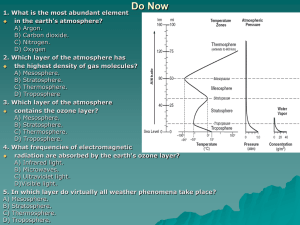
COMPOSITION AND LAYERS OF THE ATMOSPHERE Composition of the Atmosphere NITROGEN The most abundant gas in the atmosphere. It is a stable gas , it doesn’t react into the chemical combination easily. It enters the system of the living things in the form of nitrate(NO3) and ammonia(NH3). Nitrogen cycle. Nitrogen Cycle OXYGEN The second most abundant gas in the atmosphere. Living things take in oxygen during respiration. Photosynthesis contributes to the oxygen content of the atmosphere by releasing it as a by product of the process. PHOTOSYNTHESIS CARBON DIOXIDE It comprises a tiny fraction of the atmospheric gases. Living things release carbon dioxide during respiration. It is important for plants because it is a raw material for photosynthesis. Deforestation and fossil fuel combustion. Carbon dioxide-Oxygen Cycle DIFFERENT ATMOSPHERIC LAYERS LAYERS OF THE ATMOSPHERE TROPOSPHERE The layer that is nearest to Earth’s surface. It is the densest layer since it contains about 75% of the atmospheric gases enumerated from above. Clouds of all types, storms, and all types of weather phenomena characterized this layer. Tropopause the upper boundary of the troposphere. STRATOSPHERE The layer immediately above the troposphere. Less dense and relatively dry. The ozone layer is found in this layer, which absorbs the ultraviolet radiation and transform it to heat. The upper boundary of the stratosphere is called stratopause. MESOSPHERE This layer start just above the stratosphere. The temperature drops significantly in this layer to as low as -93 degrees Celsius( because the altitude increases). The mesopause separates the mesosphere from the next layer of the atmosphere. THERMOSPHERE The thermosphere start just above the mesosphere. This layer contains a tiny fraction of the atmospheric gases. Chemical reactions occur much faster in this layer due to the increasing heat from the sun. The thermopause separates the thermosphere from the exosphere. Exosphere is a thin transition layer into the outer space, here hydrogen atoms in the atmosphere flee off the outer space. At the lower region of the thermosphere, blending with the upper region of the mesosphere is a layer called ionosphere, which is thick and rich in ions. The ionosphere plays important role in radio and telecommunications operation on earth.