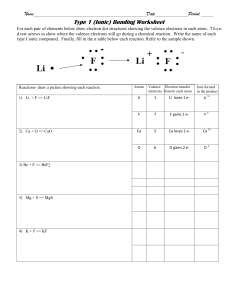
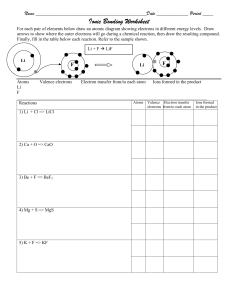
-6.1Ion Formation Objectives (P1) 01 02 Differentiate between the two types of ions based on the atoms classification using the periodic table as a model Construct an explanation for the formation of ions based on valence electrons pattern using the periodic table model Massachusetts Standard HS-PS1-2. Use the periodic table model to predict and design simple reactions that result in two main classes of binary compounds, ionic and molecular. Develop an explanation based on given observational data and the electronegativity model about the relative strengths of ionic or covalent bonds. Key Terms Ions – Cations – Anions – Octet rule – Metal – Non-metal Success Criteria Students be able to use the periodic table and octet rule to predict the ionic form of ions and classify them into metals or non-metals 01 Opening https://javalab.org/en/ionic_bond_2_en/ Share your thoughts and describe how do Na and Cl atoms turn into ions. ● Na atom lost 1 electron to be stable according to octet rule and becomes Na+ ● While Cl atom gains 1 electron to be stable according to octet rule and becomes Cl- Differentiated Tasks The leader is responsible to make sure the all the team has answered all the questions. You will work in group. Choose the task according to your learning style 01 02 You will be given 15 mins to answer the questions in PART A. Use the resources attached in each task. 03 04 Be ready to reflect on what did you solve Social Emotional Skills (SEL) This group work will sharpen your relationships skills: YOU will be able to form positive relationships, to work in teams and deal effectively with conflict Differentiated tasks Learning Style CHOOSE THE TASK THAT YOU PREFER AND LIKE MOST!!!! MAKE YOUR CHOICE Verbal Bias (Prefer Article reading) Task 3 Spatial Bias Task 1 or 2 (Prefer learning through visuals or simulations instead of words) Unbiased Task 1 or 2 or 3 Ion Formation Valence Electrons and Chemical Bonds Electron-dot structures can be used to illustrate the formation of chemical bonds. Valence Electrons and Chemical Bonds • Ionization energy refers to how easily an atom loses an electron. • Electron affinity indicates how much attraction an atom has for electrons. • Noble gases, which have high ionization energies and low electron affinities, show a general lack of chemical reactivity. • Noble gases have electron configurations with a full outermost energy level. Valence Electrons and Chemical Bonds • Elements tend to react to acquire the stable electron structure of a noble gas. • Atoms try to form an octet—a stable arrangement of eight valence electrons in the outer energy level—by gaining or losing valence electrons. Positive Ion Formation • A positive ion forms when an atom loses one or more valence electrons in order to attain a noble gas configuration. • A positively charged ion is called a cation. Positive Ion Formation • This figure illustrates how sodium loses a valence electron to become a sodium cation. • By losing an electron, the sodium atom acquires the stable outer electron configuration of neon. Positive Ion Formation • Transition metals commonly form 2+ or 3+ ions, but can also form ions of 3+ or greater. • Other relatively stable electron arrangements are called pseudo-noble gas configurations. Negative Ion Formation • Non-metals easily gain electrons to attain a stable outer electron configuration. • The figure shows chlorine gaining an electron. • An anion is a negatively charged ion. Thus, the chlorine atom becomes a chloride anion. Exit Ticket Use the periodic table to write the ionic form for: Barium atom (Ba) and Nitrogen atom (N) Ba belongs to group 2: the ionic form is Ba2+ N belongs to group 15: the ionic form is N3- Objectives (P2) 01 02 Construct an explanation for an ion formation based on the electron configuration pattern and octet rule using the periodic table model Design a simple ionization reaction for the formation of cations and anions using the periodic table model Massachusetts Standard HS-PS1-2. Use the periodic table model to predict and design simple reactions that result in two main classes of binary compounds, ionic and molecular. Develop an explanation based on given observational data and the electronegativity model about the relative strengths of ionic or covalent bonds. Key Terms Ions – Cations – Anions – Octet rule – Metal – Non-metal Success Criteria Students be able to use the periodic table and octet rule to predict the ionic form of ions and to write the ionization reaction for their formation 02 Opening Analyze the following image and then answer the question Let’s spread positivity. How would these elements behave to become positive? These elements are metals so they will lose electrons to become stable so they will be positive Differentiated Tasks The leader is responsible to make sure the all the team has answered all the questions. You will work in group. Choose the task according to your learning style 01 02 You will be given 15 mins to answer the questions in PART B. Use the resources attached in each task. 03 04 Be ready to reflect on what did you solve Social Emotional Skills (SEL) This group work will sharpen your relationships skills: YOU will be able to form positive relationships, to work in teams and deal effectively with conflict Differentiated tasks Learning Style CHOOSE THE TASK THAT YOU PREFER AND LIKE MOST!!!! MAKE YOUR CHOICE Verbal Bias (Prefer Article reading) Task 3 Spatial Bias Task 1 or 2 (Prefer learning through visuals or simulations instead of words) Unbiased Task 1 or 2 or 3 Exit Ticket Write the equation for the formation of Oxygen ion. O + 2e- ⭢ O2- Objectives (P3) 01 02 Construct an explanation for an ion formation based on the electron configuration pattern and octet rule using the periodic table model Describe pseudo noble electron configuration of d-block elements to form ions using the electron configuration pattern. Massachusetts Standard HS-PS1-2. Use the periodic table model to predict and design simple reactions that result in two main classes of binary compounds, ionic and molecular. Develop an explanation based on given observational data and the electronegativity model about the relative strengths of ionic or covalent bonds. Key Terms Ions – Cations – Anions – Octet rule – Metal – Non-metal – Pseudo noble gas electron configuration Success Criteria Students be able to use the periodic table and octet rule to predict the ionic form of ions, their electron configuration and apply pseudo electron configuration for the formation of d block ions 03 Opening https://youtu.be/zqxl3CdZ DLM Till 2:00 Explain how the transition metals lose electrons. Justify your answer. Transition metals lose electrons from the valence shell first, which is not the last subshell. This means that they are going to lose electrons from the last s. Differentiated Tasks The leader is responsible to make sure the all the team has answered all the questions. You will work in group. Choose the task according to your learning style 01 02 You will be given 15 mins to answer the questions in PART C. Use the resources attached in each task. 03 04 Be ready to reflect on what did you solve Social Emotional Skills (SEL) This group work will sharpen your relationships skills: YOU will be able to form positive relationships, to work in teams and deal effectively with conflict Differentiated tasks Learning Style CHOOSE THE TASK THAT YOU PREFER AND LIKE MOST!!!! MAKE YOUR CHOICE Verbal Bias (Prefer Article reading) Task 3 Spatial Bias Task 1 or 2 (Prefer learning through visuals or simulations instead of words) Unbiased Task 1 or 2 or 3 Exit Ticket https://dashboard.blooket.com/set/6 332dbd2b5616adbf431c99c