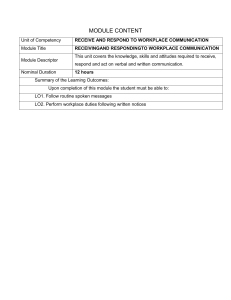
7/8 i TLE – Agri-Fishery Arts (Animal Production) - Grade 7/8 Alternative Delivery Mode Module 1: Participating in Workplace Communication First Edition, 2020 Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for exploitation of such work for profit. Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalties. Borrowed materials (i.e., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names, trademarks, etc.) included in this module are owned by their respective copyright holders. Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from their respective copyright owners. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim ownership over them. Published by the Department of Education, Division of Palawan Schools Division Superintendent: Natividad P. Bayubay, CESO VI Assistant Schools Division Superintendent: Loida Palay- Adornado, Ph.D. Felix M. Famaran Development Team of the Module Writers: Mischelle S. Sianson, Elisa C. Moreno, Vine Catherine B. Cadlaon Editors: Melissa P. Balmonte, Erma S. Bacosa Reviewers: Li Ann P. Cabutin, Evelyn T. Jardin, Rodora C. Carim Illustrator: Jerin B. Octa Layout Artist: Jerin B. Octa Management Team: Aurelia B. Marquez Rodgie S. Demalinao Clemencia G. Paduga Mary Jane D. Virrey Printed in the Philippines by ________________________ Department of Education – MIMAROPA Region – Division of Palawan Office Address: PEO Road, Barangay Bancao-Bancao, Puerto Princesa City Telephone (048) 433-6392 E-mail Address: palawan@deped.gov.ph Website: www.depedpalawan.com ii 7/8 iii Introductory Message For the facilitator: Welcome to the TLE- Agri -Fishery Arts (Animal Production) 7/8 Alternative Delivery Mode (ADM) Module 1: Participating in Workplace Communication This module was collaboratively designed, developed and reviewed by educators both from public and private institutions to assist you, the teacher or facilitator in helping the learners meet the standards set by the K to 12 Curriculum while overcoming their personal, social, and economic constraints in schooling. This learning resource hopes to engage the learners into guided and independent learning activities at their own pace and time. Furthermore, this also aims to help learners acquire the needed 21st century skills while taking into consideration their needs and circumstances. In addition to the material in the main text, you will also see this box in the body of the module: Notes to the Teacher This contains helpful tips or strategies that will help you in guiding the learners. As a facilitator, you are expected to orient the learners on how to use this module. You also need to keep track of the learners' progress while allowing them to manage their own learning. Furthermore, you are expected to encourage and assist the learners as they do the tasks included in the module. For the learner: Welcome to the TLE– Animal Production 7/8 Alternative Delivery Mode (ADM) Module on: Participating in Workplace Communication This module was designed to provide you with fun and meaningful opportunities for guided and independent learning at your own pace and time. You will be enabled to process the contents of the learning resource while being an active learner. This module has the following parts and corresponding icons: This will give you an idea of the skills or competencies you are expected to learn in the module. What I Need to Know iv What I Know This part includes an activity that aims to check what you already know about the lesson to take. If you get all the answers correct (100%), you may decide to skip this module. What’s In This is a brief drill or review to help you link the current lesson with the previous one. What’s New In this portion, the new lesson will be introduced to you in various ways such as a story, a song, a poem, a problem opener, an activity or a situation. What is It This section provides a brief discussion of the lesson. This aims to help you discover and understand new concepts and skills. What’s More This comprises activities for independent practice to solidify your understanding and skills of the topic. You may check the answers to the exercises using the Answer Key at the end of the module. What I Have Learned This includes questions or blank sentence/paragraph to be filled in to process what you learned from the lesson. What I Can Do This section provides an activity which will help you transfer your new knowledge or skill into real life situations or concerns. Assessment This is a task which aims to evaluate your level of mastery in achieving the learning competency. Additional Activities In this portion, another activity will be given to you to enrich your knowledge or skill of the lesson learned. Answer Key This contains answers to all activities in the module. At the end of this module you will also find: References This is a list of all sources used in developing this module. v The following are some reminders in using this module: 1. Use the module with care. Do not put unnecessary mark/s on any part of the module. Use a separate sheet of paper in answering the exercises. 2. Don’t forget to answer What I Know before moving on to the other activities included in the module. 3. Read the instruction carefully before doing each task. 4. Observe honesty and integrity in doing the tasks and checking your answers. 