) D) What does the using random numbers tables for assigning subject to groups eliminate? Systematic bias Ethical problems Need for a control group Unnecessary manipulation kt an k. c A) B) C) D) What is a limitation of the research design for a quantitative study? Whether there will be a theoretical context Whether there will be an intervention What types of comparisons will be made How many times data will be collected om A) B) C) D) Various criteria are used to establish causality. One criterion is that an observed relationship between a presumed cause and an effect 6. cannot be explained as being caused by other variables. What is the observed relationship between a presumed cause called? Confounding Independent variable Dependent variable Counterfactual A) B) C) D) What is occurring when the nurse researcher 8. manipulates the independent variable by introducing a treatment or intervention? Control Counterfactual Randomization Manipulation A) B) C) D) What is occurring when the nurse researcher assigns people to experimental and control 9. groups at random to make the groups comparable at the outset? Control Counterfactual Randomization Manipulation w A) B) C) D) w w .te st ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) What type of design occurs in retrospective studies with data on both the dependent and 7. independent variables collected at a single point in time? Cross-sectional Case control Prospective Correlational Everyone in the experimental group usually gets the same intervention as delineated in 10. formal protocols. What occurs when the study is tailored to meet individual needs or characteristics? Placebo Patient-centered intervention Attention control Stratification A) B) C) D) What type of study occurs when a sample of both users and nonusers of oral contraceptives 12. over a 20-year period are followed to determine if there were any long-term side effects? Controlled Retrospective Prospective Crossover w w A) B) C) D) w .te st ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) The nurse researcher wants to avoid bias stemming from participants' awareness of group status or study hypotheses. What is this called? 11. 1. Attention control 2. Stratification 3. Masking 4. Blinding 1, 2 1, 3 2, 4 3, 4 A) B) C) D) What type of correlational study begins with the outcome and looks back in time for 13. antecedent causes by comparing individuals that have a disease with controls who do not have the disease? Case control Retrospective Prospective Crossover The nurse researcher is dividing research participants into groups of men and women 14. before equating the groups on all characteristics that could affect study outcomes. What is this technique called? Placebo Patient-centered intervention Attention control Stratification A) B) C) D) 16. A) B) C) D) The nurse researcher is describing how phenomena are interrelated without invoking 17. a casual explanation. What type of study is occurring? Descriptive correlational Univariate descriptive Path analytic Cohort ba n w w w .te st A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) What is one weakness of correlational studies? Prevalence of cases Incidence of cases Relative risk of groups Self-selection of groups kt an k. c A) B) C) D) om What is occurring when the nurse researcher 15. documents the frequency of new research cases over a given time period? Prevalence Incidence Relative risk Self-selection The nurse researcher is documenting the frequency with which middle-aged women 18. performed breast self-examination. What type of study is occurring with the documentation? Descriptive correlation Univariate descriptive Prevalence Incidence What type of research design occurs when the nurse researcher gives the comparison group 19. the experimental intervention at a later point in time? Propensity matching Switching replication Time series Nonequivalent control group pretest–posttest 19. A) B) C) D) nurse researcher gives the comparison group the experimental intervention at a later point in time? Propensity matching Switching replication Time series Nonequivalent control group pretest–posttest What type of research design involves an experimental intervention but no 20. randomization and supports causal inferences? Quasi-experimental Crossover Factorial Experimental kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. A B A A B B A D C B D C A D B D A B B A w w w .te st ba n Answer Key Chapter 10. Sampling and Data Collection in Quantitative Studies Sampling is familiar to us all. In the course of daily activities, we make decisions and draw conclusions through sampling. A nursing 1. student may select an elective course by sampling two or three classes on the first day of the semester. What is sampling? Identification of a set of elements used for A) selecting study participants Established population characteristics to B) determine who could participate in a study Process of selecting a subset of the population Sampling is familiar to us all. In the course of daily activities, we make decisions and draw conclusions through sampling. A nursing 1. student may select an elective course by sampling two or three classes on the first day of the semester. What is sampling? Identification of a set of elements used for selecting study participants Established population characteristics to determine who could participate in a study Process of selecting a subset of the population to represent the entire population Technique for ensuring that every element in the population has an equal chance of being included in the study A) B) C) om D) 2. What is bias sampling? Elements are selected by nonrandom methods. Most readily available or convenient group of people for the sample. Referrals for potential participants are made by those already in the sample. Systematic over- or under-representation of an attribute vis-à-vis the population. kt an k. c A) B) C) st w .te w A) B) C) D) w A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) What type of sampling occurs in which 3. referrals for potential participants are made by those already in the sample? Convenience Snowball Quota Consecutive ba n D) 4. Which type of sampling are strata incorporated into the design? Convenience Snowball Quota Consecutive The nurse researcher is collecting information about the population sample. What is the 5. basic population unit about which information is collected called? Population Element Inclusion criteria Exclusion criteria 5. A) B) C) D) The nurse researcher knows it is important to make a distinction between target and 6. accessible populations. What is the target population? Aggregate of cases that conform to designated criteria and that are accessible for a study. Aggregate of cases about which the researcher would like to generalize. Characteristics of individuals that must not be included in the research sample. Characteristics of individuals that meet the specific population characteristics. A) om B) kt an k. c C) D) The nurse researcher knows it is important to 7. make a distinction between target and accessible populations. What is a population? Aggregate of cases that conform to designated criteria and that are accessible for a study Aggregate of cases about which the researcher would like to generalize Entire aggregation of cases in which a researcher is interested Characteristics of individuals that meet the specific population characteristics ba n A) B) w .te st C) D) about the population sample. What is the basic population unit about which information is collected called? Population Element Inclusion criteria Exclusion criteria A) B) C) D) The nurse researcher wants to use a probability sample in the research study. 