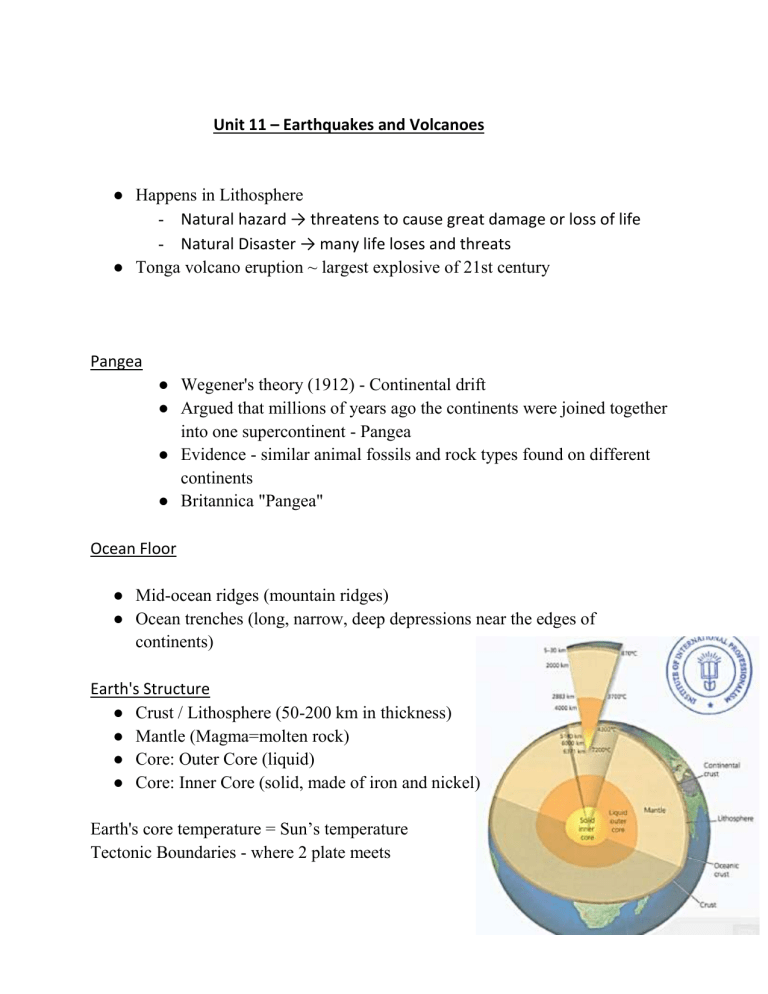
Unit 11 – Earthquakes and Volcanoes ● Happens in Lithosphere - Natural hazard → threatens to cause great damage or loss of life - Natural Disaster → many life loses and threats ● Tonga volcano eruption ~ largest explosive of 21st century Pangea ● Wegener's theory (1912) - Continental drift ● Argued that millions of years ago the continents were joined together into one supercontinent - Pangea ● Evidence - similar animal fossils and rock types found on different continents ● Britannica "Pangea" Ocean Floor ● Mid-ocean ridges (mountain ridges) ● Ocean trenches (long, narrow, deep depressions near the edges of continents) Earth's Structure ● Crust / Lithosphere (50-200 km in thickness) ● Mantle (Magma=molten rock) ● Core: Outer Core (liquid) ● Core: Inner Core (solid, made of iron and nickel) Earth's core temperature = Sun’s temperature Tectonic Boundaries - where 2 plate meets Types of Boundaries: 3 ● Destructive (Convergent) ➔ Pulls away from each other ➔ Mostly under the sea ➔ Create volcanoes and Earthquakes (weak) ● Constructive (Divergent) - only with oceanic and continental ➔ Subduction ★ Oceanic plate subducts under the continental plate ★ Create powerful volcanic eruptions due to pressure ➔ Towards each other ➔ Volcanoes and Earthquakes ➔ ➔ ➔ ➔ Collision Boundaries (continental and continental Towards each other Create fold mountains Makes earthquakes ● Conservative (Transform) ➔ Side by Side, in the opposite direction Why do tectonic plates move? Theory 1 - Earth's internal heat creates convection currents in the mantle, transferring heat, which rises and cools back down in a circular motion, moving plates above. Theory 2 - The heavy weight of the plate going down pulls the whole plate along and down, like a coat falling off a table (Slab pull) Earthquakes start - Focus Foreshocks (before) --> Mainshock (during) --> Aftershocks (after) Faults/Fault Lines = Plate Boundaries Shocks last for weeks. High-income countries ❖ Strict building codes --> safer buildings ❖ Make earthquake-resistant buildings ❖ Urbanization controlled Volcanoes When it erupts - lava, dust, stone, gas came out Magma - a mixture or hot, molten rock Lava - when magma erupt out of the volcano An opening in the earth's crust (lithosphere) where magma and gasses from inside the Earth escape onto the surface. Types of Volcanoes ● ● Composite/Stratovolcano ➔ Steep-sided, cone-shaped, tall volcanoes, formed from layers of sticky lava that doesn't flow far Shield Volcanoes ➔ Gentle slopes, wider area, formed from runny lava that spreads far. Gasses escape easily Why do people live near volcanoes? ● Fertile soil good for agriculture ● Minerals ● Geothermal energy for electricity ● Tourism Prediction - monitor volcanoes. Planning evacuation plans, and warning systems. Preparation involves educating people. Volcanologists - predict Unit 12 – Africa ● ● ● ● Africa is relatively flatter than other continents or regions. Sahara desert - the world's largest sand desert Niles River - longest - through 10 countries Half of the diamonds are produced in Africa, 22% of gold, and 30% of the remaining resources ● Rich in oil and gas ● Africa's natural resources are not evenly distributed across the continent concentrated in a few countries. Africa’s Climate and Biomes Biomes in Africa - Desert, Grassland, Rainforest, Deciduous woodland, Tropical Rainforest Biome = A large geographic area with similar environments, plants, and animals Savanna Biome - Grassland with scattered trees, wet & dry seasons, wildlife migration