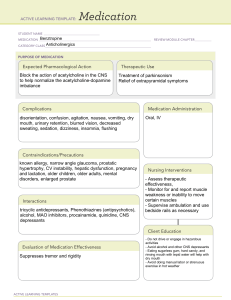
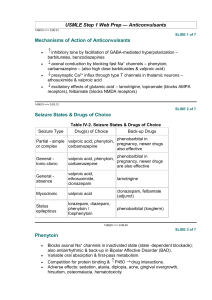
1. What is the major action of phenytoin? Why is phenobarbital also used? Phenytoin is a medication used in the management and treatment of epilepsy, generalized tonicclonic seizures, complex partial seizures, and status epilepticus without significantly impairing neurological function. Phenobarbital is used to control seizures. Phenobarbital is also used to relieve anxiety. It is also used to prevent withdrawal symptoms in people who are dependent on another barbiturate medication and are going to stop taking the medication. Phenobarbital is in a class of medications called barbiturates. It works by slowing activity in the brain. 2. What are some of the CNS effects that Carla might have in relation to taking phenytoin and phenobarbital? CNS effects of taking phenytoin and phenobarbital include nystagmus, ataxia, dysarthria, sedation, and depression. Phenobarbital is a central nervous system depressant; it may cause somnolence, headache, and dizziness. 3. You are discharging Carla; what instructions may increase her ability to manage her therapeutic regimen effectively? a. Patient should contact the physician if they develop any of the following while taking these medications: fever, rash, unusual swelling, chest pain, or experience difficulty breathing. b. Tell the patient to avoid taking antacids or calcium products within 2 hours of taking phenytoin as this can prevent the body from absorbing the drug. c. Take the medication at the same time each day. d. Encourage the patient to avoid alcohol and other CNS depressants during treatment as it might increase the occurrence of side effects. e. Encourage the patient to take the medication as directed and to continue taking it unless otherwise directed by the physician. f. Inform the patient that certain herbs, alcohol, and other CNS depressants should be avoided since they may enhance the effects of the medication. g. Encourage the patient to refrain from potentially risky activities. 4. What education points regarding her medications are of the highest priority? a. Without the doctor's approval, stopping the medicine can make the seizures worse. b. Take the medications as prescribed. c. Do not take other central nervous system depressants such as alcohol while taking the medication. d. Do not engage in hazardous activities as the patient may experience dizziness and drowsiness while using the drugs. e. Encourage follow-up appointments for monitoring the drug levels of phenytoin. f. Educate the patient that Phenytoin is not recommended for use during pregnancy. Phenytoin is a pregnancy category D drug that is a risk to the fetus. g. Notify the provider of any adverse reactions immediately. 5. What side effects should you include in your teaching instructions? a. Educate on abnormal swelling, severe skin problems, including hives, skin rash, and jaundice, as well as heart-related symptoms like a sluggish heartbeat or chest pain, and contact the provider if experienced. b. Encourage the patient to tell her dentist that she is taking phenytoin and emphasize the need for improved oral hygiene if tenderness, swelling, or bleeding of the gums occurs. 6. Give examples of medications or foods that could interfere with Carla's prescribed seizure medications, Phenytoin and Phenobarbital. Aluminum, magnesium, or calcium carbonate antacids, herbal supplements such as St. John's wort, alcohol, and opioids.