9. Which is an example of a probability sampling method? Convenience Cluster Purposive Quota w w A) B) C) D) The nurse researcher knows that samples and sampling plans vary in quality. What is a key 8. consideration in assessing a sample in a quantitative study? Representativeness Probability Nonprobability Strata The nurse researcher wants to use a probability sample in the research study. 9. Which is an example of a probability sampling method? Convenience Cluster Purposive Quota A) B) C) D) The nurse researcher is using a sampling design that is especially likely to yield a 10. representative sample. What type of sample is this called? Systematic Convenience Purposive Quota kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) 11. w w A) B) C) D) w .te st ba n A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) Which type of sample is considered to be the weakest for quantitative studies? Convenience Quota Purposive Systematic The nurse is hand picking the sample based on the researcher's knowledge about the 12. population. What type of sample is this called? Purposive Snowball Network Chain The nurse researcher is trying to yield a 13. representative sample. What type of nonprobability design should be utilized? Quota Snowball Network Chain A) B) C) D) A nurse research used a probability type systematic sampling plan. The sample size 15. was 200. The sampling interval was 250. The first element drawn was 196. What would the second element be? 396 446 496 646 A) B) C) D) A nurse researcher used a systematic sampling design. The known population size 16. is 3200, and the desired sample size is 160. What is the sampling interval? 16 20 160 320 w A) B) C) D) w w .te st ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) The nurse researcher has to consider the 14. procedure of weighing in the sample. What type of sampling design would be considered? Proportionate Disproportionate Simple random Quota A) B) C) D) What type of sampling divides the population 17. into homogeneous strata from which elements are selected at random? Probability sampling Simple random sampling Stratified random sampling Cluster sampling The nurse researcher is reviewing a research 18. article that used a cluster sample. What is a cluster sample? Selection of every kth case from a list Standard distance between the selected elements in the sample Multistaged selection of random samples from larger units Divides the population into homogeneous strata to ensure representation of subgroups 18. article that used a cluster sample. What is a cluster sample? Selection of every kth case from a list Standard distance between the selected elements in the sample Multistaged selection of random samples from larger units Divides the population into homogeneous strata to ensure representation of subgroups A) B) C) D) 19. om A) B) C) D) What type of analysis do nurse researchers use to estimate sample size needs? Power Systematic Interval Multistage kt an k. c The nurse researcher is reviewing a research 20. article that used systematic sampling. What is systematic sampling? Selection of every kth case from a list Standard distance between the selected elements in the sample Multistaged selection of random samples from larger units Divides the population into homogeneous strata to ensure representation of subgroups A) B) ba n C) st D) w w w .te Answer Key 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. C D B C B B C A B A A A A B B B C C A A 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. A A B B B C C A A Chapter 11. Qualitative Designs and Approaches A) B) C) D) What type of design occurs when the 2. researcher simultaneously manipulates two independent variables? Crossover Factorial Single-blind Cluster randomization A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) kt an k. c ba n st 3. w .te w w A) B) C) D) om A) B) C) D) What type of research design occurs when researchers start with a presumed cause and 1. then go forward in time to the presumed effect? Cohort Counterfactual Randomized controlled Factorial 4. What is a limitation of the research design for a quantitative study? Whether there will be a theoretical context Whether there will be an intervention What types of comparisons will be made How many times data will be collected What does the using random numbers tables for assigning subject to groups eliminate? Systematic bias Ethical problems Need for a control group Unnecessary manipulation What would happen to the same people simultaneously exposed and not exposed to 5. the casual factor in an idealized research model? Confounding Counterfactual Causality Manipulation A) B) C) D) Various criteria are used to establish causality. One criterion is that an observed relationship between a presumed cause and an effect 6. cannot be explained as being caused by other variables. What is the observed relationship between a presumed cause called? Confounding Independent variable Dependent variable Counterfactual A) B) C) D) What type of design occurs in retrospective studies with data on both the dependent and 7. independent variables collected at a single point in time? Cross-sectional Case control Prospective Correlational w w A) B) C) D) w .te st ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) What would happen to the same people simultaneously exposed and not exposed to 5. the casual factor in an idealized research model? Confounding Counterfactual Causality Manipulation A) B) C) D) What is occurring when the nurse researcher 8. manipulates the independent variable by introducing a treatment or intervention? Control Counterfactual Randomization Manipulation What is occurring when the nurse researcher assigns people to experimental and control 9. groups at random to make the groups comparable at the outset? Control Counterfactual Randomization Manipulation A) B) C) D) The nurse researcher wants to avoid bias stemming from participants' awareness of group status or study hypotheses. What is this called? 11. 1. Attention control 2. Stratification 3. Masking 4. Blinding 1, 2 1, 3 2, 4 3, 4 w w A) B) C) D) w .te st ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) Everyone in the experimental group usually gets the same intervention as delineated in 10. formal protocols. What occurs when the study is tailored to meet individual needs or characteristics? Placebo Patient-centered intervention Attention control Stratification A) B) C) D) What type of study occurs when a sample of both users and nonusers of oral contraceptives 12. over a 20-year period are followed to determine if there were any long-term side effects? Controlled Retrospective Prospective Crossover What type of correlational study begins with the outcome and looks back in time for 13. antecedent causes by comparing individuals that have a disease with controls who do not have the disease? Case control Retrospective Prospective Crossover A) B) C) D) The nurse researcher is dividing research participants into groups of men and women 14. before equating the groups on all characteristics that could affect study outcomes. What is this technique called? Placebo Patient-centered intervention Attention control Stratification A) B) C) D) What is occurring when the nurse researcher 15. documents the frequency of new research cases over a given time period? Prevalence Incidence Relative