Desert Biome - driest biome, rarely ever get rainfalls, extreme temperature Tropical Rainforest Biome(Congo Basin) - hot, moist biome where it rains all year long, with many tall trees Deciduous Forest Biome - rich in moisture, grows in one of the suitable seasons Suggestion to watch - Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)=A region near the Equator with high rainfall (low pressure) due to strong sunlight ITCZ and Trade Winds The Sahel Region = southern edge of the Sahara Desert Overgraze = too much grazing by livestock (animals) Clearing vegetation from lands (deforestation) to farm, to build shelter, to get firewood, to feed livestock leads to : Soil exposed to wind and water → Soil Erosion Desertification forms (Desert Spreading) from → Soil Erosion & Drought Human Geography of Africa ● French speakers in Africa - Francophone Triangle trading Route Between the 1600s to 1800s, 12-15 million Africans were sold into slavery in exchange for goods Imperial nations were keen to exploit the rich natural resources of Africa and cheap labor The 'Scramble for Africa' in the 1880s - European countries raced to occupy the continent seeking economic and strategic gains. Berlin Conference 1884-1885 - creates new borders for Africa, the partition of Africa confirmed Video Suggestion: Berlin Conference King Leopold II of Belgium, took control of the tropical rainforest in the Congo Basin - 75 times larger than Belgium - the richest part of Africa industrial Revolution drove up the demand for rubber → lead to the taking over of rubber tree sap in tropical rainforest Video Suggestion: History of Scramble for Africa Estimated 10 million Congolese people died from abuses during King Leopold's rule in Congo What colonialism did to Africa ● Little attention was given to the education, health, and training for Africans during colonial rule ● Territories were used as sources of raw materials for the benefit of the colonial powers ● No allowance for continental development Decolonization of Africa ● After World War 2 ● Between the 1950s - 1960s (In 1960, 18 colonies became independent Congo, Madagascar, etc) ● By 1966, most of Africa independent ● British colonies first to gain independence (Ghana, Nigeria, etc), Portuguese last ● Civil wars, neo-colonialism For decades, the Democratic Republic of the Congo has seen one of the world’s longest-running armed conflicts Development HDI - Human Development Index HDI measures a country's achievement in three key dimensions: ● a long and healthy life ● Knowledge/Education ● a decent standard of living Changes and Challenges for Africa Africa - 2nd most populated country on earth Africa has the fastest urbanization rate in the world. Second most populated country in Africa (Over 100 million) / Landlocked country / Rapid urbanization Landlocked Country - A country surrounded by land Slums = informal (improvised) settlements Slums lack infrastructure and are often unsafe Social Housing - Residential buildings built by governments - Affordable buildings to live in Advantages of the Railway ● Easier access to the sea ● Reduce transportation time (weeks to days) ● Reduce transportation costs ● Easier to move goods (imports & exports) ● Manufacturing sector grows ● Economy grows Trade between China & Africa ● China overtook the USA as Africa's largest trading partner in 2009 ● 15% of Africa's exports, mainly natural resources, go to China ● China provides 21% of Africa's imports (machinery, transportation, communications equipment, goods) ● China continues to fund the building of