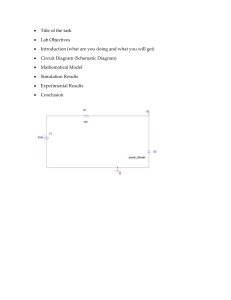
STUDY AND VERIFICATION OF KIRCHOFF’S CURRENT LAW A PROJECT REPORT Submitted by AFRAH NAJEEB In partial fulfilment for the award Of ALL INDIA SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION In PHYSCIS SANA MODEL SCHOOL,CHENNAI - 600 056 CENTRAL BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION 2022-2023 SANA MODEL SCHOOL,CHENNAI 600 056 BONAFIDE CERTIFICATE Certified that this project report“…………………………………………….” Is the bonafide work of “……………………………..………………………” Of grade ….…………….…., Register Number ……………….…………. Who carried out the project work under my(our) guidance and supervision at Sana Model School, Chennai. SIGNATURE SIGNATURE PHYSICS TEACHER PRINCIPAL Sana Model School, Chennai Sana Model School,Chennai Submitted for the physics practical examination held on ____________________ INTERNAL EXAMINER EXTERNAL EXAMINER ACKNOWLEDGEMENT With immense pleasure. I would like to thank those who have helped me in completing this project work. I extremely thank the almighty who guided me in completion of the project and who is always there to help me. I am thankful to my parents for their extreme and unlimited support for me to work with the project. I thank my principal Mrs. NAJIA TAHMEEN for her immense encouragement , providing us with all facilities and all kind of moral support to carry out this project work. I take this opportunity to give my special thanks to my physics teacher Mr. AJAS AHMED for his inevitable help. It is much of their guidance that endeavours to complete this project. I also thank the whole staff of physics department for their timely help. I would like to thank my friends who have helped me with their Suggestion for the completion of this project. CONTENTS S.NO CONTENT Pg.NO 1 Abstract 1 2 Introduction 2 3 Theory 3-4 4 Material required 5-6 5 Circuit diagram 7 6 Procedure 8 7 Analysis 1 9 8 Analysis 2 10 9 Analysis 3 11 10 Analysis 4 12 11 Analysis 5 13 12 Analysis 6 14 13 Observation 15 14 Component Analysis 16 14 Result 17 15 Application 18 16 Bibliography 19 ABSTRACT The purpose of this project is to verify “KIRCHOFF’S CURRENT LAW” and it deals solely with current. Kirchhoff’s Current Law is the most fundamental tool used in the analysis of electric and electronic circuits. The objective of applying this laws to a circuit is to determine the behavior of the currents throughout the circuit. This handout will provide a summary of law as well as examples of it’s application. i A circuit was built using the given schematic. This circuit was J also drawn in multisim. The circuit was then analysed using three separate methods: The Kirchoff’s law ,multisim stimulatio and a digital multi-meter Kirchoff’s current law was found to be valid after comparing l n . . The results from all three tests INTRODUCTION Many of the electrical circuits are complex in nature and the j computations required to find the unknown quantities in such h circuits, using simple ohm’s law and series/parallel combination K simplifying methods is not possible. Therefore, in order to simplify h these circuits Kirchhoff’s laws are used. These laws are the fundamental analytical tools that are used to find the solutions of voltages and currents in an electric circuit whether it can be AC or DC. Elements in an electric circuit are connected in numerous possible ways, thus to find the parameters in an electrical circuit these laws are very helpful. THEORY Kirchoff’s Current Law Kirchoff’s Current Law (KCL) deals with the currents flowing into and out of a given node. KCL states that the sum of all currents at a node must equal zero. This is illustrated in Figure 2. Figure 2: An example of KCL The equation obtained by KCL for the node shown in Fig. 2 is I1 −I2 −I3 =0. (2) In the case of KCL the passive sign convention deals with the direction of currents with respect to the node. Currents entering the node must have opposite signs as those exiting the node. ♦ Sum of all currents entering a node is zero. ♦ Sum of currents entering the node is equal to sum of currents leaving the node. Before going to know more about Kirchhoff’s current law, we have to consider some of the terms related to electric circuits. Node: Node or junction is a point in the circuit where two or more electrical elements are connected. This specifies a voltage level with a reference node in a circuit. Branch: The continuous conducting path between two junctions which contains electrical element in a circuit is referred as branch. MATERIALS REQUIRED 1. Battery Eliminator A device powered by an electrical source other than a battery, which then converts the source to a suitable DC voltage that may be used in the circuit 2. Decade Resistance Box An instrument for measuring and comparing electrical resistances. 3. Voltmeter An instrument for measuring electrical potential in volts 4. Ammeter An instrument for measuring electric currents in amperes. 5. Connecting wires CIRCUIT DIAGRAM PROCEDURE 1. Connections are made as per the circuit diagram. 2. Switch on the DC power supply 3. Measure the current values using multi-meter 4. Note down the corresponding reading 5. Calculate the total current theoretically . 6. Verify the values using multisim stimulation . 7. Finally verify KCL . 8. Repeat the same procedure for different values of voltages. ANALYSIS 1 Theoretical : Simulation : Practical : ANALYSIS 2 Theoretical : Simulation : Practical : ANALYSIS 3 Theoretical : Simulation : Practical : ANALYSIS 5 Theoretical : Simulation : Practical : ANALYSIS 6 Theoretical : Simulation : Practical : OBSERVATION Applied Current through the ammeter (mA) Voltage Theoretical Simulation Practical (V) %Erorr Volts 0.667 0.667 0.66 0% 1.33 1.33 1.26 0.1% 2.00 2.00 1.98 0% 2.66 2.66 2.66 0% 3.33 3.33 3.33 0% 4.00 4.00 3.86 0.04% 2V 4V 6V 8V 10 V 12V COMPONENT ANALYSIS S.NO COMPONENT NUMBER COST (in Rs) 1 Battery Eliminator 1 543 2 RDB 3 3500 3 Ammeter 1 149 4 Voltmeter 1 175 5 Connecting wires 14 10 Total = 4377 RESULT Using Kirchoff’s Current Laws the currents is theoretically calculated & practically verified. The simulation of the circuit verified KCL. This was shown by multisim found the sum of the two currents exiting the node to be equal to the current entering the node. The experimental results of the KCL test were not so close. There was less than two percent error between the measured and calculated I1’s. This error is acceptable in stating that KCL is true. APPLICATIONS • By using these laws, we can find the unknown resistances, voltages and currents (direction as well as value). • In the branch method, finding the currents through each branch carried by applying KCL at every junction . • In the loop current method, finding current through each independent loop is carried by applying KVL for each loop and counting all the currents in any element of a circuit. • Used in nodal method of finding voltages and currents. • These laws can be applied to analyse any circuit regardless of the composition and structure of it. BIBLIOGRAPHY https://www.electronicshub.org/kirchhoffs-laws/ https://webstor.srmist.edu.in/web_assets/srm_mainsite/files/ files/EC0122-labmanual.pdf https://www2.gvsu.edu/peirsonb/kvl_kcl_ohms_law.pdf https://godavaricoejal.ac.in/Admin/DOWNLOAD/27.pdf https://www.multisim.com/create/ NCERT class 12 textbook ANALYSIS 4 Theoretical : Simulation : Practical :