risk Self-selection ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) 13. antecedent causes by comparing individuals that have a disease with controls who do not have the disease? Case control Retrospective Prospective Crossover w .te w w A) B) C) D) st 16. A) B) C) D) What is one weakness of correlational studies? Prevalence of cases Incidence of cases Relative risk of groups Self-selection of groups The nurse researcher is describing how phenomena are interrelated without invoking 17. a casual explanation. What type of study is occurring? Descriptive correlational Univariate descriptive Path analytic Cohort A) B) C) D) What type of research design occurs when the nurse researcher gives the comparison group 19. the experimental intervention at a later point in time? Propensity matching Switching replication Time series Nonequivalent control group pretest–posttest A) B) C) D) What type of research design involves an experimental intervention but no 20. randomization and supports causal inferences? Quasi-experimental Crossover Factorial Experimental w w Answer Key w .te st ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) The nurse researcher is documenting the frequency with which middle-aged women 18. performed breast self-examination. What type of study is occurring with the documentation? Descriptive correlation Univariate descriptive Prevalence Incidence 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. A B A A B B A D C B D C A D B D A 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. D C B D C A D B D A B B A kt an k. c om Chapter 12. Sampling and Data Collection in Qualitative Studies Qualitative researchers use the conceptual demands of the study to select articulate and 1. reflective informants with certain types of experience in an emergent way. What is a typical qualitative sample? A) Large, random B) Small, random C) Large, nonrandom D) Small, nonrandom ba n st w .te A) B) C) D) Qualitative researchers often begin with a sample where potential participants come 2. forward and identify themselves. What type of sample is being used? Convenience Snowball Purposive Purposeful A) B) C) D) Many qualitative studies eventually evolve to 4. selecting cases that will most benefit the study. What type of sample is being used? Convenience Volunteer Snowball Purposive w w A) B) C) D) Qualitative researchers, like quantitative researchers, sometimes ask early informants 3. to refer to other study participants. What type of sample is being used? Convenience Snowball Purposive Purposeful Many qualitative studies eventually evolve to 4. selecting cases that will most benefit the study. What type of sample is being used? Convenience Volunteer Snowball Purposive A) B) C) D) The broad category of purposive sampling 5. involves general goals. What is one of the broad general goals? Find examples that are representative or typical of a specific group on some dimension of interest. Sampling to set up the possibility of comparisons or replications across similar types of cases on a dimension of interest. Find examples that are representative or typical of a broader group on some dimension of interest. Sampling to set up the possibility of comparisons or replications across random cases on a dimension of interest. om A) kt an k. c B) C) st w .te w w A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) Various purposive sampling strategies have been used by qualitative researchers. What is 6. an important purposive strategy for sampling for representativeness or comparative value? Maximum variation sampling Critical case sampling Criterion sampling Sampling politically important cases ba n D) Although many qualitative sampling strategies unfold while in the field, purposive sampling in the sequential category involves 7. deliberative emergent efforts. What is an example of this category of purposive sampling? Opportunistic sampling Reputational case sampling Critical case sampling Stratified purposeful sampling 8. A) B) C) D) What type of sample involves selecting cases that are especially important or illustrative? Critical case sampling Maximum variation sampling Homogeneous sampling Typical case sampling A) B) C) D) What type of sample adds new cases based on changes in research circumstances or in 10. response to new leads that develop in the field? Theory-based sampling Opportunistic sampling Sampling confirming and disconfirming cases Sampling politically important cases w w A) B) C) D) w .te st ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) What type of sample identifies and gains access to a case representing a phenomenon 9. that was previously inaccessible to research scrutiny? Critical case sampling Criterion sampling Revelatory case sampling Sampling politically important cases What type of sample selects cases based on a 11. recommendation of an expert or key informant? Homogeneous sampling Typical case sampling Extreme case sampling Reputational case sampling 12. A) B) C) D) What type of sample selects cases that are intense but not extreme? Typical case sampling Extreme case sampling Intensity sampling Stratified purposeful sampling What type of sample occurs when only 13. average, above average, or below average cases are selected? Typical case sampling Extreme case sampling Intensity sampling Stratified purposeful sampling A) B) C) D) 14. kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) 15. st w w D) w .te A) C) A) B) C) D) Which type of sample may require more cases to reach data saturation? Convenience sample Purposive sample Theoretical sample Extreme case sample ba n A) B) C) D) B) What main qualitative tradition is theoretical sampling guided by? Ethnography Phenomenological studies Grounded theory studies Sociology 16. What is data saturation? Sampling to the point at which new information is continually obtained Sampling to the point at which new information is continually obtained with no redundancy Sampling to the point at which no new information is obtained with any redundancy Sampling to the point at which no new information is obtained and redundancy is achieved What type of researcher often uses key 17. informants who serve as guides and interpreters of the culture? Ethnographers Phenomenologists Grounded theory researchers Sociologists A) B) C) D) 19. Grounded theory researchers typically work with what size sample? 10 or fewer 11–15 16–19 20–30 kt an k. c A) B) C) D) om Phenomenologists typically work with what 18. size sample who meets the criterion of having lived the experience under study? 