5. Finish the task at hand before proceeding to the next. 6. Return this module to your teacher/facilitator once you are through with it. If you encounter any difficulty in answering the tasks in this module, do not hesitate to consult your teacher or facilitator. Always bear in mind that you are not alone. We hope that through this material, you will experience meaningful learning and gain deep understanding of the relevant competencies. You can do it! What I Need to Know This module covers the knowledge in participating in workplace communication. Unit of Competency: Participating in Workplace Communication (TVL_AFAAPP C9-12PWC-Ia-1) Nominal Duration: 5 days Modules Lesson: Participating in Workplace Communication Learning Outcomes: Upon completion of this module, you are expected to: LO 1. Obtain and convey workplace communication LO 2. Participate in workplace meeting and discussion LO 3. Complete relevant work-related documents vi What I Know Activity 1 This module will help you understand and apply what you have learned in the world of communication. Let us see what you know about Communication. Pretest Direction: Choose the letter of the correct answer. Write your response to the separate activity sheet. 1. It is a source of information through observation. A. Listening B. Observing C. Organizing D. Recording 2. A way of communicating using hand gesture, posture and facial expression is called _________. A. authentic communication C. verbal communication B. non – verbal communication D. none of the above 3. When sharing communication there are things that one must do except_________. A. listening carefully C. speaking clearly B. making eye contact D. slouching 4. A type of communication which style is clear, honest, direct and open. A. Assertive Communication C. non- assertive communication B. Aggressive Communication D. Non – Aggressive Communication 5. What is the benefit of working together? A. We see our own faults and criticize them. B. Allows each individual to grow and succeed. C. Fails to see personal weaknesses. D. Learns to work independently. 6. Which of the following is true about teamwork? A. It teaches us not to trust other people. B. It allows us to figure out who not to trust. C. We learn how to not work with different personality types. D. Gives us preparation for the workplace. 7. The following are the things that gossiping does to a team; except ______. A. hurting relationship B. leading to a healthy competition in a team C. creating selfishness D. dampening enthusiasm 1 8. What are the clear responsibilities? a. No one understands the goal. b. Everyone understands their goal. c. The team is full of diversity and each member has individual values. d. Group has outside help. 9. Which of the following has a quality teamwork? A. with independence C. good communication B. credit for achievement D. easy decision making 10. Who is the leader? A. A member with bad behavior B. The one making decisions C. The one teaching the subject in the team D. The main source of the team Lesson 1 What’s In Activity 2. Directions: Given is the definition of sources. Arrange the jumbled letters to get the correct answer. 1. It is used for the transmission of data in coded form. O R D I A 2. It is one of our world’s most important means of communication. It shows us information programs like the news, documentaries and sports events. N E T I O S L 2 E V I 2. It’s easy to send a quick text message in a workplace that one monitors personal calls. When meetings go long employees can check their phones for important emails. L P O L E H O C E L 3. It is a periodical publication which is printed in gloss- coated and matte paper. N I Z E G A M A 4. It refers to printed media and a source of a powerful mode of mass communication. S E W E R N A P P What’s New Communication Skills for Workplace Success The ability to communicate effectively with superiors, colleagues, and staff is essential, no matter what industry you work in. Workers in the digital age must know how to effectively convey and receive messages in person as well as via phone, email, and social media. Essential Communication Skills for Your Career ▪ Listening ▪ Friendliness ▪ Open-Mindedness ▪ Feedback ▪ Confidence ▪ Non-Verbal Communication 3 What is It Participate in Workplace Communication. Workers must be able to communicate information to work effectively. Information is communicated in two directions-sometimes you receive information and sometimes you convey it. You communicate regularly with your employer or supervisor and your co-workers. Gathering information for work. Every day, you have to gather the information that you need for your work. Some information comes from your supervisor, co-workers, clients, suppliers, and other people you speak with each day. Some information such as work rosters, vehicle logbooks, or telephone messages, comes in written form. You might also gather information from your observations. For example, looking at a rain gauge, or checking supplies of materials. Information sources • • • • • • • • • • • • Letters Memos Plans Internet websites Faxes Emails Newsletters Work notes Order sheets SMS Industry Magazines Listening Quite a lot of information is collected by listening to someone. You can listen to the other person in different ways: • • • Face to face By telephone By radio Observing You can also collect information by observation. • • • • Count items of stock Check the condition of equipment or livestock Check a thermometer, vermin traps, a fuel gauge Watch a TV program or DVD Recording Information Workplaces rely on large amounts of information from many different sources to operate effectively. Most of that information is recorded either manually (on paper) or electronically (on the computer). Work schedules, product catalogues, orders and receipts, timesheets, and 4 