factories, roads, railways, ports, airports, hospitals, schools, and stadiums (infrastructure) ● More than 1 million Chinese laborers and traders have moved to Africa in the past decade Belt and Road - the name of China’s multibillion-dollar initiative/investment in infrastructures around the world Unit 13 — Glaciers Large masses of slowly moving ice (rivers of ice) made up of fallen snow that gets compressed into ice along with rock, sediment over many centuries frozen seawater that floats on the ocean surface - Sea Ice Extra large masses of glacier, also known as continental glaciers - Ice Sheet Pieces of a glacier broken off into water - Ice Bergs type of glacier covers extra large area of land and is spread out - Ice sheet Glacier move slowly downward → gravity erode the landscape, creating different landforms Glaciers form the largest reservoir of fresh water on our planet As glacier melts, it provides running water (rivers, streams, lakes) to our planet 1. Alpine Glaciers - Form on mountainsides and move down slopes through valleys Where are glaciers found? ● Where average annual temperatures are near freezing point (0ºC) ● Large amounts of snowfall during winter months ● Temperatures throughout the year are not high enough to melt the previous winter's build up of snow Scientists who investigate glaciers all over the world - Geologists, Glaciologist Snow builds up (accumulates) over many years (at least 100 years) --> Snow becomes compressed into ice --> Dense, hard ice forms and starts to flow down-slope with its weight. Accumulation (gained) Ablation (melting) Snout = the end of a glacier where water is released Crevasse = a deep opening in a glacier A period of time where global temperatures drop so significantly that glaciers advance and encompass over one third of Earth's surface - Ice Age A glacial period is the colder period where glaciers advance (AKA Ice Age) / An interglacial is the warmer break in between two ice ages were glaciers retreat Pluck - to remove forcibly Abrase - to rub off 1. Weathering When melted snow enters cracks in rocks around and below glacier --> water in rocks freezes and expands --> cracks get larger --> repeat --> break rocks apart around and below glacier 2. Erosion Rocks become frozen into the bottom and sides of the glacier. As the glacier moves downhill it 'plucks' (rips off) the rocks frozen into the glacier from the bedrock. As the glacier moves downhill, rocks that have been frozen into the base and sides of the glacier scrape the rock beneath like sandpaper, leaving behind smooth, polished surfaces with scratches in them. 3. Deposition/Erosion As the glacier moves down it transports vast amounts of rock mixed with ice. Any material (debris) carried by a glacier is called moraine. Any water from melting ice feeds a river or lake. Landforms by Glacial Erosion ● U-shaped valleys ● Hanging valleys/waterfalls ● Truncated spurs ● Misfit rivers ● Fjords ● Ribbon lakes ● Corries A series of ridges overlapping each other (in V-shaped valleys/river valleys) - Interlocking Spurs glacier cuts through the interlocking spurs, leaving behind truncated spurs in a U-shaped valley - Truncated Spurs Smaller valleys above the new U-shaped valleys. Often, streams fall from hanging valleys as waterfalls. A large, narrow (long), thin lake occupying a U-shaped valley after the ice melts - ribbon lake Small river usually flows in U shape valley after the glacier melts - misfit river After glacier melts, the sea fills the valley floor (Fjord = a long strip of sea between steep hills (inlet)) Fjords - Norwegian language A corrie is a hollow (hole) found on the side of a mountain. This is where a glacier forms. Snow collects in a hollow on the side of a mountain, compacts into ice → Back wall of the corrie gets steeper due to freeze-thaw weathering and plucking → The base of the corrie becomes deeper due to abrasion → Corrie After the glacier has melted a lake forms in the hollow. This is called a corrie lake or tarn. Large rocks (boulders) that have been carried and deposited by glaciers as part of glacial till/moraine. They are usually made of a rock type that would not be found in that area. - Erratics Glacial Processes ● Weathering (Freeze-Thaw) - weaken bedrocks ● Erosion (Plucking & Abrasion) - U-shaped valleys, truncated spurs, fjords, misfit rivers, ribbon lakes, hanging valleys, waterfalls, corries, tarn ● Transportation & Deposition (Moraine/Glacial till, meltwater) Deposited moraine = glacial till Unit 14 — Middle East *Physical Geography* ★ Middle East - region (go die if u think it is a continent, ur whole birth is a lie if u think middle east is a continent) ★ Region - an area with certain common characteristics ★ no single definition of what countries make up the Middle East Middle East = Southwest asia → Becomes a dominant region after WWII Ankara → capital of Turkey (both in Asia and Europe) Snows in parts of middle east - Lebanon Crude oil is the most abundant natural resource in the Middle East. An oil refinery is where crude oil is refined into petroleum products such as diesel, gasoline, and heating oils. Peninsula = a piece of land that sticks out from a larger area of land into the sea or a lake (e.g. Arabian Peninsula) The Arabian peninsula is mainly covered by the Arabian Desert - 2nd largest sand desert Rub' Al Khali (Means "Empty Quarter") in the Arabian Desert Desert (Arabian peninsula) / Mediterranean climate (North) / Steppe (Grassland) The Mediterranean climate (Hot, dry summers & Cool, wet winters) The North (Mediterranean climate) has more water than the South (Desert climate) Arabian Sea is apart of Indian Sea How do they get water? Desalination brines - Getting steam and making it a drinkable water Underground aquifers, Saudi Arabia - Aquifers = Underground reservoirs of water in rock, sand and gravel Unit 15 — Climate Change Climate - average weather of the whole year (long term) - average weather of the atmosphere over a long term Weather - weather for today (sunny, rainy) aka daily term - condition of the atmosphere over a short term - Earth’s average temperature → 14’C - Human activities caused global warming like burning fossil fuels to generate electricity. Greenhouse - made with glass, for plants to give heat Greenhouse Effect - the gases(water vapour/CO2) trap the Sun’s heat with the atmosphere Greenhouse Gases (GHG) - The heat-trapping gases in our atmosphere includes: 1. Carbon dioxide 2. Water vapour 3. Methane 4. Nitrous oxide 5. Ozone - The Earth produces Greenhouse Gas (GHG) is produced naturally Greenhouse Gases - Natural Cause - Water Cycle - Plants, Animals, and Humans - Volcanic eruptions 1. Water Cycle (from water vapour) - Evaporation from the Earth’s water cycle adds water vapour to the atmosphere 2. Animals & Humans & Plants (CO2 and Methane) - Animals, Plants, and Humans release carbon dioxide when we breathe by exhaling the air) - Release carbon dioxide as we exhale - When living things die, they decompose and release Co2 and Methane 3. Volcanic Eruptions (CO2) - Volcanoes —both on land and under the ocean — release carbon dioxide as they erupt.