10 or fewer 11–15 16–19 20–30 ba n Generalizability in qualitative research is controversial. What widely used model of generalizability involves judgments about 20. whether findings from an inquiry can be extrapolated to a different setting or group of people? Analytic generalization Transferability Thick description Proximal similarity w w Answer Key w .te st A) B) C) D) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. D A B D C A A A C B D C D C A D 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. A A C B D C D C A D A A D B kt an k. c om Chapter 13. Mixed Methods and Other Special Types of Research Mixed methods research involves the 1. collection, analysis, and integration of what type of data? A) Qualitative only B) Quantitative only C) Both qualitative and quantitative D) Neither qualitative or quantitative ba n w w w .te st A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) A) B) C) Mixed methods studies involve at least how 2. many questions that require different types of data? One Two Three Four In terms of sequencing, mixed method 3. designs can either be concurrent or sequential. What is a sequential design Both strands occurring in one simultaneous phase. Both strands occurring prior to informing the third and fourth strand. One strand occurring prior to and informing the second strand. Two strands occurring prior to and informing the third and fourth strand. In terms of sequencing, mixed method 4. designs can either be concurrent or sequential. What is a concurrent design? Both strands occurring in one simultaneous phase. Both strands occurring prior to informing the third and fourth strand. One strand occurring prior to and informing In terms of sequencing, mixed method 4. designs can either be concurrent or sequential. What is a concurrent design? Both strands occurring in one simultaneous phase. Both strands occurring prior to informing the third and fourth strand. One strand occurring prior to and informing the second strand. Two strands occurring prior to and informing the third and fourth strand. A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) Notation for mixed method research designates both priority and sequence. How is 6. sequence identified for the concurrent designs? All capital letters All lower-case letters An arrow Plus sign w A) B) C) D) w w .te st ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) Notation for mixed method research 5. designates both priority and sequence. How is priority identified for the dominant strand? All capital letters All lower-case letters An arrow Plus sign A) B) C) D) Notation for mixed method research designates both priority and sequence. How is 7. sequence identified for the nondominant strand? All capital letters All lower-case letters An arrow Plus sign Notation for mixed method research 8. designates both priority and sequence. What type of research is identified by QUAN(qual)? Sequential, qualitative-dominant design Sequential, qualitative-nondominant design Qualitative component embedded within a quantitative study Quantitative component embedded within a qualitative study Notation for mixed method research 8. designates both priority and sequence. What type of research is identified by QUAN(qual)? Sequential, qualitative-dominant design Sequential, qualitative-nondominant design Qualitative component embedded within a quantitative study Quantitative component embedded within a qualitative study A) B) C) D) There are specific mixed method designs in 9. the Creswell–Plano Clark taxonomy. What do (QUAL + QUAN) represent? Triangulation Embedded Explanatory Exploratory kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) There are specific mixed method designs in the Creswell–Plano Clark taxonomy. What 10. does (QUAN → qual or quan → QUAL) represent? Triangulation Embedded Explanatory Exploratory w w A) B) C) D) w .te st ba n A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) There are specific mixed method designs in the Creswell-Plano Clark taxonomy. What 11. does (QUAL → quan or qual → QUAN) represent? Triangulation Embedded Explanatory Exploratory What type of sampling strategy occurs when 12. some of the participants from one strand are in the other strand? Identical Nested Parallel Multilevel What type of sampling strategy occurs when some of the participants are either in one 13. strand or the other, but drawn from a similar population? Identical Nested Parallel Multilevel A) B) C) D) om Data collection in mixed methods research can involve all methods of structured and 14. unstructured data. In sequential designs, how are decisions about data collection made? Second phase are based on findings from the first phase. Third phase are based on findings from the first phase. Fourth phase are based on findings from the second phase. Fifth phase are based on findings from the fourth phase. kt an k. c A) B) C) C) Methods of integration of qualitative and quantitative data during analysis include data 15. conversions. What is the use of meta-matrices mean? Qualitizing of quantitative data Quantitizing of qualitative data Both qualitative and quantitative data are arrayed in a spreadsheet type of matrix. Assessment of congruence and exploration of complementarity. w w D) w .te A) B) st ba n D) A) B) C) D) Creswell and Plano Clark identified broad types of research situations that are especially 16. well suited to mixed methods research. What is one of these types of research situations? Concepts are new and poorly understood and there is a need for quantitative exploration. The qualitative results are puzzling and difficult to interpret and quantitative data can help to explain the results. The findings from both approaches can be greatly enhanced with a third source of data. Neither a qualitative nor a quantitative approach by itself is adequate in addressing the complexity of the research problem. The qualitative results are puzzling and difficult to interpret and quantitative data can help to explain the results. The findings from both approaches can be greatly enhanced with a third source of data. Neither a qualitative nor a quantitative approach by itself is adequate in addressing the complexity of the research problem. B) C) D) A) B) C) D) What type of research design involves the separate but concurrent collection of 18. qualitative and quantitative data, followed by qualitative and quantitative analysis? Convergence model Data transformation model Multilevel model Correlational model kt an k. c ba n st w .te w w A) B) C) D) om A) B) C) D) The purpose of this design is to obtain different, but complementary data about the 17. central phenomenon under study. What type of design has this purpose? Triangulation Embedded Explanatory Exploratory A) B) C) D) 19. What type of research design would use a correlational model? Triangulation Embedded Explanatory Exploratory Criteria that have been proposed for enhancing the integrity of mixed methods 20. studies included inference quality and inference transferability. What is inference transferability? The believability and accuracy of inductively derived conclusions. The believability and accuracy of deductively derived conclusions. The degree to which conclusions can be applied to different people or contexts. The degree to which conclusions can be applied to similar people or contexts. A) derived conclusions. The believability and accuracy of deductively derived conclusions. The degree to which conclusions can be applied to different people or contexts. The degree to which conclusions can be applied to similar people or contexts. B) C) D) C B A C A C B C A C D B C A C D A B B D w .te st ba n kt an k. c 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. om Answer Key w w Chapter 14. Statistical Analysis of Quantitative Data Quantitative nurse researchers typically 1. develop a detailed data collection plan. At one point is this plan implemented? A) Before beginning data collection B) During data collection C) After data collection D) Before beginning and during data collection A) B) C) D) A nurse researcher documents the number of times a mother made positive, encouraging 2. comments to the toddler. This is an example of what? Structured self-report Unstructured self-report Structured observation Unstructured observation 2. A) B) C) D) 3. A) What is the first step in the development of a data collection plan in a quantitative study? Locating existing instruments for key constructs Identifying and prioritizing data needs