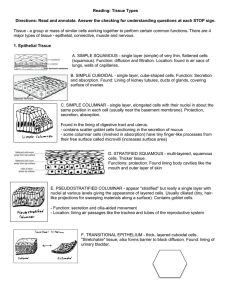
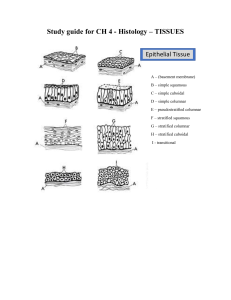
Chapter 3 Review 1. What are the 4 primary tissue groups in the body and where would you find them? 2. Draw the shapes that epithelial tissue comes in. 3. What does it mean when epithelial cells show polarity? 4. What characteristics make epithelial tissue great for protection? 5. What are the differences between microvilli and cilia? How do these differences relate to absorption and secretion? 6. Draw the different methods the exocrine glands secrete in. 7. What are the functions of connective tissue? 8. What type of connective tissue is pictured below? Name the functions of each type of connective tissue. 9. What are cartilage cells called? 10. Which type of cartilage is considered very strong? Viewed under a microscope, the cells would be highly compacted. 11. Which types of muscle are considered involuntary? Why are they called involuntary? 12. What type of muscle would you find your heart to be composed of? How many nuclei do these muscle cells have ? 13. Match the following functions/locations with its tissue type: 1) Simple Squamous ET: _____________ 2) Simple Cuboidal ET: _____________ 3) Ciliated Simple Columnar ET: _____________ 4) Pseudostratified Columnar ET: _____________ 5) Stratified Cuboidal ET: _____________ 6) Stratified Columnar ET: _____________ 7) Non-Keratinized Stratified Squamous ET: _____________ 8) Keratinized Stratified Squamous ET: _____________ 9) Transitional ET: _____________ a. Found lining the urethra. b. Diffusion and absorption of gases, also forms alveoli. c. Multi-layered, protective layer. All cells are living and intact. d. Secretion and movement, found in fallopian tubes. e. Absorption and secretion, found in simple ducts and glands in organs. Forms a lumen. f. Multi-layered, protective layer. Apical cells are dead and filled with keratin. g. Found lining the urinary bladder and ureters. Areas with constant stretch. h. Secretion and absorption, cells are taller allowing for more space for more organelles. i. Forms sweat glands in skin. 14. What is the difference between hypertrophy and hyperplasia? 15. James has smoked for over 20 years. At a recent doctors visit, they discovered the tissue lining his airways had changed. What do we call this type of tissue change? 16. Why does cartilage take much longer to heal compared to other tissues? 17. How do exocrine and endocrine secrete their secretions? 18. What type of CT is composed of osteocytes with a rigid ground substance? 19. What is the main difference between a fascia and a membrane?