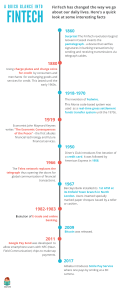
Fintech and the Future of Banking: Leveraging opportunities and mitigating risks Introduction Banking has ever played a pivotal role in the financial services sector, often acting as a driver of economic and financial progress in societies, by providing transactional services that have bridged the financing gap between different participants in the economy. This has since grown the trust of depositors in the banking institutions, as banking institutions provide complete financial solutions such as credit risk diversification, insurance, etc., which has ever since strengthened the market share that the banks hold, giving them a say in charting the future path of the financial services industry. Fintech firms are relatively a newer concept, which is defined as a company “leveraging technology to provide financial services solutions to customers to better handle their finances”. These do not possess a banking license, which does not allow them to engage in core banking activities of taking deposits and lending. However, Fintech solutions, such as Digital Commerce and Mobile Payments, have altered the way traditional banking activities have been performed, and these disruptions have helped to make the solutions further accessible and extended the last mile connectivity to the users. Investments into the Fintech space have grown ever since, owing to the disruptive power of the solutions they provide, and the potential of growth that can be achieved through them. Source: Statista Tussle between banks and fintech & the way forward A major point of contention in the financial services industry is the challenge that Fintech and new-age technology firms pose to traditional banking firms. Fintech firms have the power and technology to provide their solutions to interest groups even beyond the scope of the banking industry, and this power challenges the hegemony of banks in the financial services industry. However, without a banking license, Fintech firms cannot get access to the large database of consumers that banks hold. Moreover, customers do not easily trust new companies with their money, as they tend to be “stickier” with their money and rather on average trust the services of incumbents with it. However, banks cannot solely rely on the traditional brick-and-mortar banking model, where customers have to walk in every time to a bank branch to get their work done. And this is where new technology plays a role, in the “digitization” as well as the “digitalization” of banking services. Banks have, in major parts of the world, digitalized their entire services, which include payments and transfers, loan applications, etc., and brought it to the convenience of the user through mobile and E-banking. All other fee-based financial services, such as insurance, brokerage and mutual funds, have gone through the digitalization process by banks, and have also seen the emergence of various other platforms, that leverage technology to provide the same services, with a better customer experience. With all the innovations coming in, there could be two possible alternatives in the financial services industry: either banks and financial institutions could invest in and develop in-house fintech products, which might take a significant amount of time depending on the product, or they could partner with Fintech firms that already have in place a product and full-time R&D team that constantly works on the upgradations. Such a mutually beneficial collaboration could save up on huge amounts of costs and time, and offer customers benefits such as faster onboarding, quick and timely disbursals and a superior user experience. These collaboration options become even more crucial considering the evolving business models and threat of new entrants in the financial services space. For example, Challenger Banks and Neobanks use Technology to provide services to customers with little to no dependence on the offline branches to facilitate services. Their main focus remains on the core product and making it more cutting-edge through the provision of technology. Similarly, technology firms like Google, Amazon, Apple offer the entire value chain of services – from payments to communication, and even lending as well. And so does WeChat, which positions itself as a “one-stop-shop” offering a range of services, ranging from messaging, social networking, to incorporating payments through QR codes. Banks can learn from these emerging business models and better utilise their customer data as they can make better assessments about the credit profile and the financial needs of the customers, and use it to offer better customized products to their customers. However, a greater consideration will have to be given to privacy and the access that banks can get to the sensitive customer data. Unethical use and breach of data can hamper the trust of customers and lead them to dropping out of the bank, leading to losses of potential future revenue. Moreover, as the regulations would evolve, there would have to be constant upgrades (or degrades), as will be dictated by the regulations, which could either provide a structure for the industry to flourish, or curtail the various innovations, depending on the restrictions. Going forward, banks will have to identify various customer needs where an investment in technology could yield multi-fold benefits for the bank, however, innovation on the bank or fintech’s part would largely have to be customer centric, in the sense, the innovation shouldn’t be product focused, but focused on the customer experience, and it should be constant: continuous product evolvements would have to take place to stay ahead of the competition. A good example for the same could be “Super-app”, which is personalized based on the customer’s purchase history, providing multiple payment options, constantly working on the user experience, and offering customers full control of the access the superapp could have to their data. Conclusion Fintech has the potential to disrupt the way financial services have been conducted as of yet, and it is important to understand that more such disruptions will occur in the future. Hence, a better approach for banks and financial institutions would be to approach Fintech firms as a collaborator and not as a potential competitor. Fintech has helped to create numerous innovative products that have altered the traditional method of banking, and adoption of the technical innovation by banks has led to increased convenience for the customers. Adoption of fintech by banks requires careful planning and consideration, but the benefits would surely outlie the risks posed by the adoption.