Developing suitable forms for data collection Pretesting data collection instruments om B) C) D) comments to the toddler. This is an example of what? Structured self-report Unstructured self-report Structured observation Unstructured observation kt an k. c When a nurse researcher is selecting an 4. instrument for a research project, what is the primary consideration? Conceptual relevance Data quality Cost Reputation st A) w w D) w .te B) C) A) B) C) D) What is advisable for a nurse researcher who 5. is administering a questionnaire to a highly disadvantaged population? Pretest the questionnaire with a less disadvantaged sample. Collect data about the study participants' reactions to the study. Determine the readability level of the questionnaire. Use mostly open-ended questions in the questionnaire. ba n A) B) C) D) When would a nurse researcher not consider 6. the use of a pretest in a quantitative research design? Assess whether the sequencing of questions or instruments is sensible. Determine if the measures yield data with sufficient variability. Identify questions that participants find objectionable or offensive. Prioritize data collection requirements. The nurse researcher has finalized the instrument package and has to develop 7. various forms. Which form will not be necessary at this time? Screening Informed consent Administrative logs Referral om A) B) C) D) kt an k. c Nurse researchers develop data collection protocols to ensure accurate, valid, and 8. meaningful data. What is a data collection protocol? Spells out procedures to be used in data collection Very important in qualitative research to minimize subjectivity Developed after research staff is trained Varies only marginally from one study to another study A) B) C) ba n D) w .te w w A) B) C) D) st 9. A) B) C) D) What method of data collection is most widely used by nurse researchers? Structured self-report Unstructured self-report Structured observation Unstructured observation The nurse researcher is using a structured self-report instrument with open- and closed10. ended questions. What is an open-ended question? Permits respondents to reply in narrative fashion Offers response alternatives from which respondents must choose Offers a range of alternatives Requires a choice between two options The nurse researcher is using a structured 11. self-report instrument with dichotomous questions. What is a dichotomous question? Permits respondents to reply in narrative fashion Offers response alternatives from which respondents must choose Offers a range of alternatives Requires a choice between two options A) B) om C) D) The nurse researcher is using a structured 12. self-report instrument with forced-choice questions. What is a forced-choice question? Requires a choice between two options Offers a range of alternatives Respondents are asked to rank concepts on a continuum Requires respondents to choose between two competing positions kt an k. c A) B) C) 13. w w w .te st A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) The nurse researcher is using the FACES pain scale instrument. What is this an example of? Forced-choice question Rating question Checklist Visual analog scale ba n D) The nurse researcher is using a composite 14. psychosocial scale. What is a composite psychosocial scale? Several questions with the same response format Multiple-item self-report tool for measuring the degree to which individuals possess target attributes. Comprises a series of statements about a phenomenon Consists of a series of bipolar rating scales on which respondents indicate reactions toward a phenomenon 15. A) B) C) om D) The nurse researcher reads about Q sort in a research article. What is Q sort? Sorts a set of card statements into piles according to specified criteria Several questions with the same response format Comprises a series of statements about a phenomenon Consists of a series of bipolar rating scales on which respondents indicate reactions toward a phenomenon A) B) C) D) Structured self-reports are vulnerable to the risk of reporting biases. What type of bias is 17. occurring when the tendency of some people is to respond to questions in characteristic ways, independent of content? Response set Social desirability Extreme response Acquiescence w w w .te st ba n kt an k. c A) B) C) D) What type of research activity is used to 16. assess respondents' perceptions, hypothetical behaviors, or decisions? Q sorts Semantic differentials Event history calendar Vignettes A) B) C) D) 18. The nurse researcher is involved in time sampling. What is time sampling? Captures data about the occurrence of events Specification of the duration and frequency of observational periods and intersession intervals Selects integral behaviors or events of a special type for observation Observers rate phenomena along a dimension that is typically bipolar The nurse researcher reads that the halo effect 19. occurred during data collection. What is the halo effect? Tendency for observers to rate everything positively Tendency for observers to rate everything harshly Tendency of observers to be influenced by one characteristic in judging other, unrelated characteristics Occurs when extreme events are distorted toward middle ground A) B) C) om D) kt an k. c Answer Key A C B A C D D A A A D D D B A D A B C w w w .te st ba n 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. Chapter 15. Interpretation and Clinical Significance in Quantitative Research Researchers who collect quantitative data typically progress through a series of steps in the analysis and interpretation of their data. 1. Careful researchers lay out a data analysis plan in advance to guide that progress. What phase involves various clerical and administrative tasks? A) Preanalysis B) Preliminary assessments and actions C) Principal analysis D) Interpretation of quantitative results A) B) C) D) Careful researchers lay out a data analysis plan in advance to guide that progress. What 2. phase involves collection of data on numerous variables? Preanalysis Preliminary assessments and actions Principal analysis Interpretation of quantitative results A) B) C) D) 3. How must quantitative data be coded? Missing values Letter codes Numerical values Wild codes ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) 1. Careful researchers lay out a data analysis plan in advance to guide that progress. What phase involves various clerical and administrative tasks? Preanalysis Preliminary assessments and actions Principal analysis Interpretation of quantitative results A) B) w .te w A) B) C) D) w D) st C) A) B) C) D) 4. What is a wild code? Numerical value Missing value Values that lie outside the normal range of values Codes that are not legitimate 5. What is the error prone process that requires verification? Outliers Data cleaning Data entry Consistency checks Decisions on handling missing values must be based on the amount of missing data and how 6. missing data are patterned. When is addressing missing data especially important? Sensitivity analyses Intention-to-treat analyses Missing completely at random values pattern Missing at random values pattern 6. A) B) C) D) Steps must almost always be taken to evaluate 7. missing data problems. What occurs with a missing completely at random values pattern? Missing values are just a random sample of all cases in the population. Missing values are just a random subsample of all cases in the sample. Missingness is related to other variables but not related to the value of the