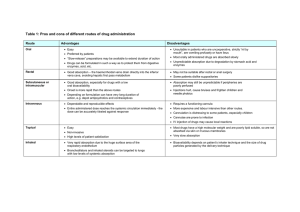
NCM 106 PHARMACOLOGY READINGS • • • • • • PHARMACOKINETICS is the process of drug movement to achieve drug action. The four processes are absorption, distribution, metabolism (or biotransformation), and excretion (or elimination). The nurse applies knowledge of pharmacokinetics when assessing the patient for possible adverse drug effects. The nurse communicates assessment findings to members of the health care team in a timely manner to promote safe and effective drug therapy for the patient. Absorption is the movement of drug particles from the GI tract to body fluids by passive absorption, active absorption, or pinocytosis. Most oral drugs are absorbed into the surface area of the small intestine through the action of the extensive mucosal villi. Absorption is reduced if the villi are decreased in number because of disease, drug effect, or the removal of small intestine. Protein-based drugs such as insulin and growth hormones are destroyed in the small intestine by digestive enzymes. o Passive absorption occurs mostly by diffusion (movement from higher concentration to lower concentration). With the process of diffusion, the drug does not require energy to move across the membrane. o Active absorption requires a carrier such as an enzyme or protein to move the drug against a concentration gradient. Energy is required for active absorption. o Pinocytosis is a process by which cells carry a drug across their membrane by engulfing the drug particles. Remember, drugs that are lipid soluble and nonionized are absorbed faster than water-soluble and ionized drugs. Drugs given IM are absorbed faster in muscles that have more blood vessels (e.g., deltoids) than in those that have fewer blood vessels (e.g., gluteals). Subcutaneous tissue has fewer blood vessels, so absorption is slower in such tissue. The process in which the drug passes to the liver first is called the first-pass effect, or hepatic first pass. • • BIOAVAILABILITY is a subcategory of absorption. It is the percentage of the administered drug dose that reaches the systemic circulation. For the oral route of drug administration, bioavailability occurs after absorption and first-pass metabolism. The percentage of bioavailability for the oral route is always less than 100%, but for the IV route it is 100%. • • • • Distribution is the process by which the drug becomes available to body fluids and body tissues. Drug distribution is influenced by blood flow, the drug’s affinity to the tissue, and the protein-binding effect. Metabolism is the process by which the body inactivates or biotransforms drugs. Drugs can be metabolized in several organs; however, the liver is the primary site of metabolism. Most drugs are inactivated by liver enzymes and are then converted or transformed by hepatic enzymes to inactive metabolites or watersoluble substances for excretion. The half-life (t 1/2) of a drug is the time it takes for one half of the drug concentration to be eliminated. Metabolism and elimination affect the half-life of a drug. • • • • Elimination The main route of drug elimination is through the kidney (urine). Other routes include bile, feces, lungs, saliva, sweat, and breast milk. The kidneys filter free unbound drugs, water-soluble drugs, and drugs that are unchanged. The lungs eliminate volatile drug substances and products metabolized to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). PHARMACODYNAMICS is the study of the way drugs affect the body. Drug response can cause a primary or secondary physiologic effect or both. The primary effect is desirable, and the secondary effect may be desirable or undesirable. An example of a drug with a primary and secondary effect is diphenhydramine (Benadryl), an antihistamine. The primary effect of diphenhydramine is to treat the symptoms of allergy, and the secondary effect is a central nervous system depression that causes drowsiness. The secondary effect is undesirable when the patient drives a car, but at bedtime it could be desirable because it causes mild sedation. PARACETAMOL is a generic name. Its common brand names are Panadol, Tylenol, and Bioflu.