memos are all examples of written information, or records, found in most workplaces. Locating written information before you can use records, you need to know where to find them. Written information may be located in: • • • • • • • Computer databases Filing cabinets Shelving Counters Drawers Pin Boards or whiteboards Organizing written information Records need to be kept in the same place all the time so that everyone knows where to get them when they want to use them. It would be very frustrating to find that the vehicle logbook was not in the truck as it should be, or that someone had moved the order book just when you needed it to answer a customer inquiry. Sometimes many records are kept together in one place, such as in a filing cabinet. They are often organized in alphabetical order so that they are easy to find. There are many ways to organize records, so you must use the method preferred in your workplace. Records stored together must be replaced in the correct order to make it easy for everyone to find them. Some records are only needed for a short time. Recording information accurately and legibly Written information is only useful if it is accurate and legible. A great deal of time and effort can be saved in the long term if you take care to check that the information is correct before you write it down. Of your handwriting is not very clear, it might be better to print the information so that it can be easily read. Communicating with people in the workplace Communicating courteously and clearly. An important part of your job is to pass on information to other people. Lots of messages and instructions that you receive in person, or by telephone or radio, have to be passed on to someone else. You could use the phone or a written note to pass on the information, or you could speak to the other person face to face. Much of the time you will be communicating with co-workers or your supervisor, but you might also have to talk to clients. Anyone that you provide with a product or service is your client. You can have both internal and external clients. Internal clients are the people you deal with in other sections of your workplace. External clients are customers, suppliers, industry bodies, government employees, contractors or anyone else in your industry network. There is good reason for you to communicate courteously and clearly with all these people. You have to get along with the people at your workplace, and you can do that better if you treat them with respect and help them as much as you can. When you are dealing with people from outside your workplace, you are representing your employer and you need to present a good image. 5 Communicating face to face Communicating face to face with other people involves: • • • • Speaking Listening Observing Being observed When you are face to face with another person, you don’t just hear the words they say, you also hear their tone of voice, see what they look like and watch how they behave. At the same time, they can hear, see and watch you. Observing and being observed Would you be convinced by the advice of a safety inspector who forgot his hard hat and steel-capped boots? Would you want a sandwich made by a lunch bar attendant with filthy hands and clothes? Your personal presentation dress and hygiene all contribute to the impression you make on others. The appropriate personal presentation demonstrates your respect for yourself, your employer, and the people you interact with through your work. Make sure your clothes are suitable for the work you do. If your work calls for personal protective equipment, make sure you wear it. In some jobs, you will need to cover long hair and jewelry. You should be neat, clean, and well-groomed for a job that involves personal contact with others especially the general public. People also notice “body language”. The way you use your hands, your posture and the expressions on your face are all examples of non-verbal behavior that you can use to get your message across. When you are face to face with someone, you pick up a lot of information from their non-verbal communication. Some people can be very quiet, yet still, show aggressive body language. They might have a pained look on their face, they might look tense, or they might shake with anger. You interpret as much from their mannerisms and gestures, tone of voice, and level of eye contact, as you do from their words. Choosing the right way to share information depends on the needs and interests of the other persons, not just on what you want to say. When sharing information: 6 • • • • • • DON’T DO Stand or sit up straight Make eye contact Smile and greet the other person Listen and observe carefully Speak clearly Get straight to the point • • • • • • Slouch Look around Read the newspaper and pretend you haven’t noticed anyone Interrupt or be destructed Mumble waffle Listening Listening is more than hearing, and it requires some effort. It involves non-verbal communication as well. When people are giving you instructions, you need to listen carefully so that the job is done safely and accurately. By being a good listener, you will follow instructions more accurately and reduce the risk of accidents. As a listener you should: • • • listen to people’s feelings show you are listening to the answer you give use non-verbal means to encourage the speaker to continue Speaking A lot of workplace communication involves asking questions or responding to inquiries. To get the answers you want, you have to ask the right questions. Be specific about what you need to find out so that the other person