variable that has the missing values. A pattern in which the value of the variable is missing is related to its missingness. A) om B) C) kt an k. c D) There are two missing values strategies that involve deletion or imputation. What is the 8. analysis of those cases for which there are no missing data? Listwise deletion Pairwise deletion Available case analysis Data transformations w w w .te st ba n A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) missing data are patterned. When is addressing missing data especially important? Sensitivity analyses Intention-to-treat analyses Missing completely at random values pattern Missing at random values pattern There are two missing values strategies that involve deletion or imputation. What is the 9. most widely used approach to delete cases selectively on a variable-by-variable basis? Listwise deletion Pairwise deletion Complete case analysis Data transformations There are two missing values strategies that involve deletion or imputation. What is 10. occurring with a regression-based estimation of missing values? Mean substitution Expectation maximization imputation Complete case analysis Available case analysis A) B) C) D) 12. 13. What is the best method for addressing missing value problems? Expectation maximization Multiple imputations Mean substitution Subgroup mean substitution 14. What is the simplest imputation procedure? Expectation maximization Multiple imputations Mean substitution Subgroup mean substitution w w w .te st ba n A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) A data cleaning procedure involves consistency checks. What does this focus on? Internal data consistency External data consistency Checking for outliers Checking for wild codes kt an k. c A) B) C) D) What is an activity that is completed during the preanalysis phase? Entering, verifying, and cleaning data Assessing and handling missing values problems Assessing data quality Assessing bias om 11. A) B) C) D) Assessing data quality is an early analytic task. A value is considered an extreme outlier 15. when if it is how many times greater than the interquartile range above the third quartile? 1 2 3 4 A) B) C) D) Researchers often undertake preliminary analyses to assess biases. What type of bias 17. should nurse researchers check for when there are multiple points of data collection? Nonresponse Volunteer Selection Attrition kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) Researchers often undertake preliminary analyses to assess biases. What type of bias should nurse researchers check for when 16. nonrandomized comparison groups are used and compared to the groups' baseline characteristics? Nonresponsive Volunteer Selection Attrition A) w .te w w D) st B) C) A) B) C) D) What is occurring with the KolmorogovSmirnov test? Tests that the distribution deviates significantly from a normal distribution. Tests that the median deviates significantly from a normal distribution. Tests that the distribution does not deviate significantly from a normal distribution. Tests that the median does not deviate significantly from a normal distribution. ba n 18. What effect can occur when a nurse researcher accumulates a sample over an 19. extended period of time to achieve adequate sample sizes? Overt effect Cohort effect Ordering effect Carryover effect What type of analysis occurs when test 20. research hypotheses using different assumptions or different strategies? Substantive Descriptive Supplementary Sensitivity A) B) C) D) A C C D C B B A B A A A B C C C D C B D w w .te st ba n kt an k. c 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. om Answer Key w Chapter 16. Analysis of Qualitative Data A) B) C) D) What is the first major step that a nurse 1. researcher must undertake in a qualitative analysis? A search for major themes Entering information into files The use of quasi-statistics Developing a system for organizing and indexing the data Before the advent of computer programs for 2. qualitative analysis, what was the main procedure for managing qualitative data? Conceptual files Core categories Memos Themes A) B) C) D) 3. om A) B) C) kt an k. c D) Some qualitative analysts use figurative 4. comparisons to evoke a visual and symbolic analogy. What is this called? Themes Categories Metaphors Quasi-statistics w C) w B) w .te st ba n A) B) C) D) A) D) A) B) C) D) What does the actual analysis of data usually begin with? A search for major themes Entering information into files The use of quasi-statistics Developing a system for organizing and indexing the data 5. What does the process of constant comparison involve? Comparing two researchers' interpretation of the data Comparing the researchers' interpretation of the data against study participants' interpretation Comparing data segments against other segments for similarity Comparing data from the study with data and categories from other similar studies 6. What is quasi-statistics? Statistical analysis Validation Thematic generation Analytic induction One approach to analyzing ethnographic data 7. is Spradley's method, which involves how many levels of data analysis? 1 2 3 4 8. kt an k. c A) B) C) D) 9. What type of analysis compares and contrasts terms in a domain? Domain Taxonomic Componential Theme 10. What type of analysis selects key domains and constructs systems of classification? Domain Taxonomic Componential Theme w w w .te st ba n A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) What type of analysis uncovers cultural themes? Domain Taxonomic Componential Theme om A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) Leininger and McFarland provided ethnographers with a four-phase ethno 11. nursing data analysis guide. What is the first phase? Collecting and recording data Categorizing descriptors Searching for repetitive patterns Abstracting major themes In Van Manen's approach, this involves efforts to grasp the essential meaning of the 12. experience being studied, researchers search for themes. What is the holistic approach? Find common patterns of experiences shared by particular instances. Viewing text as a whole. Pulling out key statements and phrases. Analyzing every sentence in the analysis A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) Hermeneutics has several choices for data analysis. One approach is the discovery of a 14. pattern that expresses the relationships among themes. What is this pattern called? Constitutive Constant comparison Similarity comparison Dissimilarity comparison om C) D) Central to analyzing data in a hermeneutic 13. study is the notion of the hermeneutic circle. What is a hermeneutic circle? Find common patterns of experiences shared by particular instances. Continual movement between the parts and the whole of the text. Pulling out key statements and phrases. Analyzing every sentence in the analysis kt an k. c A) w w w .te st ba n B) A) B) C) D) A) B) C) Benner offers another analytic approach for hermeneutic phenomenology. The 15. interpretative analysis consists of how many interrelated processes? 