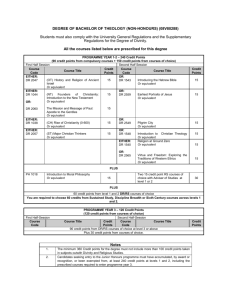
1. Anthropology in Antiquity 1. Key European systems of thought 1. Theology (gods) 1. People and nature are known through gods 2. Epic Poet, Homer (8th c. BCE) 2. Humanism (people) 1. Gods and nature are known through people 2. Herodotus (c. 484-425) 3. Science (nature) 1. Gods and people are known through nature 2. Democritus (c. 460-c.370) and other early philosophers 2. Golden Age of Greece (5th and 4th C. BCE) 1. A search for truth through thinking and questioning 2. People 1. Socrates (c. 469-399) 1. Self educated 2. Socratic method, questioning everything 2. Plato (c. 427-347) 1. "essences of things" 2. "realism" what is real? 3. Aristotle (384-22) 3. Romans and Middle Ages 1. Saint Augustine (354-430) 1. Humans are sinful, God is perfect 2. Importance of faith and obeying god 4. Dark and Middle Ages 1. Fall of Roman Empire 2. Influence of Muhammed (c. 570-632) 1. Introduced Aristotle to scholars who had been focused on Plat for centuries 2. New Epistemology - the nature and scope of knowing - what is knowledge 3. Revitalized medieval Christianity 3. Thomas Aquinas (1225-74) 1. Encouraged human reasoning and observation 2. God could be known through nature, studying nature could glorify God 3. Humanity could be curious and nature mysterious but conclusions could contradict God 5. The Renaissance (14th-16th c.) 1. Pre-Medieval arts and philosophy were rediscovered and celebrated 2. Greco-Roman philosophy appreciated and dogmatic medieval Christianity became less attractive 3. Secular humanism and the beginning of cross-cultural analysis 4. Voyages of Geographical Discovery 1. Europeans understood race, language, and culture to be inextricably linked 2. Era of Western colonialism, imperialism, and political and economic global exploration and domination 3. Ties to Christianity 4. Aboriginal people - "natural children" - led to theories of monogenesis 5. Even the Rain 6. Anthropology develops in this context 6. Scientific Revolution 1. Attempted preserve Thomistic Christianity's cosmology but 1. Ptolemy (127-51) 1. Earth at center 2. Copernicus (1473-1543) 1. Sun at center 3. Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) 4. Newton (1642-1727) 1. Law of Universal gravitation 5. What does this have to do with anthropology 6. Science Supplants humanism and theology 1. Needed epistemologies to replace intuition and faith 7. The Enlightenment: Age of Reason 1. Voyages of geographical discovery made Europeans more aware of Global diversity in plants, animals, and people 2. The need to classify 1. Linnaeus (1707-78) 2. Descriptions of other peoples by missionaries and explorers 3. Comparative studies of aboriginal peoples 4. Progress and culture 5. Universal historians 1. Dividing human history into stages 8. 18th C. foundations 1. French Revolution (1789) 2. Napoleon (1769-1821) 1. Dividing Europe into warfare until 1815 3. A surge of biblical evangelicalism after the wars 4. Rise of Nationalism 5. Rise of Socialism 6. Aversion to science as radical, atheistic, and counterproductive