understands clearly. If you need to ask several questions, it will help you to remember them all if you write them down first. Speak slowly and clearly so that you are heard and understood the first time. The other person must be able to pay full attention what you are saying, so choose a mutually convenient time. If you need to know the answer urgently, you might have to interrupt. Just make sure you explain that it is important. Before you ask a question of anyone, think about. Working in groups Work groups Many workplaces set up groups of workers to perform a certain job or achieve a particular goal. The work group may be split up afterwards or given a new job or goal. The people who make up the group may all be from the one section of the business with similar skills and qualifications. Work groups can be set up for many different reasons. They could work on: • • shutting down equipment for annual maintenance organizing a revegetation program 7 • • revising OHS guidelines planning a special event Your group discussions When people come together in groups, they bring many different ideas, experiences and skills. Working in groups fosters initiative, tolerance and trust. Work in groups can: • • • • share information solve problems make decisions accomplish tasks For work groups to be successful, people have to communicate and cooperate. Structuring meetings Meetings need a structure. Without structure, the discussion usually takes far too much time without reaching any firm decisions. An agenda is used to give some structure to a group discussion. An agenda lets people know what the meeting will be about so that they can think about it before they come. It makes sure that everything necessary is included for discussion and nothing gets forgotten at the meeting. During the meeting, it keeps the discussion on track. Formal meetings A typical agenda for a formal meeting includes the following items: • • • • • • • • • • • opening welcome and apologies minutes from the previous meeting business arising from the minutes correspondence, inwards and outwards business arising from the correspondence reports financial and subcommittees general business other business date, time and place of the next meeting close Informal meetings Informal meetings also need an agenda, although it might be much simpler than the one shown above. It should include opportunities to discuss: • • • • the purpose of the meeting what has happened so far what problems still need to be addressed how the workgroup will achieve goals 8 Obligations of workgroup members As a member of a workgroup, you have an obligation to: • • • • • • attend meetings participate to the best of your ability behave courteously towards other members of the group comply with meetings decisions carry out instructions decided at meetings keep sensitive matters confidential If your obligations are not obvious or clear, you should ask your supervisor or co-workers for advice. Types of communication Assertive communication • clear, honest • direct open communication • listens attentively to others Style Non-verbal signs • • • • Underlying value • • • eye contact relaxed posture smiles/ nods when others speak speaks in a friendly tone respects others ideas and opinions enjoys communicating with others “I’m OK; you’re OW” Aggressive communication • verbal abuse • name-calling • oneupmanship • win at all costs • does not listen to others loud voice • sarcastic tone • finger-pointing • tablethumping etc • angry tense expression • • • Does not respect others opinions and ideas Enjoys power over others “I’m OK; you’re not OK” Nonassertive communication • withholds opinion • does not share ideas • agrees with others without expressing a personal view • avoids eye contact • quiet voice closed posture • • • Believes other people’s ideas are better than their own Feels threatened by open communication “You’re OK; I’m not OK” Types of Forms In every workplace, you will be required to complete the forms. Each workplace will have forms specific to their requirements. You must make sure that you know which forms to fill in when you need to use forms and where to find the necessary forms. When filling in a form: • • Read the form carefully Fill in all the required details 9 • • • • Only include necessary information Write clearly and simply Check that you have completed it properly Send or give it to the appropriate person, or file in the appropriate place Common Errors Can Delay the Recording of Your Documents An error may result in our office having to “REJECT” and mail back your submission. Use the information below as a checklist to ensure your documents are recorded on time. • Make sure checks are signed. • Print names and titles legibly under all signatures. • Notary stamp must be legible and dark; notary stamp should not obscure document wording or notary name and expiration date. • “Return To” address is required on a document; includes a self-address stamped envelope for return of copies. • Each document must be stapled separately and be in proper order for recording. • Make sure social security number appear on non-resident tax forms. Checks with these forms should be made payable. • The consideration amount must match in all areas (front, acknowledgment, affidavit, and seller’s residency form). Identifying reporting requirements Before you begin to gather and analyze your data consider how you can ensure your collection efforts will meet the reporting needs of your primary intended users. From the very beginning, reporting is an integral part of evaluation which allows you to: • • • • • Communicate what you do Monitor and track progress Demonstrate the impact Document lessons learned Be accountable and transparent to donors, partners, and benefiting communities 10 What’s More Activity 3 TRUE OR FALSE Directions: Write T if the statement is true; F if the statement is false and underline the error in the statement. __________1. Body language is a form of non – verbal communication. __________2. Listening is more than speaking and it requires some effort. __________3. When sharing information eye contact is a must. __________4. Informal meeting does not need an agenda. __________5. Structuring meetings is used to give some structure to a group discussion. What I Have Learned Activity 4 Directions: Complete the following statements by providing what you already know and what you have learned from the lesson in 3 to 5 sentences. After I study this module, I already know something about… _______________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ I have learned that _________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 11 What I Can Do Activity 5 Directions: Conduct a phone call interview to a poultry owner on how they communicate with their people in the workplace. Interview Guide Name of Interviewee: _________________________ Address: __________________________________ Guide Questions: 1. How many employees do you have in your workplace? 2. What are the assigned tasks for each employee? 3. How do they know their tasks? 4. Are there problems in the management of your poultry as regards to the accomplishment of their work? Why did you say so? 5. Do you listen to your people's complaints or suggestions? How do you feel about this? 12 Assessment Activity 6 Post test Directions: Choose the letter of the correct answer. Write your response to the separate activity sheet. 1. A way of communicating through use of hand gesture, posture and facial expression is called ______. A. body gesture C. body posture B. body language D. body figure 2. Listening is one way to collect a lot of information through the following except____. A. e-mail B. face to face C. telephone D. radio 3. It refers to gathering information through observation. A. Listening B. Speaking C. Reading D. Observing 4. Why is it necessary to keep the records in same place at all times? A. to make it easy to find C. to make everyone worry B. to make everyone struggle D. to make everyone follow 5. Communicating face to face with other people involves the following except______. A. listening B. speaking C. reading D. observing 6. What is the advantage of working in groups or a team? A. gives more problem C. tasks are difficult to accomplish B. creates conflict D. solves problems easily 7. A type of meeting which includes the typical agenda and follows an order such as opening, welcome, reading of minutes and correspondence. A. formal B. informal C. structural D. group 8. Being a workgroup member you have an obligation to do, except ________ . A. not attending meeting B. participating to the best of your ability C. complying with meeting decision D. keeping sensitive matters confidential 9. It refers to a type of communication that includes verbal abuse, name-calling, etc. A. Assertive C. Non-assertive B. Aggressive D. Non-aggressive 13 10. The following are the right way to share information except_________. A. getting straight to the point C. speaking clearly B. making eye – contact D. slouching Additional Activities Activity 7. Enumeration Directions: Enumerate the following: A. List at least 5 sources of information. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. B. List at least 5 things where information can be located. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. C. List the things to consider in communicating face to face. 1. 2. 3. 4. D. List at least 6 things to keep in mind when filling a form. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Congratulations! You did a great job! Good luck as you move on to the next lesson. 14 15 Activity 7 A. Answer Key Letters Memos Plans Internet websites Faxes Emails Newsletters Work notes Order sheets SMS Industry Magazines Activity 1 Pre-Test 1. C 2. B 3. D 4. A 5. B 6. D 7. B 8. C 9. C 10. D Activity 2 1. Radio 2. Television 3. Cellphone 4. Magazine 5. Newspaper B. Computer databases Filing cabinets Shelving Counters Drawers Pin Board or whiteboards Activity 3 True or False 1. T 2. F/ speaking 3. T 4. F/ does not need 5. T C. Speaking Listening Observing Being observed Activity 4 Answer may vary Activity 5 Answer may vary D. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Read the form carefully Fill in all the required details Only include necessary information Write clearly and simply Check that you have completed it properly Send or give it to the appropriate person, or file in the appropriate place Activity 6 Post-Test 1. B 2. A 3. D 4. A 5. C 6. D 7. A 8. A 9. B 10. D Answer Key References Websites: https://dlb.sa.edu.au/tsftfmoodle/mod/resource/view.php?id=3453 www-entrepreneur-com.cdn.ampproject.org https://www.thebalancecareers.com/communication-skills-list-2063779 http://ecochickspoultry.com/a-list-of-poultry-farming-equipments-and-their-uses/ https://study.com/academy/exam/topic/workplace-communication-skills.html https://blog.bonus.ly/20-simple-ways-to-increase-motivation-in-the-workplace/ https://meetnotes.co/co/blog/8-tips-on-how-to-participate-in-a-meeting/ https://careers.workopolis.com/advise/interview-tips-how-to-prepare-for-the-most-... https://unsplash.com/s/photos/teamwork https://www.dynamiccap.com/effective-communication-in-the-workplace 16