1 2 3 4 One approach to grounded theory is the Glaser and Strauss (Glaserian) method, in 16. which there are two broad types of codes. What is theoretical code? Empirical substance of the topic is conceptualized. Relationships among the substantive codes are conceptualized. Capture what is going on in the data. Only variables relating to a core category are One approach to grounded theory is the Glaser and Strauss (Glaserian) method, in 16. which there are two broad types of codes. What is theoretical code? Empirical substance of the topic is conceptualized. Relationships among the substantive codes are conceptualized. Capture what is going on in the data. Only variables relating to a core category are coded. A) B) C) D) A) kt an k. c B) C) D) A) B) w w w .te st C) A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) Substantive coding involves selective coding. What is selective coding? Empirical substance of the topic is conceptualized. Relationships among the substantive codes are conceptualized. Capture what is going on in the data. Only variables relating to a core category are coded. ba n 18. D) Substantive coding involves open coding. What is open coding? Empirical substance of the topic is conceptualized. Relationships among the substantive codes are conceptualized. Capture what is going on in the data. Only variables relating to a core category are coded. om 17. 19. What are level III codes in the Glaser and Strauss approach? Axial codes In vivo codes Open codes Theoretical constructs Strauss and Corbin's method is an alternative grounded theory method whose outcome is a 20. full preconceived conceptual description. What is an axial code? Categories are generated. Categories are linked with subcategories. Findings are integrated. Findings are refined. 20. A) B) C) D) grounded theory method whose outcome is a full preconceived conceptual description. What is an axial code? Categories are generated. Categories are linked with subcategories. Findings are integrated. Findings are refined. D A A C C B D D C B A B B A C B C D D B w .te st ba n kt an k. c 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. om Answer Key w w Chapter 17. Trustworthiness and Integrity in Qualitative Research What is one contentious issue in the debate 1. about quality concerns in qualitative research? A) The sameness of the two methods Criteria to use as indicators of validity and B) reliability The place of imagination in qualitative C) research The need for high-quality research in both D) traditions A) B) C) D) The most-often used framework of quality criteria is that of Lincoln and Guba. How 2. many criteria are identified for evaluating trustworthiness of the inquiry? 2 3 4 5 The most-often used framework of quality criteria is that of Lincoln and Guba. How 2. many criteria are identified for evaluating trustworthiness of the inquiry? 2 3 4 5 A) B) C) D) 3. om A) B) C) kt an k. c D) 4. A) B) C) What is authenticity in the often-used framework of quality criteria? Confidence in the truth value of the findings Stability of data over time and conditions. Objectivity or neutrality of the data. Extent to which researchers fairly and faithfully show a range of different realities and convey the feeling tone of lives as they are lived. The qualitative study has a lot of stability of data over time and conditions. What term is 5. somewhat analogous to reliability in quantitative studies? Credibility Dependability Confirmability Transferability w w w .te st ba n D) A) B) C) D) What is credibility in the often-used framework of quality criteria? Confidence in the truth value of the findings Stability of data over time and conditions Objectivity or neutrality of the data Analog of external validity and the extent to which findings from the data can be transferred to other settings or groups 6. A) B) C) D) What term is the analog of external validity in quantitative studies? Credibility Dependability Confirmability Transferability 7. A) B) C) D) What is confirmability in the often-used framework of quality criteria? Confidence in the truth value of the findings Stability of data over time and conditions Objectivity or neutrality of the data Analog of external validity and the extent to which findings from the data can be transferred to other settings or groups A) B) C) D) In the view of Whittemore and colleagues' framework, four primary criteria are essential to all quality inquiry. The terminology 9. overlaps with Lincoln and Guba's framework regarding two criteria. Which two criteria overlap? Authenticity and criticality Creativity and congruence Integrity and creativity Credibility and authenticity w w w .te st ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) In the view of Whittemore and colleagues' framework, four primary criteria are essential 8. to all quality inquiry. What is one of the primary criteria? Credibility Creativity Congruence Explicitness A) B) C) D) An alternative framework, representing a synthesis of 10 qualitative validity schemes 10. by Whittemore and colleagues, proposed four primary criteria and six secondary criteria. What is criticality? Researcher's critical appraisal of every research decision Demonstrated by ongoing self-scrutiny to enhance the likelihood that interpretations are valid and grounded in the data Ability to follow the researcher's decisions through careful demonstration Involves rich and vivid descriptions An alternative framework, representing a synthesis of 10 qualitative validity schemes 11. by Whittemore and colleagues, proposed four primary criteria and six secondary criteria. What is explicitness? Researcher's critical appraisal of every research decision Demonstrated by ongoing self-scrutiny to enhance the likelihood that interpretations are valid and grounded in the data Ability to follow the researcher's decisions through careful demonstration Involves rich and vivid descriptions A) om B) C) kt an k. c D) ba n A) st B) w w w .te C) D) A) B) C) D) An alternative framework, representing a synthesis of 10 qualitative validity schemes 12. by Whittemore and colleagues, proposed four primary criteria and six secondary criteria. What is integrity? Researcher's critical appraisal of every research decision Demonstrated by ongoing self-scrutiny to enhance the likelihood that interpretations are valid and grounded in the data Ability to follow the researcher's decisions through careful demonstration Involves rich and vivid descriptions An alternative framework, representing a synthesis of 10 qualitative validity schemes 13. by Whittemore and colleagues, proposed four primary criteria and six secondary criteria. What is sensitivity? Degree to which an inquiry reflects respect and compassion for those being studied. Interconnectedness between parts of the inquiry and the whole, and between study findings and external contexts Comprehensive data and the full development of ideas Reflects challenges to traditional ways of thinking Strategies for enhancing the quality of qualitative data as they are being collected 14. include prolonged engagement. What is prolonged engagement? Vivid recording of information including maintenance of an audit trail of key decisions Strives at achieving adequate depth of data coverage Strives for adequate scope of data coverage Process of using multiple referents to draw conclusions about constitutes the truth A) B) om C) kt an k. c D) 15. What is triangulation? Use of multiple data sources to validate conclusions Use of multiple methods to collect data about the same phenomenon Process of using multiple referents to draw conclusions about constitutes the truth Independent coding and analysis of at least a portion of the data by two or more researchers A) B) ba n C) w w A) B) C) D) w .te st D) A) B) C) D) What is a strategy for enhancing quality 16. during the coding and analysis of qualitative data? Investigator triangulation Data triangulation Method triangulation Research credibility 17. What is theory triangulation? Use of multiple data sources to validate conclusions Use of multiple methods to collect data about the same phenomenon Use of competing theories or hypotheses in the analysis and interpretation of data Independent coding and analysis of at least a portion of the data by two or more researchers A) B) C) D) A formal scrutiny of the research process and audit trial documents occurs by an 19. independent external auditor. What is the term for this process? Negative case analysis Peer debriefing Inquiry audit Research credibility A) B) C) D) There is widespread agreement that qualitative researchers need to devote time and energy to analyzing and documenting 20. their presuppositions, biases, and ongoing emotions. What commitment does this represent? Transparency Absorption and Diligence Verification Reflexivity w w Answer Key w .te st ba n kt an k. c om A) B) C) D) 18. What is the purpose of a peer briefing? Internal validity of data Reliability of data External validity of data Reliability and validity of data 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. B D A D B D C A D A A B A C C A C 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. A D A A B A C C A C C C D kt an k. c om Chapter 18. Systematic Reviews: Meta-Analysis and Metasynthesis What is similar in the steps for both 1. quantitative and qualitative integration? A) Searching for a problem to solve B) Searching the literature for primary studies C) Reviewing the summary data D) Developing a statistical model ba n st A) w w D) w .te B) C) Evidence-based practice relies on rigorous integration of research evidence on a topic 2. through systematic reviews. What is a systematic review? Use of carefully developed sampling and data collection procedures that are spelled out during data collection Use of methodically integrated data collection procedures that are spelled out during data collection in a protocol Use of carefully developed sampling and data collection procedures that are spelled out in advanced in a protocol Use of methodically integrated data collection procedures that are spelled out during data collection 3. A) B) C) D) What is a criterion for using meta-analytic technique in a systematic review? The evidence among the studies is highly conflicting with many variables. The hypotheses vary in their predictions; both null and directional hypotheses are used. The number of studies can be varied from few to many. The independent variable and the dependent variable should be similar enough to merit integration. A) conflicting with many variables. The hypotheses vary in their predictions; both null and directional hypotheses are used. The number of studies can be varied from few to many. The independent variable and the dependent variable should be similar enough to merit integration. B) C) D) 4. A) om B) kt an k. c C) D) 5. What is considered an advantage of a metaanalysis? Use for broad research questions Use for substantial inconsistency of findings Subjectivity Enhanced power w w .te st ba n A) B) C) D) A) B) C) D) What is a common scenario for meta-analysis in a nursing study? Comparing the percentage of adolescents using hard drugs to the percentage using alcohol Comparing two groups on a continuous outcome Predicting health-related behavior from five different variables Providing descriptions of caring for the chronically ill 6. What is the most common effect size index used in nursing? Standardized deviation Variance Odds ratio Sensitivity index A) B) C) D) Statistical heterogeneity is an issue in metaanalysis and affects decisions about using a 8. single true effect size. What is the name for this single true effect size? Inverse variance Fixed effects model Random effects model Forest plot w A) B) C) D) 7. How can heterogeneity be examined? Inverse variance Fixed effects model Random effects model Forest plot A) B) C) D) Statistical heterogeneity is an issue in metaanalysis and affects decisions about a 9. distribution of effects. What is the name for this distribution of effects? Inverse variance Fixed effects model Random effects model Forest plot A) B) C) D) Effects from individual studies are pooled to yield an estimate of the population effect size 10. by calculating a weighted average of effects. What is often used as the weight? Inverse variance Fixed effects model Random effects model Forest plot kt an k. c ba n st w .te w w A) B) C) D) om A) B) C) D) Statistical heterogeneity is an issue in metaanalysis and affects decisions about using a 8. single true effect size. What is the name for this single true effect size? Inverse variance Fixed effects model Random effects model Forest plot A) B) C) D) 11. What is the purpose of subgroup analyses? Random heterogeneity Nonrandom heterogeneity Sensitivity analysis Nonrelated effects Constructing a funnel plot will assist in determining how many studies with what type 12. of results to reverse the conclusion of a significant finding? Significant Nonsignificant Clinically significant Clinically specific There is no consensus on whether systematic 13. reviews should include the grey literature. What is grey literature? Published in a nonpeer review journal Published in a peer review journal Published report Unpublished report A) B) C) D) 14. What is a publication bias? Stems from over representation of significant findings in the published literature Stems from underrepresentation of significant findings in the published literature Stems from over representation of nonsignificant findings in the published literature Stems from underrepresentation of nonsignificant findings in the published literature om A) kt an k. c B) C) 15. st A) w w D) w .te B) C) A) B) C) D) Paterson and colleagues' meta-study method 16. integrates three components. What are the three components? Metadata, metaeffect, metatheory Metadata, metamethod, metaeffect Metatheory, metamethod, metaeffect Metadata, metamethod, metatheory 17. A) B) C) D) What is an issue with which metasynthesists have grappled? Combining studies with findings from different research traditions. Including some quantitative analysis of the demographics of the participants. Omitting any study that has questionable quality. Using studies with subjects form many different populations ba n D) What is a summary according to Sandelowski and Barroso? Interpretative explanation of the data Statistical explanation of the data Descriptive synopsis of the data Preliminary explanation of the data 17. A) B) C) D) What is a summary according to Sandelowski and Barroso? Interpretative explanation of the data Statistical explanation of the data Descriptive synopsis of the data Preliminary explanation of the data A) B) C) D) What is a synthesis according to Sandelowski and Barroso? Interpretative explanation of the data Statistical explanation of the data Descriptive synopsis of the data Preliminary explanation of the data A) B) C) D) A metasummary involves developing a list of 19. abstracted findings from the primary studies and calculating what effect size? Intensity Frequency Specific Manifest st ba n kt an k. c om 18. w w .te A) B) C) D) A metasummary involves developing a list of abstracted findings from the primary studies. 20. What is the percentage of studies that contain a given findings called? Intensity Frequency Specific Manifest w Answer Key 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. B C C B D C D B C A B B D D om D C D B C A B B D D A D C A D B w w w .te st ba n kt an k. c 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20.